In order for the system to work perfectly, it is necessary to calculate the number of heating radiator sections!

Correct calculation of the number of radiator sections - the key to creating a high-quality heating system. To do this, you need to perform several calculations. three methods.
Sections are calculated based on area, volume and using many different coefficients.
Content
What are the dimensions of standard heating batteries?

The dimensions and capacity of radiators depend on the material from which they are made.
Cast iron devices have a width 93 or 108 mm, depth from 85 to 140 mm and height 588 mm.
The dimensions of the aluminum batteries are respectively equal 80, 80-100 and 575-585 mm, and bimetallic ones - 80-82, 75-100 and 550-580 mm.
Reference. The named values sometimes fall outside the specified ranges, which determined by the manufacturer.
Volume of sections calculated by multiplying the named numbers.
How to calculate the number of radiator sections based on the square footage of the room
It is the simplest option and allows you to estimate the required number of sections only approximately. Many studies have determined the standard capacity for one square meter of area, which is necessarily taken into account in the calculation. The climate of the region is also taken into account: for the middle zone and the south the value is 60-100 W, and for northern regions — 150-200 W.
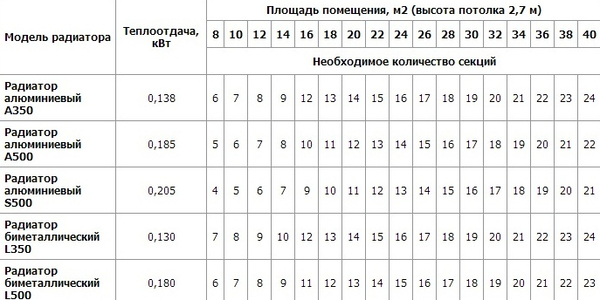
Photo 1. Calculation of the number of sections of bimetallic and aluminum radiators depending on the area.
The indicators are presented as ranges, which allows you to take into account the width and material of the walls, various insulation materials, etc.The number is selected depending on the thermal conductivity of the structure.
Attention! All the above indicators are calculated for rooms with a ceiling height 2.7 meters and below.
The number of sections is determined by the formula:
N = S * Q / P, Where
- S — area of the premises.
- Q — the cost standard used.
- P — the power of one section.
The value of Q is taken from the Building Codes and Regulations, A P — from the device passport, which is planned to be installed. Multiplication of the indicators determines the heat loss of the room during operation, and division determines the number of sections to cover this value.
For example, let's calculate the required number of sections for a corner room with an area of 15 square metersIt is assumed that it is located in a brick house in the central part of the country, and the radiator has the rated power 140 watts. The standard range is — 60-100 W.

The brick structure has average losses, but it should be taken into account that the room is in the corner. Thus, the estimated total power will be 15 * 90 = 1350 W; 1350/140 = 9.64.
The resulting number is always rounded up, creating a reserve. In this case, you will need 10 sections.
This calculation is very easy to perform, but it is far from the truth, because takes the height of the room as average.
Calculation formula based on room volume
This method is similar to the previous one in principle. All the same values are required, but the area is additionally multiplied by the height. The standards also differ and are indicated in Building Codes and Regulations. SNiP represents a variety of different materials, although the values for bricks and panels are most often used. They are respectively 34 and 41 watts per 1 cubic meter.
The formula for calculation is as follows:
N = V * Q / P, Where
- V — the volume of the room.
- Q — the cost standard used.
- P — the power of one section.

Let's make a calculation for the room considered in the previous case. We will take the ceiling height as equal to three meters:
15 * 3 * 34 = 1530 W;
1530/140 = 10.93 => 11 sections.
So if the room has a non-standard ceiling height, as in the example, it may need more heat. Calculating by volume is much more accurate than by area, but it does not take into account additional sources of losses - windows, thermal insulation and other factors.
Exact calculations: how many coefficients are applied
Unlike the previous methods, it takes into account all the details. The formula looks like this:
Q = 100 * S * G * I * R * T * N * A * H, Where
- Q — total heat consumption of the room.
- 100 W/m2 — basic power calculation factor.
- S — the area of the heated room.
- Other meanings are described in more detail below.
The most important 7 indicators, taken into account in the formula.
Coefficient G - glazing of the room. He is accepted as equal 1.25 for rooms with single glazing, 1.0 with double and 0.8 with triples.

I — wall insulation index. Low-efficiency material is characterized by the coefficient 1.27.
If the insulation is good (double layer of brick or high-quality thermal insulation), the value drops to one. For more stable materials, the indicator will be 0.82.
R is a coefficient that is responsible for the ratio of the area of window openings to the floor surface. Average value - 0.3, that is, the area of the windows is 30% from the floor. In this case R = 1For each percent the number changes accordingly. by 0.01. For example, for 25% - 0.95, and for 32% - 1.02. This value is more variable than the others and has a limit only from below. The minimum coefficient is 0.7Although the window area is rarely larger than the floor surface, it is possible, so there is no maximum.
T is the average temperature in the cold season. The maximum value is -10 °C, in this case the coefficient is taken equal to 0.7For every degree down it increases by 0.04 up to -25 °C, then on 0.02 to -35 °C and finally on 0.01 for each subsequent degree.
Characteristic values of T (temperature coefficient):
- 1.5 — -35 °C;
- 1.3 — -25 °C;
- 1.1 — -20 °C;
- 0.9 — -15 °C;
- 0.7 — -10 °C.

N is the number of external walls of the room. If there are none, the value is taken as equal to one. For each wall in contact with the street, the coefficient is increased by 0.1.
And the room above also has an effect. The unheated attic or roof acts as an external wall.
A heated room, on the contrary, reduces the value one tenthIf there is another apartment or a residential floor of a private house above, the coefficient is reduced. by 0.2. A corner room has at least two external walls, but it requires by 5% more heat. Therefore, the indicator is additionally increased by 0.05.
A — type of premises. For residential premises the coefficient is 1.0. Rooms with additional heat sources, such as kitchens, require by 20% less heating. The bathroom, in particular the bathtub, usually requires by 10% more power from the batteries. Accordingly, for these cases the values will be 0.8 and 1.1.
H is the last element on the list, but not the least important. This is the height of the heated room. The coefficient is taken equal to one at the ceiling height 2.5 m. For every 10 cm the meaning is changed by 0.01. For example, for 2.7 m it will be 1.02, and for 3 m – 1.05.
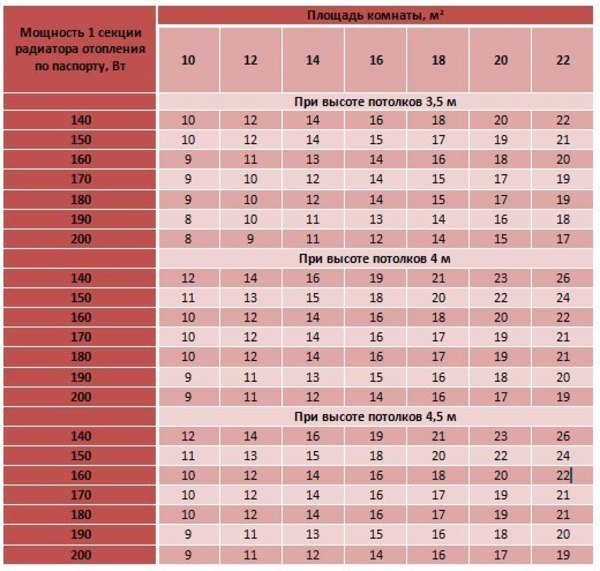
Photo 2. Calculation of the number of radiator sections depending on their power, room area and ceiling height.
This calculation method takes into account seven factors, capable of determining the number of battery sections required for heating. To obtain the final figure, the calculated heat loss value is divided by the rated power of one part of the device. The final value is rounded strictly upwards.
Let's calculate the room from the example above, but arbitrarily Let's take into account all possible factors:
100 * 15 * 1.0 (G) * 1.0 (I) * 0.9 (R) * 1.1 (T) * 1.25 (N, corner) * 1.0 (A, residential) * 1.05 (H, 3 m) = 1,949.06 watts.
1 949.06 / 140 = 13.92, so 14 sections will be needed.
This calculation method is the most accurate., but allows you to create a high-quality heating system. It observes an important factor: it provides the room with both the necessary and sufficient amount of heat.
Useful video
Watch the video, which explains how to calculate the number of heating battery sections.
The more complex the calculations, the more accurate the result!
Any of the options considered can be used, but their accuracy must be taken into account. It is better to define several coefficients and take them into account in the calculation, than to get a battery with insufficient power. It should be noted that the exact calculation can be made using a special calculator.