The procedure for self-installation of heating: how to make a system inexpensively and safely?

The quality of heating plays an important role in creating comfortable conditions inside residential premises.
For a safe, efficient and economical heating system, various factors are taken into account: the type of boiler, the type of coolant, the developed heating system, the materials used materials and quality of installation.
Therefore, the creation of communication is approached with great responsibility.
Content
Heating installation

A heating system is a set of structural elements designed to transfer heat and heat rooms. Components:
- heat source;
- coolant;
- heat pipe;
- heating devices;
- additional elements (pumps, controllers, shut-off and control valves, expansion tank).
Select type
For the heating system are defined Basic requirements and criteria, to which she must respond:
- Sanitary and hygienic — provide a set temperature for the interior of the building and in the heating circuit units.
- Economic — reduce financial costs for heating the house to a minimum.
- Construction — comply with architectural solutions without violating design features.
- Stylistic — take up little space.
- Mounting — use an industrial installation method using standard units, with a minimum number of standard sizes.
- Operational - reliability and ease of maintenance.
Characteristics of the heated room
When choosing a heating system, an important role is played by technical characteristics of the houseBased on them, heat engineering and hydraulic calculations are made. A working project is drawn up.

Photo 1. Working design of the heating system in a two-story house with an attic and underground parking.
To do this, the following parameters are taken into account:
- square;
- house size;
- number of floors;
- floor height;
- number, size of windows;
- material of windows and their location;
- floor material, its thickness (insulation type and size);
- roofing material;
- floor material, its thickness (type of insulation and its size);
- the location of the house relative to the cardinal directions.
Climate conditions

In addition to the technical characteristics of the house and the operating principle, the choice of a particular heating system is influenced by climatic conditions.
Depending on the difference between the average air temperatures inside and outside the building, they select the most efficient way of heating.
They calculate energy costs during the heating period and determine, which energy source is more economically profitable to use for a home in specific climatic conditions.
Availability of certain energy sources
The choice of energy carrier determines the further development of the working project of the heating system. Each of the energy carriers has its own pros and consFor heating, the following are most often used:
- Natural gas — the cheapest in price, but with a very expensive connection.
- Solid fuel - cheap equipment, but requires storage space, not available everywhere.
- Liquefied gas. It is economically advantageous to use in the long term, but a large one-time investment is required to install a special storage facility. Liquefied gas in cylinders is suitable as a temporary measure or for heating a country house.
- Electricity available, but has a high cost.
- Diesel fuel — both equipment and raw materials are expensive.
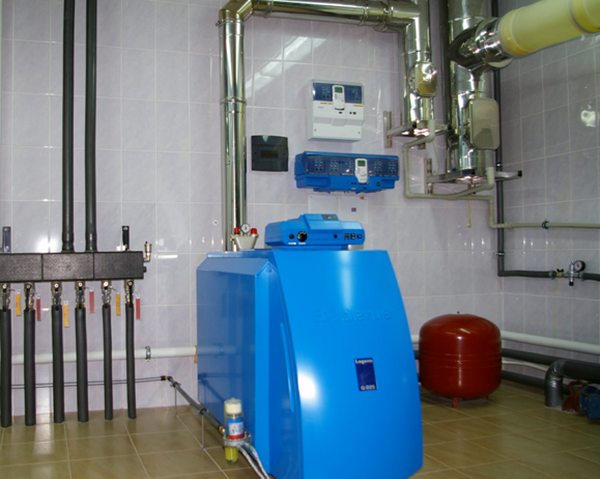

Photo 2. A boiler running on diesel fuel installed in the basement of a private house.
Engineering calculations for heating systems
To ensure comfortable conditions in the room and service life heating system, it is necessary to make engineering calculations: they take into account the main technical characteristics of the house, as well as the coefficients describing its current state.
Important! The heat loss coefficient has a direct proportional effect on the required power boiler equipment and batteries.
Thermal engineering
Calculation of the amount of heat required to maintain the temperature regime inside the house. Conducted in two stages:
- Calculation of heat losses of a building.
- Calculating the required boiler power and heating devices while maintaining the temperature level. According to European standards, the temperature of the boiler, radiators and air in the room is 75°C, 65°C and 20°C respectively.
Hydraulic
It is used to calculate the parameters of various elements of the heating system and the required volume of coolant.
When calculating the amount of liquid required for the heating circuit, take into account three indicators: total power of the heating system, temperature difference between the input and output, heat capacity of water (4.19 kJ).
Lastly, the pump power and the volume of the expansion tank are determined. The SNiP for heating systems sets a range of coolant speeds to prevent air from entering the circuit. It is 0.25–1.5 m/s (at a pressure not exceeding 20 MPa).
Working draft
The finished working project of the heating system of a private house has:
- diagrams and drawings of the location of all elements;
- calculations of boiler and heating radiator power;
- metric characteristics of pipes and shut-off and control valves;
- pump power calculation;
- calculated value of the expansion tank;
- numerical value of the volume of the required coolant.
Selection of equipment
Based on calculations and taking into account the use of a specific coolant, a suitable boiler and basic communication elements are selected.
Heat source
They are used for heating different types of heat sources: boilers, stoves, fireplaces, convectors, heat guns. Boilers are considered the most popular. They are divided by the type of fuel consumed into:
- gas boilers - reliable, use the cheapest fuel;
- electric boilers - environmentally friendly, silent;
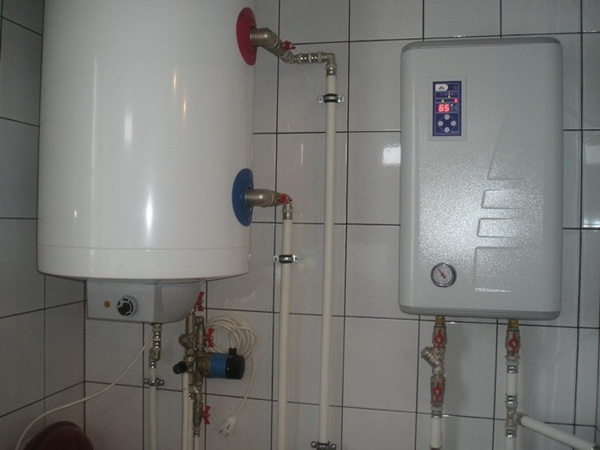

Photo 3. Wall-mounted electric boiler with a connected boiler, operates silently and is environmentally friendly.
- solid fuel — more often used in summer cottages, where you can replenish your supplies of firewood, coal or briquettes;
- diesel - reliable, but very noisy;
- combined — are gradually gaining popularity, replacing solid fuel ones.
The required boiler power for a standard house is 1 kW per 10 sq. m.
Air ducts or pipes
Depending on the type of coolant, after purchasing boiler equipment, they produce purchase of a pipeline or air duct. For the production of pipelines and air ducts the following are used: metal, metal-plastic and plastic.
For a water heating system, polypropylene pipes are purchased, which are distinguished by their durability, low cost and ease of installation. Air ducts are mainly made of metal, due to their versatility, resistance to high temperatures and pressure.
Heating devices

An important element of the heating system are radiators.
There are many different types of heat exchangers on sale, varying by price, shape, size and material of manufacture.
The choice of radiator is mainly based on the required heating power.
- Steel radiators They are distinguished by their low price and resistance to temperature changes, but are sensitive to pressure changes in the system.
- Cast iron radiators are widespread due to their high heat output.
- Aluminum radiators They are suitable for any room, easy to install, lightweight and provide good heating, but are not reliable or durable.
- Bimetallic radiators are becoming increasingly widespread due to their reliability, low price, but high level of heat transfer and long service life.
Auxiliary elements
In most cases, private homes use a closed heating system, which requires an appropriate pump to ensure continuous circulation of coolant throughout the entire hydraulic circuit. The pump is purchased based on the volume of the coolant and the number of floors of the heated house.
In addition, any heating system uses expansion tank open or closed type, various types of shut-off and control valves and manifolds. Their selection is made based on hydraulic calculations.
How to properly replace the system and configure it?
Before installing the heating system, preparatory work in the building, if the house had a heating system, it will be dismantled.
Preparation

Installation and replacement of a heating system is a labor-intensive process that requires various tools.
Among them should be a hammer drill, a grinder, a welding machine, a gas burner, all kinds of keys, a level, pliers, a tape measure and other necessary things.
Without this equipment, dismantling may result in to disastrous consequences.
Attention! When dismantling the structure be extremely careful to avoid injury and damage to the heating system itself.
Dismantling of the old structure
Before dismantling the old heating system, turn off and drain the water. Disconnect all heating devices, for this the joints are preheated with a gas burner. Then the pipes are disconnected.
To maintain the integrity of the heating circuit, extreme care is needed, especially when caulking the sockets. Using a blowtorch, bend the damaged pipes, burn off the remains of the sealant, and burn off the paint.
Markup

When replacing a heating system, they produce markings for new structural elements. Initially, the openings in the walls and ceilings are determined.
They mark the places of fastening connections for pipes and radiators. When marking, the developed heating installation scheme is fully taken into account.
Installation
During installation, a certain sequence is followed:
- install the boiler;
- they are laying a pipeline;
- connect the radiators;
- test the system;
- are put into operation.
Choice

When choosing a heating system, an important nuance is the process of correct installation. So for gas heating, in addition to the high cost of the units, the costs are taken into account for bringing gas to the house and connecting it.
Hydronic heating requires proper adjustment and preliminary high pressure testing.
For electric heating, they carry out additional cable routing, corresponding to the power of the equipment.
How to assemble and install a boiler?
According to building codes and regulations, boilers up to 60 kW can be assembled and installed in the kitchen. More powerful units require a separate room with sufficient air ventilation. In addition, it is necessary chimney. The boiler is installed at such a level that its return pipe is located below the first floor radiators. The boiler is secured with the attached holders.
Scheme and principle of operation
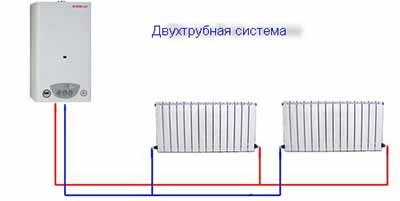
There are two schemes heating circuit. Single-pipe with serial connection of radiators and two-pipe with parallel connection.
One-pipe scheme most popular in private homes due to lower financial costs for materials.
In a two-pipe system the coolant enters each radiator independently.
Reference! The two-pipe system is more versatile and suitable for any home. regardless of area and number of floors.
Pipeline layout: how to install them?
During installation of the heating system, it is possible variations of pipe layout:
- vertical lower;
- vertical top;
- horizontal - implies the presence of a riser and a horizontal distribution system on each floor.
The choice of installation scheme and type of wiring depends on the size of the house, financial investments, and the capacity of the heating system.
Connecting radiators

Fastening radiators produced last, after all the equipment has been installed and the pipelines have been connected.
Heating devices are attached to the wall with the necessary connecting elements and connected to the pipes.
Distinguish three types Radiator connections:
- lateral — the most common and effective;
- diagonal — used for long batteries, ensures uniform distribution of the coolant;
- lower - used when pipes are hidden under the floor, has low efficiency.
Setting
The heating system must be adjusted and regulated in a special way after startup. To do this, balancing temperature readings changes in shut-off valves (mixers, taps and servo drives). The temperature difference at the inlet and outlet should be within 15–20 °C. Adjusting the pressure using an expansion tank, air vents, and Mayevsky taps.
Useful video
From the video you can learn how to make a heating system from polypropylene pipes yourself.
What do you need for a trial run?
Before commissioning the heating system undergoes mandatory hydraulic testing at elevated pressure. This procedure will allow identifying installation defects and ensuring the stability of the most important communications in the house in the future.










Comments