No worse than wall-mounted ones! Floor heating radiators: steel, cast iron or aluminum

A floor radiator is a heating device that differs from its wall-mounted counterpart in the mounting method and the presence of legs.
There are other features that must be taken into account when choosing: material of manufacture, method of connection to the heating system, thermal power rating.
Among the new products are radiators built into the floor. These devices have advantages and are optimal for panoramic glazing of rooms.
Features of floor radiators

Floor radiators - reliable and durable sources of thermal energy.
They are necessary where it is impossible to install wall-mounted devices: on partitions made of plasterboard and glass blocks, with a large area of glazing of vertical surfaces.
Operating principle
Floor radiators are elements of a water heating system, which works on the following principle:
- in the boiler room the water is heated to the required temperature;
- It is supplied through a pipeline to the radiators and fills them;
- the body of the devices heats up.
Heat transfer to the room is carried out in two ways:
- radiation (up to 80% from the total power);
- convection.
The convection-radiation percentage ratio depends on the design of the device. Batteries panel and sectional type They mainly work on the principle of heat radiation. In this case, the waves are directed perpendicularly to the surface of the device and at a slight angle in both directions.
If the radiator has a heat exchanger, which is a finned pipe, then air fills the space between the rib plates. In this case, heat transfer is carried out mainly by natural convection. Heated air masses rise to the sub-ceiling space, and cold ones come in their place. Floor-mounted devices operate on this principle.
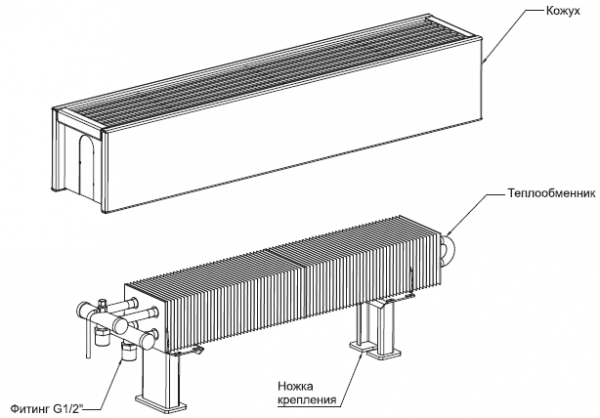
Photo 1. Construction of a floor heating radiator. The arrows indicate the components of the device.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of floor-standing radiators is considered to be minimal heat loss. This effect is achieved through a carefully thought-out design and shape of the device body. Other benefits include:
- simplicity and ease of installation;
- aesthetic appeal inherent in modern models of heating equipment;
- a wide range of equipment with different thermal capacities;
- affordable price;
- the ability to regulate the heating temperature.
Flaws:
- uneven heating of the room: the upper space becomes warm faster, while at floor level the air is cool;
- are not always able to fit harmoniously into the design of the room;
- cannot be masked by furniture or partitions placed in front of them.
Installation

Connecting a floor radiator to the heating system is technically no different from installing a wall radiator. Perform the same actions:
- Mayevsky taps or taps with a thermostat are installed at the inlet and outlet of the battery;
- threaded connections are sealed using flax and sealing paste Unipack;
- Check the correct installation using a bubble level: the top panel of the heating device must be strictly horizontal.
Reference. Each line of floor radiators includes Pass-through and end models. The first ones are intended for installation at any point of the heating system. The end ones are installed at the end of each branch of the utility network.
Floor-standing panel radiators are prefabricated. Before connecting to the heating system, several steps must be completed:
- remove the top and side panels;
- install the legs;
- secure the previously removed panels in their original places.
In order to make floor-standing appliances more stable, heating equipment manufacturers have developed special brackets. They are attached to the floor surface, after which the legs or the battery housing are screwed on. If necessary and for greater ease of installation, height-adjustable brackets are used.
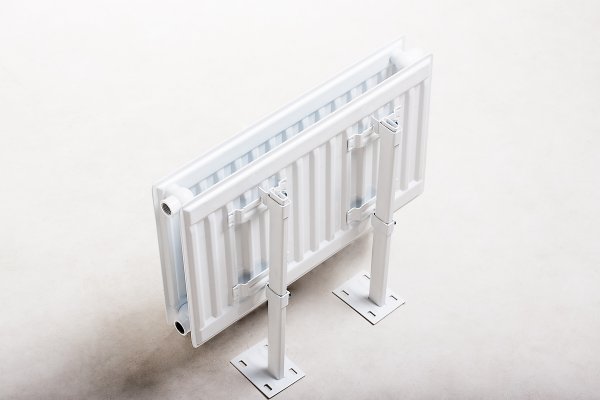

Photo 2. Special brackets with a floor-standing bimetallic heating radiator suspended on them.
Types of floor radiators
The main criterion for choosing heating equipment is the material, from which the device is made. An important characteristic of the radiator depends on this - its thermal power.
Steel
Steel ones are characterized by fast heating and high heat transfer: 1200-1800 W. Maximum coolant temperature — 130°СThis is a standard requirement for Russian heating systems. The power of the device depends on two parameters:
- dimensions;
- steel thickness (varies in the range 1.15-1.25 mm).
The thicker the metal, the higher the thermal inertia of the device: it cools down slower and heats the room better. Steel radiators differ in the number and type of sections. They can be heating (solid) and convection (with internal ribs-crossbars). The main disadvantage of heating equipment made of steel is considered to be susceptibility to corrosion when the protective coating is damaged.
Attention! When choosing, it is recommended to focus on the power of the device, which is calculated using the formula: 100 W per 1 m2 premises.
Bimetallic made of aluminum and copper
Bimetallic radiators are those whose design includes Two types of metals are used. Moreover, the finning is always made of aluminum. Steel or copper pipes act as a heating element.

Aluminum-copper devices are distinguished by the highest efficiency among all types of radiators. This is due to the outstanding thermal conductivity of copper, corresponding 400 W/μA.
In this respect, steel loses out: its index is equal to 47 W/μA. Copper with a minimum amount of impurities is used to produce batteries.
Advantages:
- have a highly durable heat exchanger consisting of a copper tube and aluminum fins;
- minimal risk of leaks, compared to sectional type devices;
- Only copper, which is highly resistant to corrosion, comes into contact with water;
- are lightweight, which ensures that installation is not difficult.
Made of aluminum and steel
Such radiators have the best properties of steel and aluminum:
- high heat transfer;
- light weight;
- fast heating;
- reliability;
- durability.

This became possible thanks to the special design of such heating equipment. It consists of two elements:
- steel pipes (horizontally laid collectors and vertical heat-conducting channels) located inside the device;
- aluminum body.
There are two types radiators:
- having steel collectors and channels;
- Only vertical heat-conducting pipes are made of steel.
Devices The first type is stronger, more reliable and more expensive. The second is cheaper and lighter. by weight, but warm up faster. The service life guaranteed by the manufacturers is at least 20 years.
Aluminum
The distinctive feature of aluminum floor radiators is their high strength and ability to withstand pressure. up to 16 atm. Heating devices of this type are produced in two ways:
- casting;
- extrusion.
In the first option, each section of the equipment manufactured using injection molding. Subsequent multi-stage surface treatment allows achieving ideal smoothness. The sections are coated outside and inside to provide protection against the effects of chemicals present in the coolant. At the final stage, the device body is coated with powder paint.
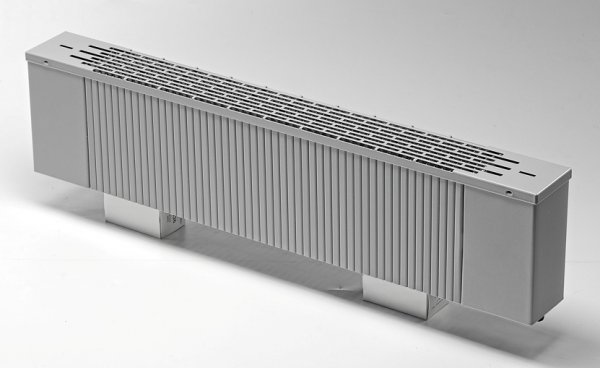
Photo 3. Aluminum floor heating radiator. The upper part of the structure has holes for the warm air to escape.
The extrusion method involves the production of vertical elements from aluminum, and the collector - from silumin (is an alloy of aluminum and silicon). All parts are hermetically connected to each other, which eliminates the risk of leaks. Regardless of the manufacturing method, aluminum devices are sensitive to mechanical impact and pressure surges in the heating system.
Cast iron
Cast iron radiators are highly reliable, but less popular compared to other types of heating devices. Available in classic and modern designs. The legs are cast in one piece. There are models ready for painting, which allows them to be adapted to any interior.
There are two types cast iron radiators: with one and two channels in each section. Regardless of this, cast iron heating devices are able to withstand pressure. up to 9 atm., which does not exclude the risk of leaks. The advantages include:
- high heat transfer;
- corrosion resistance;
- large cross-section of channels;
- Long service life: not less than 30 years.
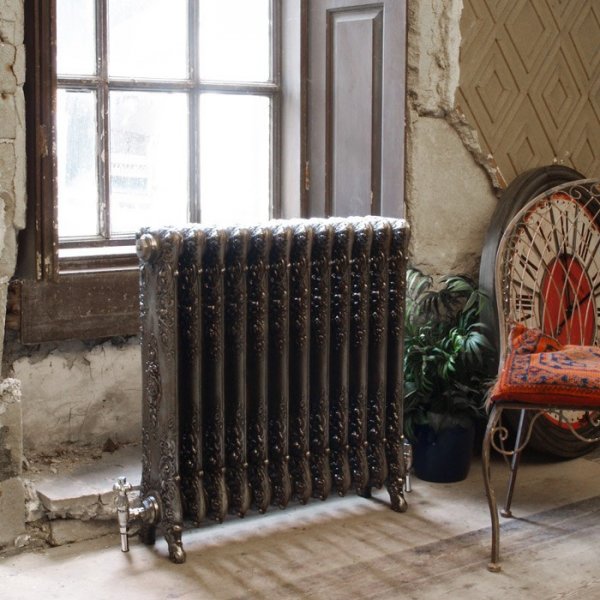

Photo 4. Cast iron floor heating radiator. The device has an original design with an unusual pattern.
The following are noted as disadvantages:
- heavy weight;
- difficult to maintain surfaces: it is inconvenient to remove dust from the space between the ribs of the sections.
Floor-mounted
Floor heating radiators can be fully called water convectors. These devices have a heat exchanger consisting of pipes with a coolant and ribs (finning) strung on them. There are models with additional functions:
- forced convection provided by a built-in tangential fan;
- condensate drainage;
- temperature control;
- climate control system.

Photo 5. Heating radiator built into the floor. The device is covered with a special grate from above.
Manufacturers offer decorative radiator grilles with transverse and longitudinal arrangement of lamellas. The device body is a hollow metal box in which a heat exchanger and control sensors are installed.
Important! Floor-mounted radiators have the advantage of having a relatively large heat exchanger area, which guarantees high power and efficiency.
Installation of underfloor heating devices has its own peculiarities.
- The heating system pipes are laid below floor level.
- The radiator is installed in a niche specially prepared for this purpose, the dimensions of which should be several centimeters larger than the dimensions of the device.
- The height of the body relative to the floor level is adjusted using special screws.
- The legs are attached to the bottom of the niche.
- They remove the plugs from the heating pipes.
- A thermostatic valve is installed on the supply line, and a shut-off valve is installed on the return line.
- Connect the pipes to the radiator.
- A decorative grille is installed.
Floor radiators are indispensable for heating rooms with panoramic glazing, shop windows, greenhouses, entrance areas in high-traffic areas to cut off the flow of cold air from the street.
Useful video
Watch a video demonstrating the installation of floor heating radiators.
Conclusions
The range of floor radiators is wide: it includes models of different sizes, from miniature plinth models to large-sized ones. Inconspicuous devices are installed near panoramic windows, along display cases and glass partitions. The most effective are decorated radiators, which can decorate a room with any interior style.






