So that the most severe cold is nothing! Calculation of heating radiators
You are viewing the section Calculation, located in the large section Installation.

A carefully thought-out home heating system is one of the most important tasks during construction and subsequent improvement of housing conditions, since a comfortable temperature in the room is not only a guarantee of coziness, but also an important condition for human life.
Calculation and selection must be made depending on a number of conditions, such as the radiator material, the area being heated, the climatic conditions of the region, etc. For the correct installation of the heating system, you can contact professionals, or you can carry out this process using your skills and abilities.
Content
- Measurements for determining heating radiators
- Determining battery parameters depending on various factors
- Formula for calculating heat output of radiator devices for apartments
- Calculating the number of radiator sections
- The most accurate definition of the power parameter of the heating system in kW
- Useful video
- Correct calculation of the device is the key to a comfortable temperature
Measurements for determining heating radiators

Determining the heating parameters in an apartment should begin from obtaining the necessary data taken by measurement.
These data are: length of the room, width of the room, area of the room, number of external walls, height of ceilings, number of doors, number of windows, area of each window.
Determining battery parameters depending on various factors
The calculation of heating radiators is influenced by many factors.
By living space area
Taking the desired parameter as Q, the calculation is the formula:
Q = S×100 W (1), where
S ? the area of the space for which the radiator calculation is made, m2;
100 W ? a value accepted as a standard, denoting the amount of heat required for 1 m2 living space.
Features of calculations using refinement factors

The clarifying factors for this calculation are coefficients that take into account the structural features of the estimated housing.
Definition Q using them will allow you to most accurately determine heat costs for each individual case.
The coefficients clarify formula (1) and bring it to the following form:
Q=S×100W×α×β×γ×δ×ε×ζ×η×θ (2), where
α - the multiplier that takes into account the number of external walls that increase heat losses is taken as:
| The value of α | Number of walls |
| 1.0 | 1 |
| 1,2 | 2 |
| 1.3 | 3 |
| 1.4 | 4 |
β - a factor that takes into account the degree of natural heating of the living space. Depends on the side of the world that the window faces. β is taken to be equal to:
| The value of β | Cardinal direction |
| 1,1 | North, East |
| 1.0 | South, West |
γ - a multiplier that takes into account local climatic conditions. Depends on the average minimum temperature in January. The value is specified according to reference books or the local hydrometeorological service. γ is taken to be equal to:
| The value of γ | Temperature |
| 0.7 | up to -10°WITH |
| 0.9 | up to -15°С |
| 1,1 | up to -20°С |
| 1.3 | from -20°С to -35°С |
| 1.5 | from -35°C and below |
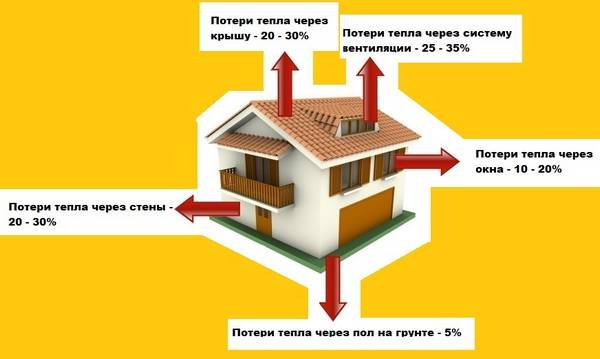
Photo 1. Heat loss in a private home. They must be taken into account when installing heating radiators.
δ - a multiplier that takes into account the presence of wall insulation in the premises. δ is taken to be equal to:
| The value of δ | Insulation level |
| 0.85 | High |
| 1.0 | Average |
| 1.27 | Short |
ε - a multiplier depending on the height of the ceilings of the home. ε is taken to be equal to:
| The value of ε | Ceiling height |
| 1.0 | up to 2.7 m |
| 1.05 | from 2.8 m to 3.0 m |
| 1,1 | from 3.1 m to 3.5 m |
| 1.15 | from 3.6 m to 4.0 m |
| 1,2 | over 4.1 m |
ζ - a multiplier that takes into account heat loss due to the room located above the calculated one. ζ is taken to be equal to:
| The magnitude of ζ | Type of room above |
| 0.8 | Heated |
| 0.9 | Insulated |
| 1.0 | Unheated |
η - a multiplier that uses the dependence of the desired value on the type of window installed in the room. η is taken to be equal to:
| The magnitude of η | Window type, double glazing |
| 0.85 | Three-chamber |
| 1.0 | Two-chamber |
| 1.27 | Double frames, regular |
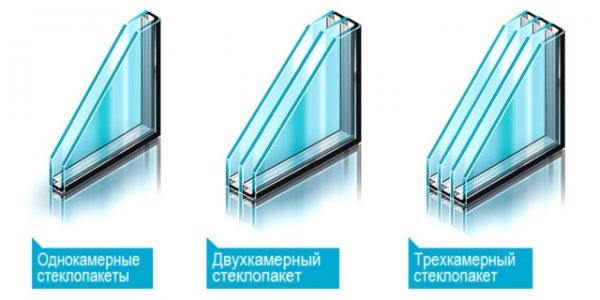
Photo 2. Single-chamber, double-chamber and triple-chamber glass units. The type of window affects the number of radiators installed.
θ - a multiplier that takes into account the percentage ratio of the window area to the floor area when calculating. θ is taken to be equal to:
| The value of θ | Attitude |
| 0.8 | 10% |
| 0.9 | 20% |
| 1.0 | 30% |
| 1,1 | 40% |
| 1,2 | 50% |
Depending on the volume of the room

Taking into account the volume of living space will allow you to obtain more accurate data when calculating the heating device, and formula (1) will take the form:
Q=S×h×41 W (3), where
h — height of room ceilings, m;
41 W ? a value accepted as a standard, denoting the amount of heat required for 1 m3 living space.
Attention! Heat loss ? an inevitable minus when heating an apartment.
Formula for calculating heat output of radiator devices for apartments
It is best to calculate heat for an apartment taking into account the total heat loss. according to the formula:
TPgeneral = V×0.04×TP0×n0×TPd×nd (4), where
V — the volume of the calculated space, m3;
0.04 — standard value of losses for 1 m3;
TP0 — the standard value of losses from one window, TP0 = 0.1 kW;
n0 — the total number of windows in the apartment;
TPd — standard value from one door, TPd = 0.2 kW;
nd — the number of doors in the apartment.
The total heat loss of an apartment is also determined by a special device? thermal imager, which also performs the function of searching for hidden construction defects and defective materials.
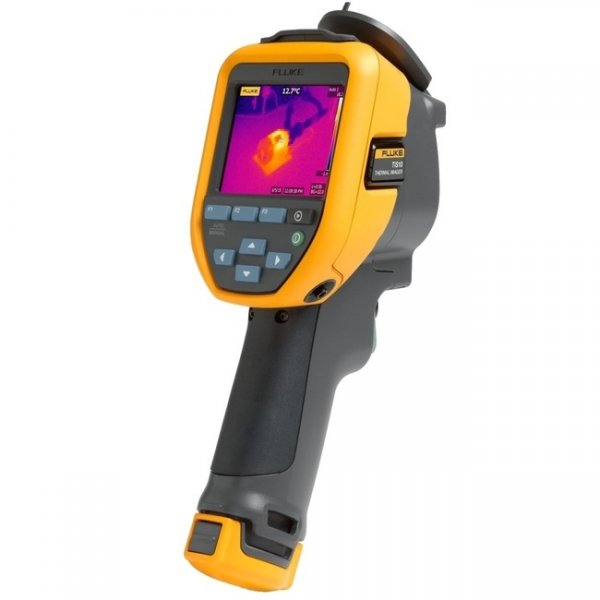

Photo 3. Thermal imager from the manufacturer Fluke. The device allows you to measure the temperature of heating radiators.
The overall calculation is also influenced by the radiator power:
Rst = TP0/1,5×k (5), where
Rst — radiator power;
1.5 — a coefficient that takes into account the operation of the device at a temperature from 50?C to 70?C;
k — the safety factor is applied equal to:
| The desired k | Type of housing |
| 1,2 | Apartment |
| 1.3 | Private house |
- Features of determining radiator devices for a multi-storey building
The calculation is carried out according to the formula:
Q = S×80 W (6), where
80 W ? a value accepted by the standard, meaning the amount of heat required for 1 m2 living space, starting from the second floor and above.
Calculating the number of radiator sections
To calculate the number of radiator sections, a special formula is also required.
By room area

In providing the necessary heat supply to the room, one of the important values is the number of radiator sections.
Correctly selected, it will provide the consumer with the necessary level of comfort in unfavorable winter temperatures.
The number of sections by the area of the room is determined using the formula:
nc = S×100 W/q0 (7), where
q0 — heat output of one section of the radiator, data from the technical documentation supplied with the product.
By volume of the house
Using calculation by volume will allow you to more accurately determine the required number of sections:
nc = V×100 W/q0 (8)
- Features of determining the section power with a correction factor:

To determine the correction factor, it is necessary to determine the temperature head of the heating system using the formula:
hT = (tin-tout/2)-tpom (9), where
tin — temperature at the radiator inlet;
tout — temperature at the radiator outlet;
tpom — the required room temperature.
The next step is to find the correction factor. k, depending on the obtained parameter hT according to the table:
| hT | k | hT | k | hT | k | hT | k |
| 40 | 0.48 | 49 | 0.63 | 58 | 0.78 | 67 | 0.94 |
| 41 | 0.50 | 50 | 0.65 | 59 | 0.80 | 68 | 0.96 |
| 42 | 0.51 | 51 | 0.66 | 60 | 0.82 | 69 | 0.98 |
| 43 | 0.53 | 52 | 0.68 | 61 | 0.84 | 70 | 1.0 |
| 44 | 0.55 | 53 | 0.70 | 62 | 0.85 | 71 | 1.02 |
| 45 | 0.58 | 54 | 0.71 | 63 | 0.87 | 72 | 1.04 |
| 46 | 0.58 | 55 | 0.73 | 64 | 0.89 | 73 | 1.06 |
| 47 | 0.60 | 56 | 0.75 | 65 | 0.91 | 74 | 1.07 |
| 48 | 0.61 | 57 | 0.77 | 66 | 0.93 | 75 | 1.09 |
The final stage? We find section power parameter according to the formula:
qWith = k×q0 (10).
The most accurate definition of the power parameter of the heating system in kW
 ?
?
The most accurate determination is made according to formula (2) taking into account the refined thermal calculation:
Power, kW = ((Ld×Lsh)×Hp)/2.7))/10 (11), where
Ld — length of the room;
Lsh — width of the room;
Hp — ceiling height.
Useful video
Watch the video, which explains how to calculate the number of sections in heating batteries.
Correct calculation of the device is the key to a comfortable temperature
Correct calculation of heat loss, for example, through windows and doors, as well as the selection of radiators will ensure the successful completion of the repair and will guarantee a constant standardized temperature in the room, and, consequently, the well-being of residents. A serious approach to the process ensures success in all endeavors.



