Power, dimensions of bimetallic heating radiators and other important characteristics

Bimetallic heating devices have appeared recently and have already become popular among buyers. Bimetallic radiator - construction of two types of metal.
Pipes made of steel, filled with coolant, make up the core, and on the outside is a casing-shell made of thermally conductive aluminum.
Content
- Types of bimetallic heating radiators
- Other technical specifications
- Algorithm for calculating the number of batteries based on thermal power
- Corrosion resistance level
- Variety of designs
- Heat transfer and pressure requirements
- Service life
- What is better: cast iron or bimetallic devices? Comparison table
- Useful video
- Summary: Which Model to Choose
Types of bimetallic heating radiators
Products are being manufactured two types:
- Fully bimetallic radiators (the core and the body are each made of its own material). Such models never leak, are strong and durable. The domestic market is supplied with Italy. But several Russian variants are also presented.
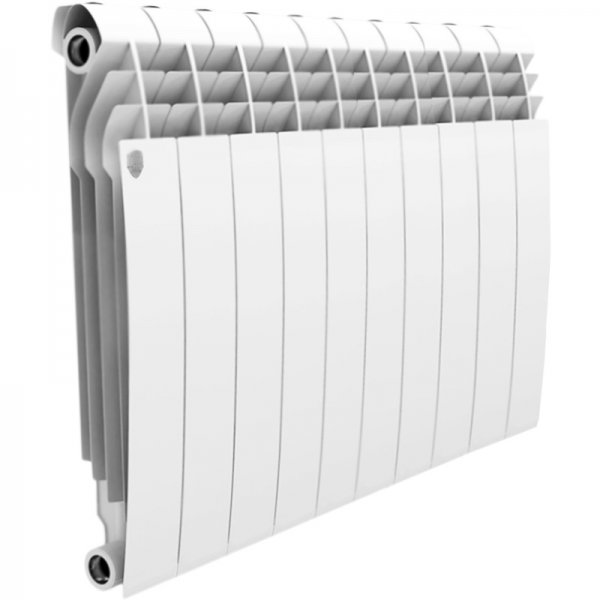

Photo 1. Bimetallic radiator model Biliner 500, power 1710 W, manufacturer - "Royal Thermo".
- Semi-metallic radiators (only part of the pipes are steel, aluminum elements partially come into contact with water). This type of radiators has a higher heat output and a lower price. They are produced by manufacturers of our country, and also Chinese and Italian companies.
According to size and design, radiators are divided into sectional and solid.
Sectional
A separate section of the radiator is a ready-to-install device. They are assembled at the factory in Multi-section panels with nipple connection. If necessary, extra sections are removed or additional ones are added, which is done under specific conditions during installation.
Whole
This is a core that is originally manufactured to the required size. The size of such a radiator is not adjusted, so when buying a product, you must immediately know the exact size required. Solid options withstand pressure up to 100 atmospheres.
Other technical specifications
The following characteristics of radiators are important.
Height and other dimensions
The height, width and depth of the radiator sections are important.
The height usually depends on the center distance and exceeds it by 80-100 mm.
Depth varies from 80 to 100 mm.
Dimensions between axles

This is a geometric parameter (from axis to axis), measured in mm. (200-800).
A range of batteries with different values is available, allowing you to select a product for any system configuration and layout.
Standard distances are - 200, 300, 500 mm.
Volume
Bimetallic radiators are economical in terms of the required amount of coolant. Standard section of the battery (600/80) needs in a quarter liter of liquid. Cast iron radiator options (580/75 and 600/110) demand 1 and 1.7 liters respectively.
Algorithm for calculating the number of batteries based on thermal power
It is important to correctly determine the number of batteries required to maintain the optimum temperature during the cold season.
A calculation based on this will help to establish this value indicators of thermal power of radiators. The installed devices must fully compensate for the heat losses that occur during the passage of the circuit.

As an example, we can consider a certain room in an insulated house in a temperate climate zone, for which there is a standard power value at 41 W per cubic meter.
All parts of the living space (floors, ceilings, walls, windows, subfloors and attics) must be insulated so that heating is directed specifically at the living space and not at the surrounding environment.
To determine the total required power of the radiators, the following formula is used:
Q=41xV, Where
V — the volume of the room.
If you calculate the number of radiators using different coefficients, you need to start from the relative value 100 W, which is conditionally necessary for heating each meter of the room area.
The formula used is:
Q = (100xS), Where

S — room size, sq. m.
The result is then modified by multiplying by coefficients (determined based on specific conditions) that will help to clarify the calculation and make it as close to reality as possible.
When calculating, it should be remembered that It is better to consider errors in the direction of increase, since the lack of heat will be more difficult to correct.
Coefficients
The following coefficients apply.
Cardinal directions
The coefficient depends on which side the windows of the room face. R. If they go out to:
- south — the value is 1;
- west — 1 (if the area is closer to the north and the day is short, then 1.05);
- East — 1,1;
- north — 1,1 (in northern latitudes even more - 1.15).
And also, if necessary, the coefficient is increased in areas characterized by strong winds - by 20%.
Walls

The influence of walls is indicated by the coefficient "TO"It increases depending on the number of walls facing the street.
Each outer wall will increase it by 10%. Accordingly, the four external walls will be reflected in the calculations by the value 1,4.
Insulation
The number of radiators can be reduced by high-quality thermal insulation of the walls, which is indicated using a coefficient U.
This value is equal to one when the walls are insulated according to the climate. If professional insulation is carried out with preliminary calculations, then the U value decreases. up to 0.85.
With “cold” walls the coefficient increases up to 1.27.
Climate
This factor is included in the calculations as T. The indicator has a value equal to 1, if there is no temperature on the thermometer scale less than 20°CThis temperature regime is considered normal.

If the average frost values in a particular area do not exceed 15°C, then T is equal to 0.9. Average value in -10°С will reduce the coefficient to 0.7.
In the north T will be higher:
- up to -25°С — 1.1;
- up to -35°С — 1.3;
- below -35°C — 1.5.
Ceiling
The ceiling height also affects the number of radiators. It is designated by the letter H: The indicator is formed as follows:
- up to 2.7 m - 1;
- up to 3 m - 1.05;
- up to 3.5 m - 1.1;
- up to 4 m - 1.15.
Every half a meter heights are added 5% to the coefficient. For even higher ceilings, the value is used 1,2.
Ceiling and floor

The coefficient should be taken into account W, reflecting the presence of a warm or cold attic and floor.
The amount of the correction depends on the degree of insulation of these rooms from the cold:
- uninsulated and unheated attic - 1;
- insulated attic without heating - 0.9;
- insulated attic or room above — 0.8.
An uninsulated floor will increase the value by 40%, if there is thermal insulation, then only by 20%.
Window
The quality of the frames introduces a correction into the calculation, indicated by the letter G.
- double glazed window — G = 1 (three-chamber package reduces G to 0, 85);
- old frame — G = 1.27.
Number of windows

The level of heat loss is affected by the number of windows in the room, the coefficient is indicated by the letter X.
A standard has been established for the ratio of window and room areas: when dividing the window and room areas, the resulting value should not exceed 0.3. In this case X = 1.
- up to 0.4 - 1.1;
- up to 0.5 - 1.2.
If the windows are panoramic, then it is added 10% for every tenth when calculating the ratio of areas.
The value of X also increases the door to the uninsulated balcony - it is added 30%.
External factors
Size Y reflects the presence or absence of obstacles to the movement of warm air:
- if the battery is installed under the windowsill, then this is the standard location, Y is equal to 1;
- if the radiator open on all sides, then the coefficient becomes decreasing - 0.9;
Reference! The appearance of the radiators allows their use without masking, additional screens, this increases heating efficiency.
- barriers, curtains, casings increase Y.
Connecting the battery
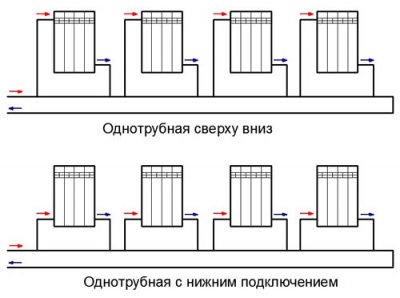
Size Z reflects how efficiently and technologically correctly the radiator is connected:
- use of the technique "diagonally" is considered standard (Z = 1);
- "from the side" — a technique used when the length of the pipes is short (Z = 1, 03);
- "two-sided below" - a common method used when using plastic pipes (Z = 1.13).
Corrosion resistance level
Possible rusting core radiator (as an option, purchasing a product with pipes made of aluminum, oxidized copper or stainless steel is being considered).
Important! The rate at which the radiator fails for this reason depends on quality of the coolant. For example, in private homes it often contains antifreeze, which speeds up the process.
Variety of designs
The appearance of the radiators allows them to fit into any interior. These are stylish and beautiful products of neutral color. The radiators can have different configurations, even semicircular models are produced for rooms with rounded walls.
Heat transfer and pressure requirements
The main part of bimetallic radiators is produced for systems in which the coolant is water, therefore the permissible heating of the liquid medium is limited 90°С. And the maximum temperature value is 130°С.

The possible pressure in atmospheres is indicated by the manufacturer and, as a rule, is in the range 16-35.
In ordinary houses this value is about 14 (with a common heating system). In private home systems it is on average 10 atmospheres.
The product documentation specifies the critical pressure at which it will begin to break down. The manufacturer tests the product by crimping the radiators at a pressure exceeding the operating value. 1.5 times.
Service life
Standard battery life is 20 years old.
What is better: cast iron or bimetallic devices? Comparison table
| Material | Cast iron | Bimetal |
| Heat dissipation, W/section | 100-160 | 150-180 |
| Pressure, atm | up to 12 | up to 50 |
| Resistance to coolant quality | little dependent, retains properties many decades | as a result of draining the system begins to rust |
| Coolant temperature, °С | 110 | 130 |
| Durability, years | 50 and more | up to 25 |
| Ease of installation | professional help is required due to the considerable weight of the radiators | you can install it yourself (if you have some plumbing skills) |
The price of bimetal will be 2 times more expensive.
Useful video
Watch the video which explains the rules for choosing a bimetallic heating radiator.
Summary: Which Model to Choose
It is better to specify the data in relation to a specific model, but for some parameters modern options radiators superior to traditional cast ironThey surpass them in power (kW) and reliability.
At the same time, cast iron radiators are an unrivaled durable type of device and do not lose their positions. Now they are being released in an updated form, which is almost as good as bimetallic radiators.







