Affects the performance of the entire structure! What should be the pressure in the heating system
You are viewing the section Pressure, located in the large section Heating.

The heating system in a modern home is a complex mechanism. To maintain its smooth and efficient operation, take into account many factors.
The main parameter reflecting the stability of the heating system is considered to be working pressure.
The quantitative value of the pressure indicator directly affects the efficiency of heat transfer, the safety of the equipment used and wear resistance.
Maintaining a certain level of working pressure in the heating mechanism, first of all strive to ensure maximum efficiency heating. Thanks to the working pressure, it is possible to achieve the required productivity, which allows to guarantee a stable temperature of batteries and pipes. Stable pressure reduces energy loss when the coolant moves from the heating elements directly to the heating radiators.
Types of pressure
Types of pressure in heating systems of private and apartment buildings:
- Static — occurs due to the force of attraction acting on the liquid. Water presses on the components of the heating structure with its own weight. The force of impact on the walls of the structure is proportional to the height of the rise of the coolant. Pressure from a height of 10 meters is 1 atm.

Photo 1. A special device - a pressure gauge, which is used to measure the pressure in the heating system.
- Dynamic — is formed due to the pumping of liquid or movement due to heating.
- Working — the sum of the static and dynamic pressure values.
Important! The working pressure is regulated by certain SNiPs. The probability of occurrence of emergency situations capable of causing a threat to life and health of people increases in case of neglect of established norms and rules.
What should be the pressure in the heating system?
The pressure level is calculated individually and is based on specific needs. In schemes with natural circulation, the value of the indicator is close to static. In cottages with installed injection pumps normal worker pressure 2 bar (±0.5) is considered.
As the number of storeys of the building increases, the required pressure also increases to achieve the required circulation of the coolant. For a five-storey building, the norm is considered to be 4 bar, ten-story - 7 bar, in high-rise buildings it reaches up to 10 bar. Taking into account the impact on the components of the structure, the appropriate type of pipes and batteries is selected.
Standards in a closed heating system
The requirements that the working pressure must meet are:
- Do not go beyond the working limits of the boiler and other components of the structure.
- Have the ability overcome resistance heating schemes, depending on the length, structure, size of pipes and the speed of movement of liquid in them.

However, there is no need to perform labor-intensive calculations.
To achieve sufficient working pressure, it is only necessary to adjust the pump operation so that the temperature difference between the coolant at the inlet and outlet is insignificant, approximately 20 °C.
In low-rise buildings, to ensure normal operation of heating equipment, pumps must have a pressure that, in combination with the static type, will give 1.5—2.5 atm. working pressure. These indicators are sufficient to ensure good heating in private low-rise houses.
The data is easily obtained using closed systems using air-filled expansion tanks. Using an open expansion tank seems questionable, since it takes a lot of pressure to achieve at 1 atm. it is necessary rise to a height of 10 meters, otherwise the coolant will spill out.
Pressure tests
The procedure for checking the heating system, before putting it into operation or during the off-season period, is carried out masters of energy enterprises. The mechanism is filled with coolant and pressed through under pressure close to critical.
The main objective of the operation is to test all elements of the structure to identify and eliminate possible faults, determine the building's heating potential and check the efficiency of heat transfer. Testing of heating structures is carried out hydrostatic (water) And manometric (air) methods.
Important! When pressure testing a heating structure, the most common problems that occur are: ruptures of old worn-out pipes and leaks in radiators.
Cold
Cold hydrostatic testing is carried out in stages:
- water supply to system components;

- removing air by opening air collectors and taps;
- closing the air collectors after filling the heating system with water;
- increasing the pressure level to the test level;
- maintaining the heating structure under test pressure for a certain period of time;
- drain water.
Cold testing are considered the safest. But they are produced only in the warm season at a positive temperature in the rooms of the house, to avoid possible "defrosting" of the pipes. Water temperature for hydraulic tests should be above 5 °C.
For water heating structures, during hydrostatic testing, the test pressure is approximately 1.5 MPa, but should be more at the lowest point 0.2 MPa. The expansion tank and boilers are disconnected from the structure for testing. It is required that the pressure drop during testing be below 0.02 MPa for 5 min. Identified deficiencies that do not interfere with the hydrostatic testing are recorded and later eliminated.
Hot check

The circuit is tested using hot water closer to the heating season. The coolant is supplied at a pressure higher than the working pressure.
This test is a control test before the cold weather. and often allows us to identify critical violations in the efficiency of equipment operation.
Hot check must be carried out without fail.
Thanks to such testing, the probability of accidents in each individual house is reduced.
Air check
When testing the heating mechanism with manometric tests, you can not be afraid of flooding and "defrosting". But when testing the pipeline with compressed air, there is a risk of destruction of various elements. Therefore, in order to preserve the lives and health of people, access to the premises where the inspection is being carried out should be restricted.
Manometric testing of the structure heating is carried out by filling it with compressed air under the required test pressure. After the appropriate measurements, the pressure is reduced to atmospheric.
Using air, heating circuits are tested not for strength, but for leaks. Initially, pressure is applied to 0.15 MPa and search for damage by ear. Then check for 5 minutes under pressure of 0.1 MPa. Pressure during testing should not fall below 0.01 MPa.
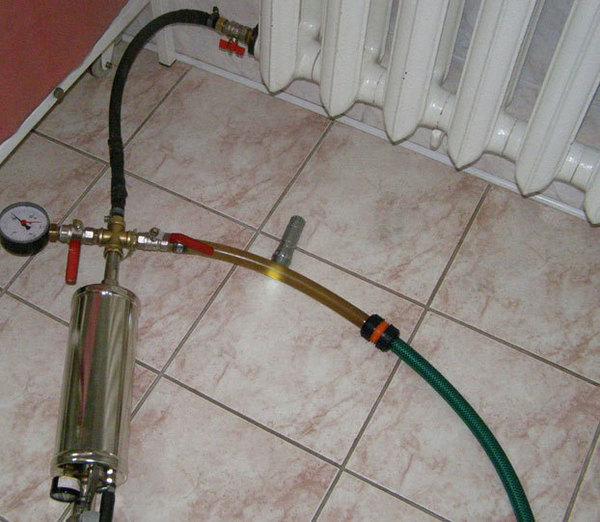

Photo 2. The process of checking the heating using a pressure gauge. The system is filled with compressed air through the batteries and measurements are taken.
Why does pressure drop?
Reducing pressure in the heating structure observed very often. The most common causes of deviations are: discharge of excess air, air leakage from the expansion tank, and coolant leakage.
There is air in the system
Air has entered the heating circuit or air locks have formed in the radiators. Reasons for the appearance of air gaps:
- failure to comply with technical standards when filling the structure;
- excess air has not been forcibly removed from the water supplied to the heating system;
- enrichment of the coolant with air due to leaky connections;
- malfunction of the air release valve.
If there are air cushions in the coolant noises appear. This phenomenon causes damage to the components of the heating mechanism. In addition, the presence of air in the heating circuit units entails more serious consequences:
- pipeline vibration contributes to the weakening of welded seams and displacement of threaded connections;
- the heating circuit is not deaerated, which leads to stagnation in isolated areas;
- the efficiency of the heating system decreases;
- there is a risk of “defrosting”;
- There is a risk of damage to the pump impeller if air gets into it.

To eliminate the possibility of air penetration into the heating circuit it is necessary to correctly put the circuit into operation, checking all elements for functionality.
Initially, a high pressure test is performed. During pressure testing, the pressure in the system should not drop. within 20 minutes.
The first time the circuit is filled with cold water, with open taps for draining water and open valves for bleeding air. The network pump is turned on at the very end. After removing air from the circuit add the amount of coolant required for operation.
During operation air may appear in the pipes, to get rid of it you need to:
- find a section with an air gap (in this place the pipe or radiator is significantly colder);
- After turning on the structure's feed, open the valve or tap further downstream and get rid of the air.
Air comes out of the expansion tank
Causes of problems with expansion tank are as follows:
- installation error;
- incorrectly selected volume;
- nipple damage;
- membrane rupture.
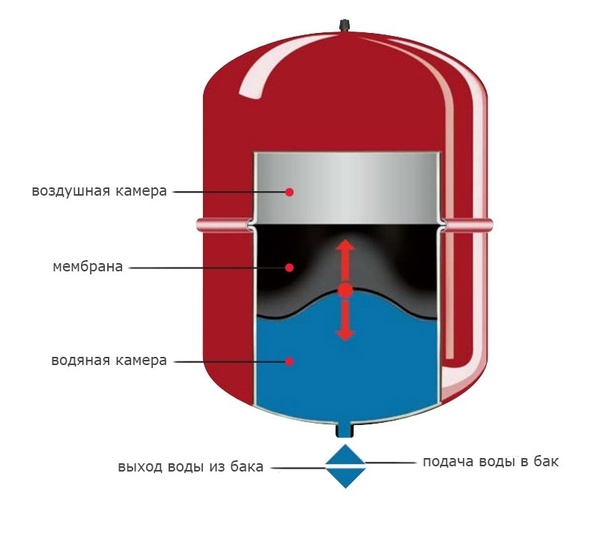
Photo 3. Diagram of the expansion tank device. The device can release air, which causes the pressure in the heating system to drop.
All manipulations with the tank are carried out after disconnecting from the circuit. For repairs, it is necessary to completely remove water from the tank. Next, it should be pumped up and the air should be released a little. Then, using a pump with a pressure gauge, bring the pressure level in the expansion tank to the required level, check for leaks and install it back on the circuit.
If the setting is incorrect heating equipment will be observed:
- increased pressure in the heating system and expansion tank;
- pressure drop to a critical level at which the boiler does not start;
- emergency emissions of coolant with a constant need for replenishment.
Important! There are samples of expansion tanks on sale that do not have pressure regulation devices. It is better to refrain from purchasing such models.
Flow
Leak in the heating system leads to a decrease in pressure and the need for constant replenishment. Fluid leaks from the heating circuit most often occur from connecting joints and places affected by rust. It is not uncommon for fluid to leak through a torn membrane of the expansion tank.
Identify a leak you can do this by pressing on the nipple, which should only let air through. When a coolant loss is detected, the problem must be fixed as soon as possible to avoid serious accidents.

Photo 4. Leak in the heating system pipes. This malfunction can cause the pressure to drop.
Useful video
Watch a video that discusses possible causes of pressure changes in the heating system.
Normal pressure is the key to stable heating
Pressure is a critical parameter on which the efficiency, comfort, and safety of the heating structure depend.

High-quality care for home heating elements will allow this value to be stable.
The difference is a sign of problems in the operation of the heating mechanism, which may cause an accident.
Therefore, in private homes it is important to monitor the performance of pressure gauges, and in apartment buildings, with a low heating level, it is worth considering their individual installation.





