How not to get confused by the abundance of options? Tips for choosing a gas condensing boiler

A condensing gas boiler is a unit used as the central element of the liquid heating system.
The scope of application of condensing boilers is very wide – these units are used for heating housing (apartments and private houses).
And also to ensure heat supply on the territory enterprises and institutions of industrial, commercial, social and other directions.
Content
Advantages and disadvantages of condensing boilers

Among the indisputable advantages condensing boilers distinguish:
- High Efficiency, exceeding 90%.
- Compact dimensions and small weight.
- High rate fuel economy, located in the limit 35% compared to classic models of gas boilers.
- Low noise levelThis feature significantly affects the comfort of operation of condensing boilers.
- Low exhaust gas temperatureThis allows the use of cheaper chimneys made of plastic.
- High eco-friendliness. Volume emissions of harmful substances compared to traditional gas boiler models 70% less.
Main shortcomings
The device has few disadvantages, but they deserve attention.
Cost of the boiler and components
First of all, the price of such units depends on the characteristics of a particular model — condensing boilers 30-80% more expensive than traditional ones. At the same time, such a device pays for itself due to savings in fuel consumption. However, the payback period largely depends on the frequency of operation, the temperature regime used, and other factors.
Low temperature in heated rooms

The temperature of the coolant in the direct and return circuits in a heating system equipped with a condensing boiler is in a ratio of 55 °C to 35 °C.
Similar indicators for classic models within 75 °C—55 °C respectively.
In this case, the described disadvantage is leveled out if the heated premises are equipped with "warm floor" systemOtherwise, installation of additional radiators will be required.
Sensitivity to air quality
Condensing boilers are very sensitive to the quality of the air they take in due to the peculiarities of their design. Instead of an open combustion chamber, as used in convection boilers, condensing models implement a closed-type chamber with forced circulation: outside air is pumped into the burner, and the decay products are also discharged outside.
Important! To preserve the internal elements of the boiler (primarily the injection turbine) key meaning have both purity air (absence of dust and other impurities), and its temperature (under low temperature conditions, the boiler efficiency is significantly reduced).
Condensate disposal
Condensate formed during boiler operation must not be discharged into the local sewer system (septic tank) due to the high concentration of chemically active substances, in particular acids. For devices with a capacity of up to 35 kW, installed indoors with central sewerage, this restriction loses its relevance.
Attention! When designing a condensate disposal tank, it is important to consider that even when operating low-power boilers (~25 kW) within 24 hours is formed from 35 to 70 liters condensate.
The manifestation of the described advantages and disadvantages, first of all, depends on the characteristics of a particular model devices. Depending on the characteristics of the unit used and the existing operating conditions, the described properties are manifested to a greater or lesser extent.
The structure and operation of liquefied gas boilers
As with traditional models, condensing boilers use gas as an energy source. main or liquefied gas.
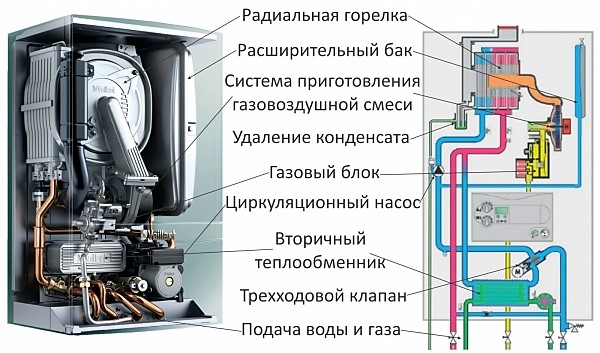
Photo 1. Image of the internal structure of the boiler (left) and its diagram (right). The main parts of the design are labeled.
More commonly used first option, primarily due to the high cost of liquefied gas (and, as a consequence, due to the low economic efficiency of this heating method). However, second This option is often implemented in industry.
The main difference condensing boilers is slightly different principle of operation. In traditional models for heating the coolant circulating in the heating circuit, only thermal energy generated directly from gas combustion is used. At the same time, part of it is lost, remaining in the combustion products.
When the condensing unit is operating boiler, lost under normal conditions, heat is extracted from the combustion products by transferring kinetic energy from the constantly forming condensate to an additional heat exchanger.
Elements and operating principle
Main elements condensing boiler:

- pipes forward and reverse feed;
- pump, responsible for circulation;
- combustion chamber with a burner, gas supply nozzles and a fan that forces air;
- primary (basic) heat exchanger And capacity for heating water;
- cooling chamber — in it the temperature of the resulting combustion products is reduced to a temperature as close as possible to the “dew point” (~56 °C);
- secondary (condensing) heat exchanger And capacity for condensate;
- chimney for the removal of cooled gases.
Operation of a condensing boiler it happens as follows: the gas-air mixture is fed into the combustion chamber and ignited, after which the released thermal energy passes through the main heat exchanger, thereby heating the coolant. The combustion products move to the condensation heat exchanger. The steam is cooled to a temperature below the "dew point", as a result of which condensate is formed.
The released energy is captured by the secondary heat exchanger and is also used to heat the coolant. Thus, due to the condensation of steam additional volumes of thermal energy are accumulated.
Peculiarities
Among the main design features of condensing boilers The following solutions are highlighted:

- The heat exchanger, consisting of tubes, has spiral shape to increase the area of contact with the circulating coolant.
- Cooled coolant (return flow) first heated by condensation heat exchanger and only then receives the main volume of thermal energy from the primary heat exchanger.
- Due to the high chemical activity of the resulting condensate, main components boilers are produced made of stainless steel or silumin — an alloy of silicon and aluminum.
- The boilers are designed using high-tech burners, which most effectively mix main gas and air.
Factors influencing the choice of device
The choice of one model or another is largely determined by personal preferences and financial capabilities buyer. The efficiency of further operation of the boiler depends on the characteristics of the model you like, the parameters of the premises that need to be heated, as well as other existing operating conditions.
When choosing a boiler It is important to take into account the following characteristics:
- power and gas consumption indicators;
- possibility of connecting an additional water circuit;
- set of control functions;
- installation option;
- price.
Power and gas consumption

To select the optimal power, the following is taken into account: area and height of ceilings of heated rooms, as well as their thermal insulation indicators in combination with the level of natural heat loss.
The recommended power depends on climatic conditions - for the middle zone This 1-1.5 kW per 10 m2 area. Fuel consumption directly depends on the boiler capacity.
Number of connected circuits
The ability to connect an additional water circuit will allow, in addition to heating, to provide hot water supply or functioning "warm floor" systems.
Feature set
All modern models of condensing boilers automated to a greater or lesser extent. At the same time, more expensive units have additional functions: automatic temperature control depending on the time of day, the possibility of remote control from a phone, response to the presence of residents, etc.
Installation options: single-circuit and double-circuit
Both floor-standing and wall-mounted condensing boilers are available for sale. Floor structures are best suited for use in larger spaces. Most floor-standing models only have the ability to connect one circuit and have more power (exceeding 100 kW) compared to wall-mounted devices.

Floor standing boilers have good compatibility with other heating units - connection is made by circulation pumps.
Wall models there are dual-circuitThey are more compact and are suitable for installation in small spaces, easy to install and do not require the installation of a full-fledged smoke exhaust system - the drain pipe is led out to the street through the wall.
Price
The boiler models available for sale are divided into three conditional categories depending on the price:
- Economy class. The cheapest boilers - minimum twice cheaper compared to premium class units. The low price determines minimum set of functionsAt the same time, the models are most adapted to Russian conditions.
- Middle class. In most cases - optimal choice. The boilers are distinguished by good performance, quality of execution, and availability of spare parts.
- Premium class. The equipment has the best characteristics, maximum set of functions, high ergonomics and safety, meets world environmental standards. The price of such boilers the highest.
Advice. When choosing a condensing boiler, in addition to personal preferences, experts also recommend taking into account availability of spare parts and opportunity quick repair the model you like.
Useful video
Check out this video that clearly demonstrates the internal structure of a condensing boiler, its features and how the device works.
Optimal choice
Choosing a condensing boiler is a very complicated procedure, primarily because many non-obvious nuances, escaping the attention of amateurs - personal knowledge of such equipment is not always a guarantee of the right choice.
You should not buy a boiler from non-specialized retail outlets, because only qualified consultants the seller company (often an official dealer) have comprehensive information and will help you make the best choice.

The guarantee of efficient operation and long service life is a proven brand.
As experts note, condensing gas boilers produced by under the following trade marks:
- Baxi (Italy);
- Buderus (Germany);
- Viessmann (Germany);
- Wolf (Germany);
- Vaillant (Germany).








Comments