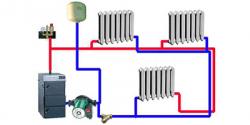
A cheap and efficient heating option is a one-pipe system
A simple and inexpensive way provide warmth in the house - one-pipe system. Heat in the cold season is provided by one highway, this allows you to save on materials.
This type of heating device makes it possible to make heating completely autonomous.
In this case, it is possible to increase efficiency install pump and use it as needed.
Content
Single-pipe water heating system of a multi-storey building
In multi-storey buildings, such a system is often used, and the main material used is steel pipe (in private heating systems, the use of polypropylene or metal-plastic is acceptable).

- the design of the system and its project are calculated in accordance with SNiP for laying pipelines;
- sections of the main line that run outside or in the basement, are being insulatedso that heat is not wasted;
- is used in buildings vertical one-pipe system — a cheap and effective heating option;
- design and calculation are carried out at the construction stage — the optimal option, diagrams and drawings with calculations related to heating are approved by the relevant authorities before the start of construction;
- before launching into operation, it is carried out pressure testing and commissioning works.
The principle of operation in an apartment building
In a one-pipe system there is no clear division for supply and return, only conditionally. The sequential connection of radiators and the ring structure often make it impossible to define a certain section as the reverse one.
In large apartment buildings, wiring to the apartment is often done two-pipe, and within a floor or apartment - single pipe.
What does a single-circuit flow heating system look like?
In multi-storey buildings of various purposes within the boundaries of a populated area, heating is carried out centralized, i.e. the house has a heating main input and water valves, one or more heating units.
- heating unit is located in a separate room, locked for safety;
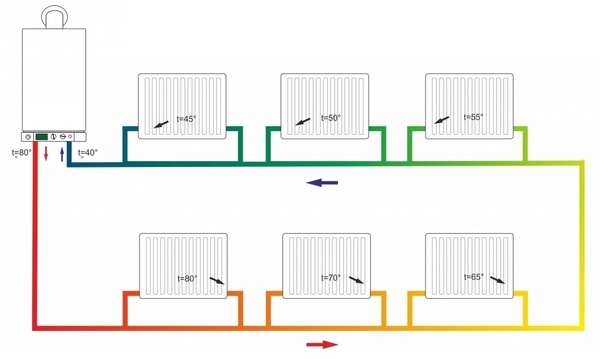
Photo 1. A schematic representation of what a single-circuit heating system looks like, indicating the temperature of the coolant throughout the entire circuit.
- first come first water valves;
- after the valves are installed mud filters, in which foreign inclusions in the coolant are retained: dirt, sand, rust;
- then follow DHW valves, installed on the return and supply (or at the beginning and end of the circuit).
Their purpose is to provide hot water supply, which can be supplied from the feeder or return. In winter, the coolant comes very hot, much more than 100 °C (boiling does not occur due to high pressure in the pipeline).
Reference! In a one-pipe system, a similar principle is realized by DHW supply from the end of the circuit, where the water has already cooled to an acceptable temperature. Accordingly, if the temperature at the supply from the main line is reduced, then the DHW changes the source to the beginning of the contour.
Such water cannot be used for domestic purposes, so the supply from the return line, where the temperature has already been reduced to an acceptable level, is activated. In the autumn-spring period, when the heating is less intense, the water on the return line turns out to be too cool, so the supply of hot water is carried out from the supply.

One of the convenient and common schemes is open water intake:
- boiling water from the thermal power plant enters elevator unit, where it is mixed under pressure with water that is already circulating in the system, resulting in water with a temperature about 70 °C, which enters the radiators;
- the excess of the cooling coolant goes into return line;
- heat distribution occurs with the help of valves or manifold with valves for each part of the house.
The return and supply are usually located in basement, sometimes they are separated: the return line is in the basement, and the supply line is in the attic.
Pros
The advantage of a one-pipe system is considered to be cheapness, and this is the only advantage of this system. With the spread and improvement of the two-pipe system, the one-pipe system is used less and less in apartment buildings.
In private homes, the cost-effectiveness and simplicity of the design are valued higher - it can be assembled with your own hands, easy to maintain and make non-volatile.
Cons

There are more of them:
- the need for accurate calculation of pipe diameters main pipeline and branches;
- in the radiators at the end of the circuit the temperature will be lower, so you will have to think about increasing the volume of heating devices;
- for the same reason number of radiators on one branch will be limited, since uniform heating of a large quantity is impossible.
Options for using a single-pipe radiator connection scheme: photo
The following options are available.
Wiring diagram - one of the main schemes, which is selected taking into account the number of floors, the number of radiators, and the planned amount.
Vertical with more batteries
Usually the main line is in the basement, and other lines branch off from it. risers with a smaller diameter, heating devices in the apartment and pipes are connected to them. The scheme is extremely simple and the work is cheap.
There is a scam here lower or upper. If it is upper, the feed is laid in the attic or technical floor. The risers are connected in series, through which the coolant enters the apartments.
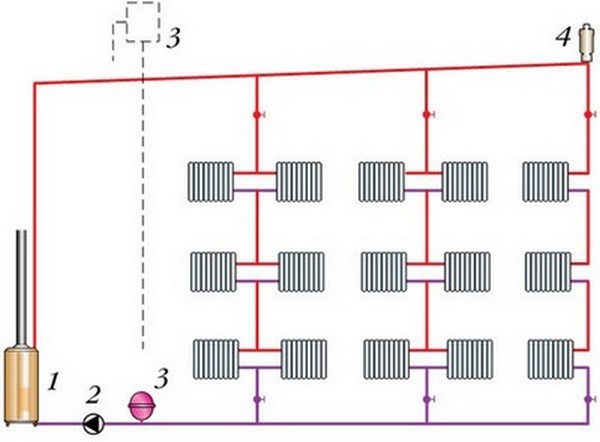
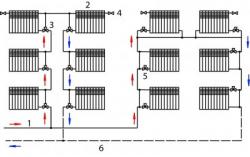
Photo 2. Diagram of a vertical single-circuit heating system: 1 - boiler, 2 - circulation pump, 3 - expander, 4 - air collector.
This scheme is not flexible, plus you should immediately calculate for a large number of radiators. If the project is designed to use the gravity movement of water, this design will work well.
Horizontal with a riser through all floors
The basis for the application of horizontal wiring is a riser that goes through all floors, Pipes are connected to it, supplying the coolant to each apartment.
Important! The use of such a scheme requires thermal insulation of the main riser - the source of heat for all branches. In most cases, a a separate shaft or insulate it with materials with low thermal conductivity.
Single-pipe systems are used in residential houses, but two-pipe ones are the best option.
Bottom wiring
The diagram assumes the movement of water first through a horizontal pipeline, then vertically up to the radiators.
Adjustment of such a system is arranged quite simply, it is also easy to shut it off.
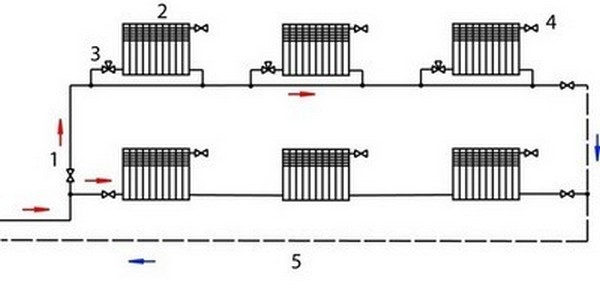
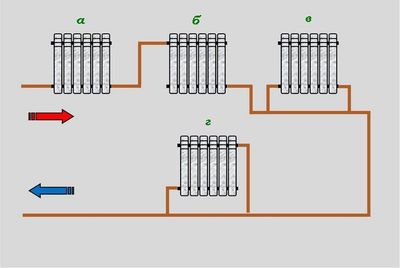
Photo 3. This is what a single-circuit heating system with bottom wiring looks like: the pipes are located at the lowest point of the room.
Upper wiring
First, the coolant rises upward, then along the branches of the horizontal distribution along the risers.
This scheme requires increased circulation and is mounted with installation calculations circulation pump. Natural circulation is also applicable.
In such a system there are no problems with air locks; they are easily removed from the central riser.
To regulate the intensity of heating in single-pipe systems, use bypass sections on the radiator, which are isolated from the circuit using valves.
Important! Radiators are installed taking into account the features of this type of system. The hottest batteries are at the beginning of the contour, accordingly, as they move away from the source of the hot coolant, the radiators should become larger in size, as the coolant will cool down.
Open or closed
Open means installing a non-hermetic expansion tank.
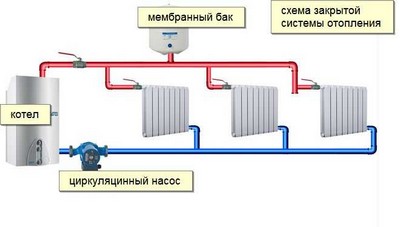
When the pressure increases, water enters the tank excess volume of coolant, which allows to stabilize the system operation.
Excess coolant flows back into the boiler or is drained into the sewer.
Since the tank is installed at a high point, air removal is not a problem.
The single-pipe open version is the easiest to do yourself. Any scheme of this type of heating device consists of from 4 components:
- heat source (boiler);
- pipes;
- radiators;
- expansion tank.
If the expansion tank is closed from the external environment, the coolant does not come into contact with air, then the system becomes closed. Such a heating device is more demanding to additional devices, There are a number of advantages:
- automation allows you not to waste time on system status monitoring;
- coolant May be any, including antifreeze;
- the house's water supply is maintained pressure, it is possible to install automatic washing machines, dishwashers and other units;
- air isolated system less susceptible to rust and lasts longer;
- expansion tank does not require installation on top, it is placed anywhere;
- some other tangible advantages.
Disadvantage - energy dependence. The closed type of system makes natural circulation almost impossible. Theoretically, it is possible to ensure the movement of water without a pump by changing the diameter of the pipes in different areas, but the calculations and implementation of such a project are complex.
Attention! If we consider a closed-type one-pipe system, then this is a quite successful option. for low-rise buildings. The scheme includes a pipe and radiators connected in series (“Leningradka”), with a passing or dead-end water flow.
Natural or forced circulation: what is it
In open heating systems, the following are used: two types organization of coolant movement:
- gravitational;
- forced.
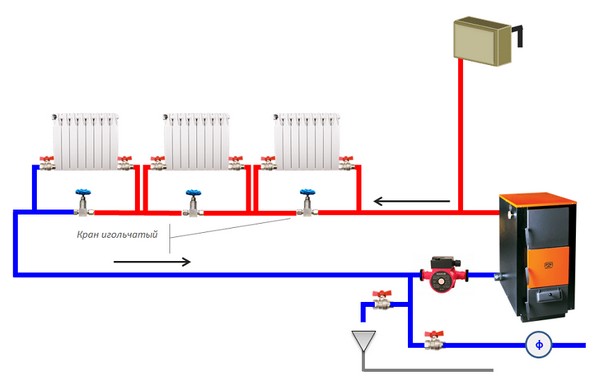
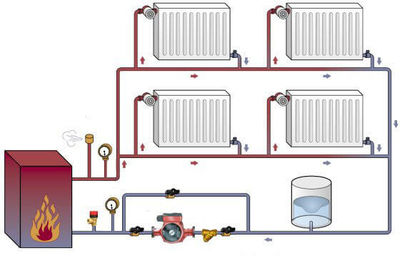
Photo 4. Single-circuit heating system with forced circulation: provided by a circulation pump built into the system.
Natural circulation is ensured by the expansion of water; in addition, when laying the main lines, the required technological slope is observed.
The forced system does not work without a pump. Completely energy dependent.
The system can be changed and improved at any stage: with the installation of a pump, a gravity system dramatically increases its effectiveness, while remaining energy independent. If the power goes out, the movement will continue naturally, and the house will be heated.
To increase the speed of movement, an acceleration riser with a height of from 3.5-4 meters. Without it, the speed will be low.
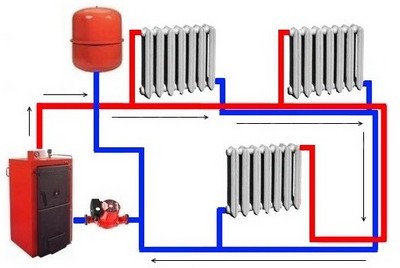
This scheme is suitable for heating rooms with a total area of no more than 60 sq. m., the total length of the contour is also limited - no more than 30 m.
If it is not planned to heat the coolant to a hot state, it will also be necessary to install a pump.
The picture will improve acceleration riser - therefore the number of floors matters, in this case the system will be able to work better.
The system can be designed with partial coercion. For example, in a warm floor system, water circulates with the help of pump, the remaining rooms are heated by residual acceleration and natural movement. In this case, power outages will not leave the house without heat either.
Useful video
Check out this video that explains the benefits of a one-pipe heating system and common mistakes made when installing one.
Traditional approach or full automation
If we consider options for heating systems for an apartment building with several floors, then a single-pipe system will ultimately create more problemsIn the long term, one can foresee uneven heating and additional costs to improve the efficiency of the heating structure.
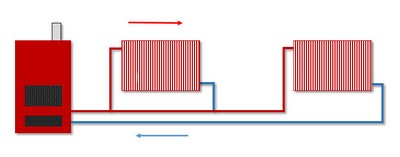
If a one-pipe system is chosen, then its most difficult part will be a carefully calculated professional project.
There are many supporters of this option, they are inspired by low cost of work and old houses, in which such a system has been successfully functioning for many years decades.
A more flexible option is a combination of two-pipe and one-pipe systems. It will allow and save money, and take advantage of the benefits of both systems.