Won't it cost a pretty penny? Gas consumption for heating a private house

There are three factors that influence gas consumption: boiler capacity, heat loss of the house and temperature during the heating season.
Calculating gas consumption for heating a private home will help you understand how rational it is to heat a room using a gas boiler.
Content
Natural Gas Calculation Methods
There are four types of gas consumption calculations: by heater power, heat loss or type of heating system.
For centralized strapping

The formula is quite simple:
V = N / (Q * J), Where:
- N — the power required for the room.
- Q — heat of combustion of fuel.
- J — Heater efficiency.
Q for gas G20 are taken equal 34.02 MJ per cubic meter, for G30 — 45.65. And there is also a substance G31, which has slightly better characteristics than G30.
Attention! Efficiency depends depending on the specific device and other factors, for example, the presence of insulation.
For autonomous heating for an area of 50, 60, 80 sq. m and 400 m2
Three parameters are used in the calculations: the area of the building, the recommended boiler power and its efficiency. Any values in Joules are converted to Watts: 1 W = 3.6 kJ. The heat of combustion of gas is 9.45 kW. Recommended power is the amount of energy required to heat a house during the heating season.

Since heating is not required in summer, only half the value is used. Let's assume that it is necessary 10 kW: In the calculation we use five: V = 5 / (9.45 * 0.9) = 0.588 cubic meters per hour.
Thus, it will take a day 14.11 m3The heating season lasts about 7 months: from October to April. In 213 days 3006 cubic meters will be consumed natural gas.
This calculation is made for a house with a total area of 100 square meters. Depending on the actual value, the calculation changes:
- Building in 50 squares will require half as much fuel, and in 60 - by 40%.
- House area 80 m2 will take 2405 cubic meters of gas, and in 400 m2 - a little more 12 thousand.
The calculations are approximate, since they do not take into account various factors. For example, on some days it is warmer and less fuel is needed, on others - vice versa. The result also depends on the gas used. The calculation presented uses G 20.
By heat loss
It is necessary to know the amount of heat that leaves the room per hour. Let's assume that the value is 16 kW per hour. For calculations they take 70% from the indicator. Thus, the house requires 11 kW per hour, 264 per day and 7920 per monthTo convert to cubic meters, simply divide the value by 9.3 kW/m3 — specific heat capacity of combustion of natural gas.
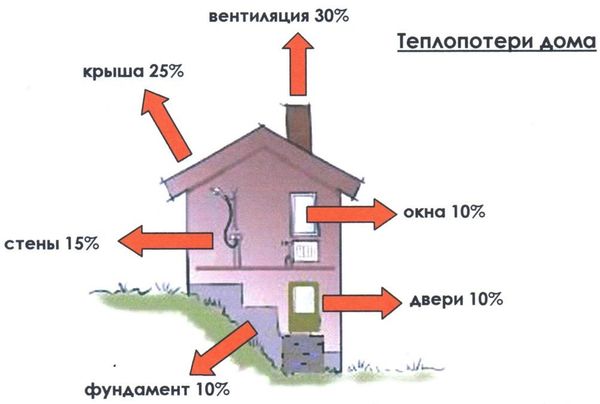
Photo 1. Heat loss of the house through its various parts. They affect the gas consumption of the heating boiler.
And you also need to make an adjustment for efficiency by dividing the number by the passport value. In the proposed example, gas consumption for one month will be 864 cubic metersThis is an average value, which is sufficient to multiply by the number of months in the heating season.
By the power of the gas boiler
The simplest calculation among those presented. It is enough to find out the heater power in the passport. The indicator is divided in half and they proceed to calculations. This is due to the actual consumption: the heating season lasts 7 full months out of 12In particularly cold winters, much more heat will be required.
Let's assume that the boiler creates 24 kW of energy. Half - 12 kW. We take the heat requirement as this value. To determine fuel consumption, this indicator is divided by the specific heat capacity of fuel combustion. For natural gas - 9.3 kW/m3It turns out that approximately 1.3 cubic meters of fuel are needed per hour, 31.2 per day, and 936 per monthThe obtained value is divided by the efficiency coefficient and the actual result is obtained.
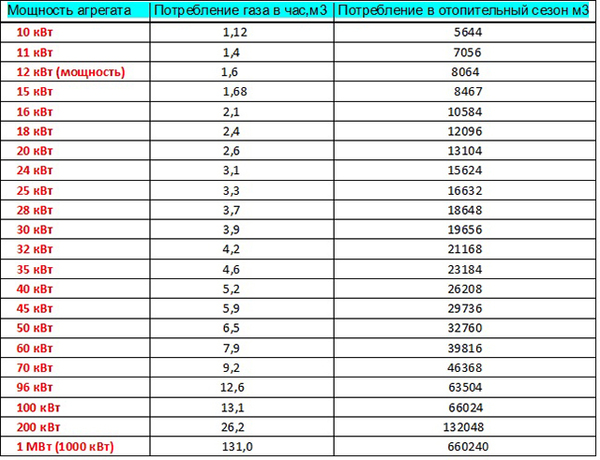
Photo 2. Gas consumption per hour and per season depending on the capacity of the heating boiler.
Calculation of consumption of liquefied propane and butane in liters
In some settlements there is no centralized fuel supply. In such situations, natural gas cooled to a liquid state is used for heating. It is usually transported in cylinders. For transportation also gas holders are used — special tanks designed for large volumes of gas. They are installed in pits underground, leaving a tap on the surface. Fuel is filled and consumed through it. Usually, only one pipe can be connected to one gas tank.
To calculate, you need to know two important characteristics. G30 — a substance that combines propane and butane. It is used in most systems. The density is 0.524 kg/l and specific heat of combustion 45.2 MJ/kgSome systems use pure propane - G 20. It has slightly better performance but is less stable.
A standard gas cylinder holds 50 liters. To comply with safety regulations, they are filled in no more than 85%, respectively, about 42 l. It is better to translate the values presented above to facilitate calculations. 45.2 * 0.524 = 23.68 MJ/l. The value is converted to Watt: 23.68 / 3600 = 6.58 kW/l.

To calculate gas consumption, use the following formula:
V = N / (J * Q), where:
- Q — specific heat of combustion of fuel.
- J — Heater efficiency.
- N — average generator power.
Typically, the efficiency of a device is 88%, A N are accepted as equal 4.7 kW/h. Thus, V = 4.7 / (0.88 * 6.58) = 0.81 l/h. Daily consumption will be approximately 19.5 liters.
According to these calculations, one cylinder will be enough for about for 48-50 hoursIt will take a month. 15 refills, and for the heating season - 105This is quite a large volume, and the purchase and delivery of liquefied gas cannot be called cheap.
Reference. Despite this, this method of heating the room effective and quite economical, compared to the consumption of solid fuel.
How to reduce heating costs for a private home
There are 5 options:
- Insulation of walls using polystyrene or mineral wool. Both substances are usually placed on the outside of the building, covered with decorative material on top.

- Placement of various substances in the roof slopes to retain heat. They use the same as for the walls, as well as wood shavings or cheaper materials, such as polystyrene foam.
- Additional floor heating, including using convectors or pipes.
- Replacement of windows with new ones with double or triple glazing. If they are of good quality, you should check the joints, the presence of various cracks. If necessary, they are sealed.
- Installation of additional heat sources in the roomThese can be standard combinations of boilers with radiators or convectors.
Useful video
Watch the video, which talks about the consumption of liquefied gas for heating a private house.
Depends on the season
Despite all the calculations presented, in fact the costs will differ. This is due to with an increase in consumption in the cold season and a decrease in the warm seasonIt is important to remember that heaters differ not only in their rated power, but also in their efficiency.