It will be warm even in the most remote corners! Heating systems for spacious buildings and non-residential premises

Organization of heat supply systems in public and non-residential buildings significantly different from that in residential buildings.
The difference lies in the choice of thermal regime, the volume and area of the building, and the availability of energy sources.
Since the area of non-residential premises is large, the possibility of heating with minimal energy costs is taken into account.
It is important to organize heating of the working area And rapid temperature control throughout the building. It is necessary to ensure fire safety and choose the option that will require the optimal amount of funds for installation and laying of pipes. Taking into account all these parameters, they choose different heating supply options.
Types of heating systems for non-residential premises

Heating spacious rooms has always been considered a non-standard solution.
Unlike residential rooms, the size of public and industrial buildings can reach several thousand square meters.
Water
The water heating system is a closed circuit, where the main components are the boiler, radiators and pipeline. Additionally, circulation pumps, safety control equipment, drainage devices are connectedThere are several types of water heating:
- gravity flow;
- with forced circulation;
- combined.
In gravity systems water circulates from the heating boiler through the pipeline to the radiators and back under hydrostatic pressure. It occurs due to the difference in density of the cooled and heated coolant. The heated water acquires a lower density and rises along the riser, distribution pipes to the radiators. Giving off heat, the coolant acquires a higher density and begins to move down the return pipes, returning to the boiler.
Important! The natural circulation solution is suitable for heating a private home small sizes.
Operating principle in forced circulation heating systems is based on the uninterrupted movement of the coolant due to the operation of pumps. They create a pressure difference between the forward and reverse stroke. This option is effective for heating multi-story buildings.

Among the features it is worth noting the high pressure in the system, the high temperature of the coolant and the use as a “standby” heating of buildings.
Pros:
- Energy independence when using solid fuel.
- The ability to regulate the thermal regime in different areas of the building when installing a heated floor system.
- It is permissible to use plastic pipes, which reduces financial costs and installation time.
Cons:
- The gravity-flow design does not allow you to regulate the temperature in different rooms.
- With a gravity flow system, it is necessary to use large diameter metal pipes.
Air
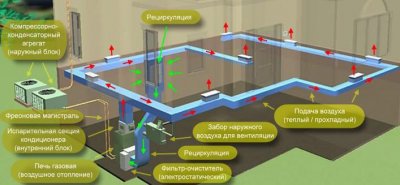
This type of heating of buildings, public and non-residential premises has gained popularity in the 70s of the last century. The operating principle is based on the use of heat generators, steam or water heaters. The air temperature increases, it enters through collectors where a certain climate should be maintained. Air flows are supplied through special blinds or distribution heads. The organization of air heating is carried out based on the use of different types of boilers.
Reference. The main feature of this system is that it uses heat carrier air masses, not liquid.
Uniform heating can be arranged for the entire room or for individual areas.
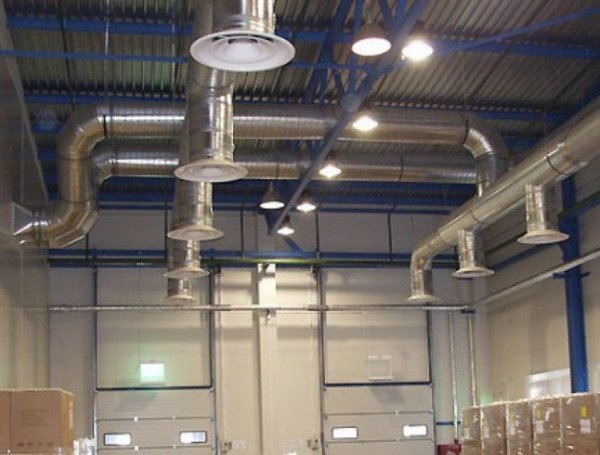

Photo 1. Air heating system in a non-residential building. Warm air circulates through special metal blinds.
Pros:
- rapid heating of air masses;
- heating can be combined with ventilation;
- heating the entire room or individual areas.
Cons:
- To maintain a certain climate, this type of heating must operate continuously.
- The heated masses move upward, which creates a warmer zone under the ceiling. The difference between the temperature at the top and bottom of the room depends on the height of the ceilings.
Radiant
For heating buildings and non-residential premises they use "dark" and "light" devices with infrared radiation. The heat source can be liquefied or natural gas.

In rooms where installation of gas equipment is not permitted, heat sources are radiant panels that are mounted to the ceiling.
The operating principle of radiant heating varies and depends on the type of IR heater:
- «Light" devices. The gas is burned using a special burner, on the surface of which the temperature reaches 900 degrees. The hot burner produces the required radiation.
- "Dark" ("pipe") devices. These are emitters, the radiant energy from which is supplied to reflectors. They direct heat to specific areas. The heating of tubular infrared devices reaches 500 degrees.
- Hanging panels are distinguished by their versatility. They are used in almost all rooms. The system has an intermediate heat carrier: water or steam. Water heating reaches 60-120 degrees, and a couple - 100-200 degrees.
Pros:
- High heating speed (achieved in 15 minutes).
- Possibility to heat only certain areas in unheated buildings.
- Savings due to the absence of energy losses when heating unnecessary areas.
- It does not require maintenance, since the system does not require installation of filters and pumps.
- Creating a comfortable microclimate (the air maintains an optimal percentage of humidity).
- The floor warms up and acts as a secondary heat emitter.

Cons:
Infrared heaters must not be installed where:
- the ceiling height does not reach 4 meters.
- radiation may affect production processes or product quality;
- Fire category A or B is established.
Useful video
Watch a video that talks about the features of air heating of a large room.
What SNIP standards govern the installation of heating systems in spacious buildings
There are many basic SNiP provisions for this branch of construction, and all of them are extensive. The essence of them comes down to several rules:
- When designing heating for industrial premises and non-residential buildings, it is necessary to take into account heat loss and heat consumption not only for heating the air, but also the equipment. The difference between the temperature outside and inside premises should not exceed 3 degrees.
Attention! It is recommended to use water as a heat carrier. In other cases technical justification is required.
- The coolant has maximum permitted parameters should not exceed 1.0 MPa and 90 degrees.
- When using gas equipment combustion products required delete closed.
When installing any heating system, it is necessary to follow safety regulations and instructions.






Comments
In Russia, 90% use radiator heating. Through the heat carrier, the radiator heats the air passing through it. The already heated air rises to the ceiling, where it cools down and goes down. This is how the room is heated.
Air heating is also good (heated air is transported around the room) Operating principle: there is equipment that heats the air and transports it into the room through a system of air ducts. Developed in the USA. Perfect for industrial premises.
P.S. A profitable heating system is something that gives a huge advantage.