Simplicity and reliability of a single-pipe design! Heating system "Leningradka": what is it
You are viewing the section Leningradka, located in the large section Systems.

One-pipe heating It has the simplest radiator connection scheme.
It's manageable cheaper than others heating circuits and can be installed by yourself.
It can be installed in a one-story house or a small cottage.
Content
Single-pipe steam and water heating or "Leningradka"

Water supply and return pipe are one, hence the name - single-pipe. The main pipe comes out of the heating boiler and goes to the heating batteries, passes through them and returns to the boiler.
Passing successively through each radiator, the water gives off part of its heat for heating. Thus, it arrives at the very last radiator cooled down.
Temperature difference between the first and last battery can be 10—20 °C.
Pros and cons, can it be used in a multi-storey building
The advantages of a one-pipe system, which ensure its popularity:
- Simplicity and affordability — this is the most technologically simple heating system. Its construction requires a minimum number of pipes, which will cost a relatively small amount of money.
- The coolant in the pipes can move by gravity, which is relevant for autonomous independent heating operation.
Main flaw systems — uneven heating of rooms. It limits the possibility of using the scheme for multi-storey buildings. Accordingly, the one-pipe scheme is not suitable for heating apartments, it is usually used in small houses with an area of up to 100 sq. m.
Horizontal and vertical wiring: diagrams and description, which is better
There are different options for organizing one-pipe heating:
- The heating circuit can be equipped on one floor. This type of circuit layout is called horizontal.
- The heating circuit can be equipped on two floors. This scheme is called vertical.
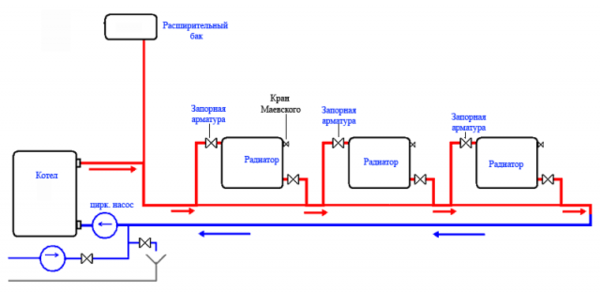
Photo 1. The Leningradka heating system diagram. The red color shows the movement of the coolant from the boiler to the radiators, and the blue color shows the opposite.
For vertical one-pipe scheme the following options are possible:
- Water can be supplied to the circuit from a distribution manifold located at the top - the so-called upper spill.
- Water can enter the circuit from below and move along the “first floor – second – first” loop – the so-called lower spill.
Variations of radiator connection:
- Insertion directly into the main pipe.
- Connection via pipes.
This option is - represents a distant model of a two-pipe system. In it, the radiators are connected to the main pipe through connecting tubes - pipes. The main flow of the coolant passes along the batteries, into each of which only part of the hot water is directed. The main flow moves on, without entering the radiator. This scheme allows for even distribution of heat between the rooms.
Besides It is more technologically advanced and convenient for repairs. If replacement is necessary, one of the batteries is removed, while the system continues to function. Unlike the scheme in which the batteries are cut into the main line directly, without pipes, and the entire volume of the coolant passes through each battery.
Leningrad system with pump

The main advantage one-pipe scheme - possibility autonomous work and movement of the coolant by gravity.
However, the efficiency of such heating depends on several factors, each of which can slow down the movement of water in the radiators and reduce the air temperature in the rooms.
For example, the speed of the coolant depends on the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the boiler. The larger it is, the higher the pressure difference and the faster the flow.
However, with a relatively small drop in temperature outside, +8 +10 °C, There is no need to heat the water too much. It is enough +50 +60 °C. And at such a temperature the flow rate will be noticeably lower than when heated. up to +80 °C.
For single-pipe gravity flow system a specific location of the boiler is required - as low as possible, in the basement or semi-basement. And high position of the distribution manifold - in the attic. Which is not possible in every building.
And also - gravity is impossible in large houses with heating area more than 150 sq. m. Therefore, for large buildings, an additional device is built into the single-pipe heating system - circulation pump.
Pump provides forced circulation of the coolant. It pushes water through pipes by rotating small blades. It works from a separate power source - an electrical outlet. It ensures the movement of the coolant regardless of the water heating temperature, the location of the boiler and the height of the outlet pipe. In a house with any heating area.
The principle of operation of the circuit

Under the outer casing of the pump is located engine and rotating bladesWhen connected to a common pipeline, the blades are rotated by an electric motor.
Their rotation forces the water in the pipe to move further. The vacated space is filled with the next portion of water, which also passes through the pump blades.
So The coolant moves in a circle, pushed by the working blades.
The pump is built into the system before entering the boiler. Here is the minimum natural flow rate, and therefore the most appropriate location for forced circulation.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage heating schemes with a circulation pump - its guaranteed job at any temperature and with any arrangement/connection of radiators. And also the ability to heat a house of different sizes, with one or more floors.
Of the disadvantages schemes with pump — addiction heating from electricity.
Scheme with pump
The circuit diagram includes the same devices and elements as a conventional one-pipe system. And additionally has a pump. It can be embedded in two ways:
- Directly into the return water pipe. With such a connection, the movement of the coolant by gravity is impossible.
- Through the pipes — with such a cut-in, the pump is connected parallel to the common main line. If it is turned off, water can move along the main pipe without obstacles. Thus, it is possible to combine an autonomous and dependent system in one circuit. When the pump is connected, the coolant will circulate forcibly. When it is turned off, water will flow along the pipe by gravity.
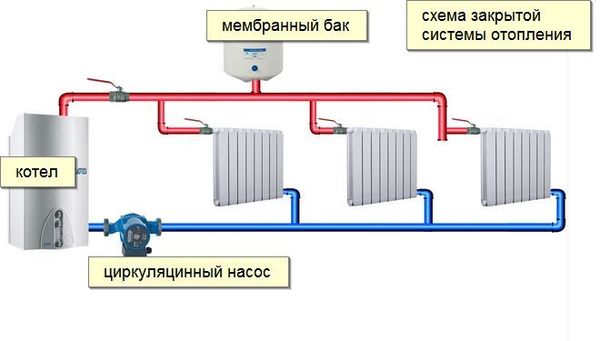
Photo 2. Diagram of a closed-type single-pipe heating system using a circulation pump.
How to make a heating structure from polypropylene with your own hands?
The production of the Leningrad heating system is underway in several stages.
Calculations
Proper arrangement of heating is impossible without individual calculations. What needs to be calculated before installation one-pipe scheme:
- Heating power — the maximum amount of heat that may be needed to heat a house. The power is calculated in a special program taking into account the size of the rooms, the material of the walls, the presence of insulation, the number and size of window/door openings.
- Power of each radiator — is determined by their number in the system, based on the total capacity of the heating system.
- Hydraulic calculation of the system — determination of hydraulic resistance — necessary for organizing effective gravity flow.
- Volume of coolant and heating system — the volume of the boiler and radiators (indicated in the technical data sheets) + the internal volume of the pipes (calculated using volume formulas — the length of the pipe is multiplied by the square of the internal radius and by the number “pi” — 3.14).
- Calculation of the volume of the expansion tank — must be 15% from the volume of coolant in the system.
Thermal calculations are also taken into account when choosing a heating scheme.
Installation
Let's give an example step-by-step instructions for installation of a single-pipe system:
- Installation of a heating boiler — in a separate room or a fenced-off part of the corridor, veranda, kitchen. For gravity flow, it is desirable that the place where the boiler is installed be deepened by 0.5—1 m into the basement space (the floor level was lowered, a step).

- Installation of heating radiators — aluminum, steel, cast iron. Any type of radiators can be cut into a single-pipe system. They are necessarily installed under each window and, if desired, along the blank walls of the building.
- Fastening the transfer manifold: in a system with natural circulation - at a height, under the ceiling or in the attic.
- Fastening the expansion tank - it is also led into the attic space.
- Connection of the boiler, radiators, tank, collector with polypropylene pipes. It is important to note that the boiler pipes and radiator outlets are made of metal. To connect them to plastic pipes, you will need special fittings. These devices have a smooth coupling on one side and a thread on the other. First, they are screwed onto a metal pipe, then soldered to the edge of the plastic pipe.
- If necessary - together with pipes into the system a circulation pump is built in.
- Filling the system with water, checking for possible leaks.
- Connecting electrical appliances (pump, possibly boiler), test run of heating.
Attention! Further it is desirable towarm up the distribution manifold and expansion tank — to reduce heat loss and prevent freezing of the heater in the attic containers.
Useful video
Watch a video that talks about the features of the Leningrad heating system.
One-pipe scheme for a private house
The single-pipe Leningradka scheme is one of the most popular heating systems designed for heating a private home. proven by decades of reliable operation. An accessible installation scheme, low installation cost, and the possibility of autonomous operation made Leningradka one of the most popular heating circuit schemes.


Comments