Combines many advantages! Principles of organizing heating "Leningradka" in a private house

"Leningradka" - the simplest heating system, which got its name from the place where it was invented (Leningrad).
She is an independent one-pipe system, consisting of a boiler, radiators, expansion tank and pipe. Installation is simple and does not require special skills.
Content
Heating "Leningradka" in a private house
Most often, this heating system is used in private houses. combining simplicity, accessibility and qualities that make existing shortcomings insignificant.
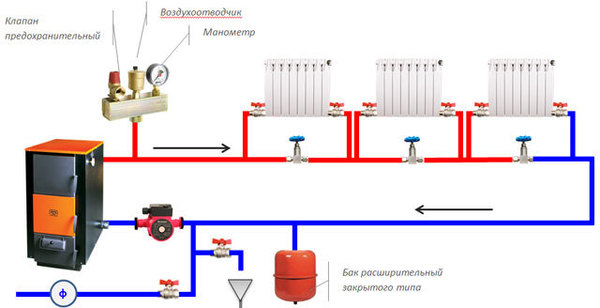
Photo 1. Diagram of the Leningradka heating system with a solid fuel boiler and a circulation pump.
Peculiarities
It consists of the following:
- Temperature of heating radiators adjustable in each individual room.
- Since the batteries are connected in parallel to the pipe, any radiator can be disconnected or completely dismantled, which will not affect the operation of the system in any way.
Advantages
"Leningradka" has a number of advantages, for which it is chosen by owners of private houses:
- Easy installation and restoration work in case of malfunction.
- No special skills required for installation: once figured out, anyone can do it.
- Pipes are laid anywhere, including under the floor.
- Available materials and equipment.
- Profitable operation.
Flaws
Despite its advantages, the system has a number of disadvantages:

- For maximum efficiency high pressure required. For these purposes, a circulation pump is installed and the temperature of the coolant is increased.
- With a horizontal scheme arise difficulties with connecting the second circuit (warm floor).
- With natural circulation the distant radiators give off less heat due to the cooling of the coolant, and the temperature at the entrance is much lower, than at the exit.
- Low efficiency at long lengths highways.
For efficiency and uniformity of coolant distribution, larger diameter pipes, and this spoils the appearance and leads to an increase in the cost of heating.
Types of systems
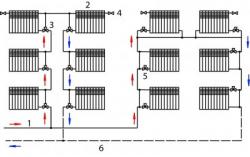
Using a one-pipe heating system Two-story houses are also heated.
She's like that is divided into horizontal and vertical.
Horizontal
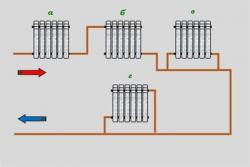
The most popular piping. If the length of the main line more than 30 meters, horizontal junction is preferable. Pipes are laid under the floor or above it along the walls in a circle, closing in a ring. The coolant is ordinary water.
Vertical
Gives a more effective result: the room warms up faster. This type is suitable for a two-story house.
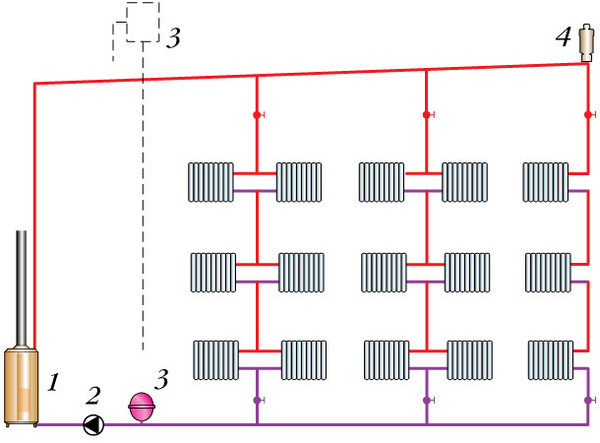
Photo 2. Scheme of the heating system "Leningradka" with vertical type wiring. In this case, a circulation pump is required.
And also implies mandatory installation of a circulation pump. The main pipe is laid inside the attic and well insulated. The outlet pipes are lowered down. If the house has several floors, the radiators are installed one under the other.
Attention! The heat carrier usually used is antifreeze diluted with waterso that it doesn’t freeze in the attic.
Operating principle
It consists of the following:
- All heating devices are connected in series, including heated floors.
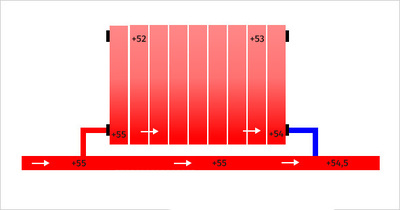
- It goes from the boiler through the pipe hot coolant. Passing the "ring", he gradually cools down, in each subsequent radiator the temperature is lower than in the previous one, and at the inlet to the boiler the temperature is much lower than at the outlet.
- Cold water pushes out hot water and due to the temperature difference, the movement of the coolant in a circle is maintained.
Important! The problem of cooler last batteries in the chain is solved installation of subsequent radiators of a larger area, increasing their number in distant rooms. Also, the first radiators in the chain are tried to be installed in rooms with the greatest heat loss (rooms with windows or on the windward side).
Circulation
If the choice falls on a vertical scheme, then the method of circulation of the coolant is selected: forced or natural.
- With natural circulation The diameter of the pipes should be more than 2.5 cm. If the pipes are steel, the resistance increases, so they should be abandoned.
- Forced circulation is the most popular, since the diameter of the pipes and other characteristics do not affect it. A special circulation pump is installed, which raises the coolant upwards. Even with a minimum pipe diameter, heating will occur quite quickly.
Calculation
For maximum efficient heat transfer with minimum energy consumption It is important to correctly calculate the heating system.
For this you need to know the power:
- boiler;
- radiators and their number in each room;
- expansion tank. As well as the diameter and length of the line.
Determining the boiler capacity
To determine the capacity of the boiler installation, heat losses of each room are calculated. Heat losses occur through the ceiling, under, windows and walls. The following formula is used for calculation: The area (walls, windows, ceilings) is multiplied separately by the corresponding loss coefficient for each of them. Then, the result is summed up and a conclusion is made about the capacity of the boiler plant.

There is another faster calculation method. There are recommendations for the specific boiler power depending on the region.
The calculation is made according to the formula Wк = Wуд x S/10; where: Wк — boiler power; Wood — recommended specific power.
After this, you can draw a heating diagram and select radiators.
Calculation of the power of radiators and their quantity
The number of radiators and sections in them depends on the area of the room, heat loss, which is affected by the wall materials and the presence of windows.
Calculate the volume of the room: V=S*h, where is the area and height of the ceilings.
Per 1 square meter brick houses for comfortable temperature are necessary 0.034 kW. The required thermal energy for heating the room is calculated by multiplying 0.034 per volume.
Next, select a radiator, find out the power of one section and divide the previous result by its power. Thus, calculate the required number of sections.
Determination of pipe diameter and material
One of the main points when calculating the parameters for the Leningradka is determining the pipe diameter for maximum efficiency.

For natural circulation necessary big "passage". In this case, the pipe system is clearly visible. With forced circulation Pipes in different sections can be of different diameters to balance the circuit.
To determine what material to use for pipes, calculate hydraulic resistance at each section and compare it. This is done using formulas taking into account the following factors: roughness, bends and length of pipes, connection (by tap, tee, balancing device).
Next, heat loss is determined. taking into account resistance. This requires data on the outside diameter of the pipe, wall thickness, feed rate and water consumption.
Volume of expansion tank
For the calculation, data on the amount of circulating coolant is required. The expansion tank has a volume of 110 volumes of liquid. The amount of coolant is calculated using the formula W = π (D2/4) L, taking into account the internal diameter of the pipe and the length of the entire line.
Reference. Anyone can calculate a one-pipe system by yourself manually or using professional and simple programs for the average user.
Installation
If the horizontal system is mounted under the floor, it is necessary to insulate the pipes to reduce heat loss. Above the floor, this does not need to be done. The installation of the system consists of the following:
- Installing a boiler, and from it, along the perimeter of the room pipes are being laid and close into a ring.
- They cut in into the boiler at an angle supply line.
- On this section they install expansion tank.
- The latest connect the radiators.
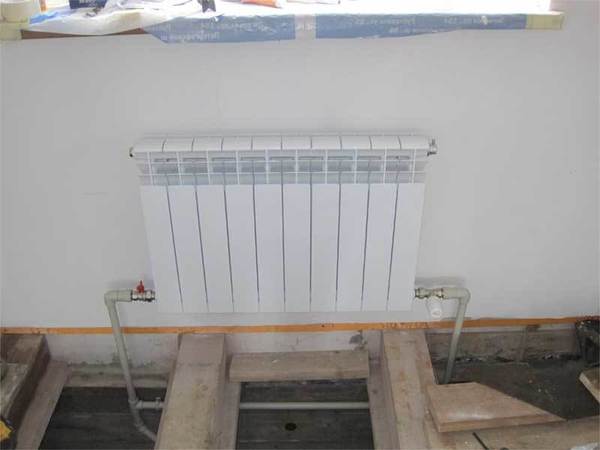

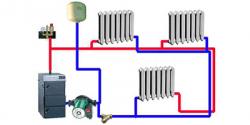
Photo 3. Connecting heating radiators to the Leningradka system. The pipes are connected to the bottom of the devices.
The vertical system is mounted in a similar way, is supplemented with a circulation pump. The radiators are installed one above the other, and bypasses are installed on each of them so that in the event of a malfunction, the water can be shut off, the battery can be disconnected from the system, and repairs can be carried out.
There are two options for connecting radiators with a bypass: lower and diagonal.
Recommendations for heating with Leningradka in a house
For unimpeded circulation of the coolant, the supply The pipe is installed at a slight angle. This condition is met both for the horizontal type and for the vertical type (otherwise the water will stagnate in the riser).
The radiators are installed at the same level one after the other for horizontal connection and one above the other for vertical connection; a Mayevsky crane to remove air from the system.
Useful video
Watch a video that talks about the errors in the one-pipe heating system "Leningradka".
Let's sum it up
"Leningradka" is a convenient and practical heating system for a private home, time-tested. easy to install and operate, and also easily repaired without significant costsThis is a budget and effective solution that meets the basic requirement of “price - quality”.