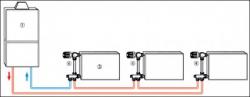
Sometimes absolutely irreplaceable in heating systems - a water pump for heating

In modern individual heating systems (cottages, apartments, small workshops, shops) water pumps are widely used.
Their main task is ensure constant circulation of the coolant inside the heating device.
Content
- Characteristics of water pumps for heating systems
- Main types of pumps for pumping and moving water
- Selection criteria
- Technology of installation and connection of the circulation device
- Removing the device, how to check its operation before reinstalling
- Why is the pump noisy or does not move water
- Useful video
- Latest operating instructions
Characteristics of water pumps for heating systems

Pumps for heating systems are selected based on a number of parameters.
It is necessary to take into account productivity, pipe diameter, operating conditions, the presence of automation, configuration, required power and a host of other factors.
It is important to select all the elements correctly., since otherwise the system will operate unproductively or installation and operating costs will be unreasonably high.
For example, a pump with a large power reserve will not only be expensive, but also too noisy.
How do they work?
The circulation pump has a simple design. The centrifugal or vortex principle is used. That is, a small turbine is installed on the electric motor shaft, which makes the flow of working fluid flow in a given direction. All these elements are enclosed in a housing made of corrosion-resistant material.
Pumps are mainly divided into:

- By performance (what volume they are able to pass per unit of time). The quantity is measured in l/min.
- Under pressure. These are meters or meters multiplied by 10. That is, the number 100 will mean that the pump is capable of creating a pressure sufficient to lift the water 10 meters.
- Maximum pressure in the system. Here or atmosphere, or bar.
- Power consumption. Some models are equipped with step or electronic regulators, which makes it possible to apply flexible system settings.
- Diameter of threaded pipes, required for connection.
Device
The first heating systems operated with natural circulation of the coolant. Such a scheme is easy to install and requires a minimum of equipment, but includes a number of inherent operational limitations:
- All highways have a large cross-section (which makes the structure heavier and increases its cost).
- Only open circuit can be used (with expansion tank).
- Return lines require a slope, and the boiler should be located at the lowest point of the system.
- The dimensions of the heated volume are limited.
It is quite difficult to organize multi-level heating, since the temperature gradient near the boiler and at the maximum distance from it is extremely large. Careful calculation of the complete structure is required, but any interference with the configuration (for example, the cross-section of the pipe has changed over time) leads to incorrect operation of the entire heating system.
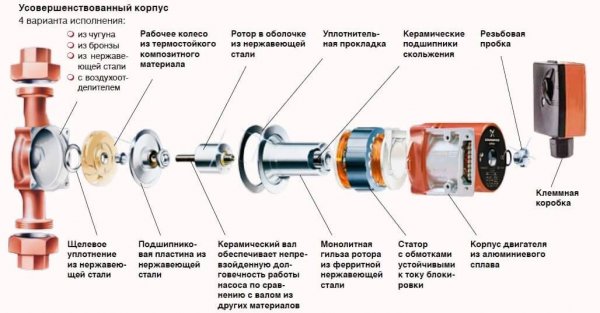
Photo 1. The device of a circulation pump with a wet rotor. The arrows indicate the components of the device.
The forced circulation of the coolant in the system helped solve the problem. This allowed not only to remove restrictions on the number of storeys of the structure, but also to reduce its inertia. Now, heating a room remote from the boiler takesIt's not hours, but minutes. And the principle of regulation has become simpler - a rotary valve on the main line or a separate radiator is enough. The coolant temperature has leveled out, which reduced the load on all elements of the system and eliminated inertia.
Marking
Each manufacturer has its own equipment marking. Below is an example Grundfos Group symbol system, as their pumps account for half of the world market.
- UP - circulation.
- S — equipped with a rotor speed controller.
- D - paired.
- 30 — diameter of connecting pipes.
- 60 — maximum pressure in decimeters.
- F — connection of pipes through a flange (the letter is missing for threads).
- N — body material (the absence of a letter indicates a cast iron frame), N — stainless steel.
- B — bronze body.
- A — the pump is equipped with a tap for releasing air.
- K — special frame design that allows the use of antifreeze.
Main types of pumps for pumping and moving water

All circulation pumps are divided into two large groups, differing in the design of the rotor.
- With dry rotor.
- With wet.
In the first case The engine rotor does not come into contact with the working fluid. The engine is connected to the pump via a coupling, only the working wheel is immersed in the liquid.
In the second option There is no clutch between the impeller and the rotor of the electric drive, so both the rotor and the impeller are in contact with the coolant in the system.
With dry rotor
First of all, it is worth noting that such devices are more complex than their "wet" classmates. Consequently, they are more expensive and their cost reaches up to 500 USD and above. In addition, the devices require special care — regular lubrication of the rotor and sealing elements with a special compound.
The second disadvantage of dry rotor mechanisms is their noise. Therefore, when installing, you should carefully select a location - preferably in a separate room.
Important! Dry rotor pumps have a shorter service life. Although, with proper care and maintenance, it still lasts for years.
But, taking into account the shortcomings, these mechanisms also have significant advantages. Firstly, they have very high efficiency. Therefore, a system with such a device is several times more economical. Secondly, The dry rotor pump is much more powerful than its counterparts. Therefore, their area of application is high-performance, large heating systems for cottages or apartment buildings.
Among other things, dry rotor pumps insensitive to the quality of the pumped liquid And capable of operating at higher temperatures coolant. And even with aggressive environments or at negative degrees.
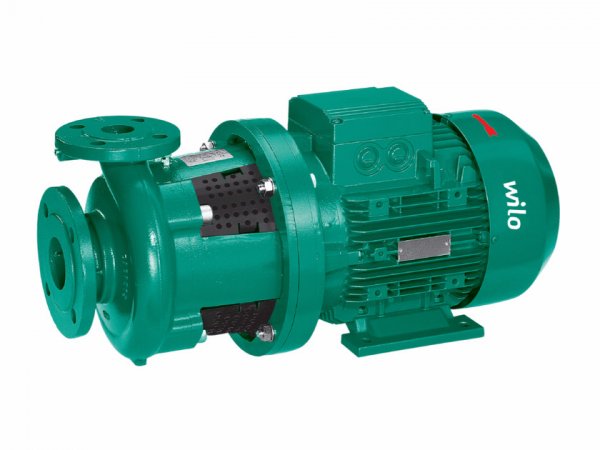

Photo 2. Circulation pump for heating systems with dry rotor. Manufacturer Wilo.
With a wet rotor. How to install it correctly?
In such devices, the engine rotor is located in the working fluid. Therefore, they are simpler, more compact and cheaper. The cost starts at about from 80 USD, depends on performance.
The working fluid is both a lubricant and a cooling medium. Therefore, such equipment does not require maintenance. And if installed correctly, it functions for a very long time - 20 years is considered a completely normal period.
The downside of the scheme is low efficiency (about 50%), which is unpleasant, but not critical given the generally low energy consumption figures. The usual power consumption is from 10 to 100 W. Depends on the model and operating mode.
The second point is sensitivity to the quality of water or other active liquid.
Attention! When installing wet rotor pumps, always place a install a mesh mud filter, to avoid the rotor becoming jammed by dirt particles.
Selection criteria
Usually there is one circulation pump in the system. In case several separate circuits are used (for example, two independent wings of the building or the presence of underfloor heating), The number of circulation pumps may be different. But the general selection formula is the same.
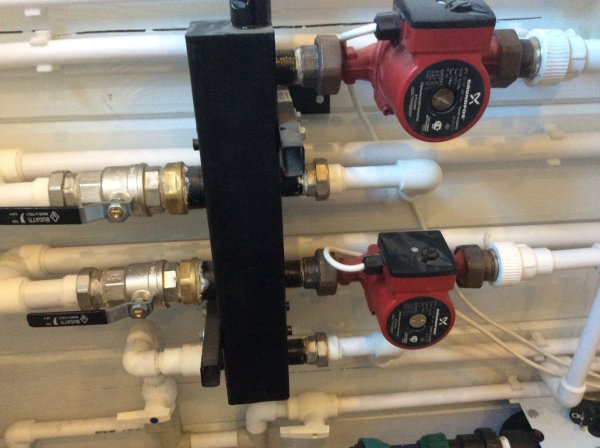

Photo 3. Two wet rotor circulation pumps installed in the heating system.
It is difficult to take into account the individual characteristics of the heated room: number of windows, quality of sealant and thermal insulation characteristics of walls, ceilings. There are complex tables for this, taking into account a lot of factors. It is important to note that a simpler formula is most often used.
At first calculate heat loss of the house. They are usually designated by a letter F.
To calculate this value, you first need to calculate square, involved in heat loss. Simply put, you need to calculate the entire external set of the house.
Important! They only count External area: roofs, first floor ceilings, external walls. The totality will be designated by the Latin letter S.
Final equation:
Ф = U*S*(Tk—Tn), where:
F — total heat loss of the house in W/m2, S — external area of the premises,
U — heat transfer coefficient,
Tk — required room temperature,
Tn — outdoor air temperature.
If someone finds it difficult to calculate using this formula, then for most European territories you can simply multiply the area S on 21True, in this case there will be heat loss not in W/m2, and in kcal. Which will have to be taken into account in subsequent calculations.
The second step is to calculate the coolant flow rate, expressed in m3/hour. It is calculated using the formula:

Q = Ф*0.86/(Тн—То), where:
Q — coolant consumption,
F — heat loss of the room in W/m2,
0.86 — conversion factor W/m2 in kcal,
Tn — the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the heating boiler,
That — temperature of the coolant in the return line.
Accordingly, knowing the final Q value, you can select a pump based on performance.
Then they select according to pressure. Or, as this parameter is commonly called in scientific circles, "dynamic pressure". Here the selection principle is simple: the pump must compensate for pressure losses in the system.
What causes them? What hinders the flow, stands in its way. Namely: all the equipment, automation systems, pipes, bends. On average, we can say that the losses will be as follows:
- In a regular boiler - from 1 to 5 kPa.
- In a compact design boiler - from 5 to 15 kPa.
- The heating radiator produces losses - 0.5 kPa.
- Radiator valve - 10 kPa.
- Automatic control system valve - up to 20 kPa.
- Check valve - up to 10 kPa.
- Mud filter (clean) - 20 kPa.
- Losses in pipes depend on the length and diameter. They can be from 0.1 to 6 kPa per linear meter (with a pipe diagonal 3/8 to 1.5 inches).
Technology of installation and connection of the circulation device
Connecting a circulation pump to a heating system with your own hands is not that difficult. It is enough follow simple rules.
Attention! The pump is connected on the return line between the boiler and the expansion tank (if any). This increases the service life of the equipment.
The pump is connected via a bypass line - bypass using a detachable connection - an American. This will allow the pump to be replaced and repaired.

Photo 4. American shut-off valve for heating systems. Allows you to shut off access to the coolant.
A ball valve is installed in the gap of the return line (or a valve - for automatic switching of operating modes), blocking natural circulation. And a bypass line is made in the bypass of this tap. And a circulation pump is included in it. When the tap is open, natural circulation is possible, when closed - only forced through the bypass.
Shut-off ball valves must be installed at the inlet and outlet of the bypass. — so that the pump can be removed without disrupting the operation of the system. It is highly recommended to install a mud mesh filter - it will protect the device from jamming. A manual or automatic one is mounted here air bleed valve.
It is important to ensure that the rotor of the device was in a strictly horizontal position, since, if the required position is deviated, areas may arise (in a wet rotor pump) where lubrication and cooling will be insufficient.
The electric part of the pump is connected directly to the power supply network via a differential circuit breaker or to automatic devices - a thermal relay or timer. The terminal designations are simple: N is the neutral wire (blue), L is the phase (red). Grounding: green or variegated wire, has traditional national markings.
Removing the device, how to check its operation before reinstalling

During operation, it sometimes becomes necessary to remove the pump. To do this, the device is disconnected from the network. The tap is opened, allowing the system to operate in natural circulation mode.
Then both taps on the bypass are closed, cutting off the pump from the main line. The union nuts are unscrewed - the device is removed.
Reverse assembly is carried out in the reverse order. But before starting, carefully check for air in the system. It is best When first starting, let the pump run for a few minutes, then turn it off and check the system again for air.
Why is the pump noisy or does not move water
Frequently, complaints arise about the excessive noise of the pump. There are several reasons:
- Incorrectly selected device parameters. It is either overpowered or constantly working at the limit of its capabilities. The disease is treated by replacing the equipment.
- Presence of air in the pumpYou need to try to remove air from the system through the built-in valve or through the general system valve.
- Debris particles entering the wheel's working area. To remove them, you need to remove the pump and rinse it with clean water. If this is not enough, you can disassemble the pump for subsequent defect detection. In this case, you need to unscrew four screws on the body (You may need a socket wrench—a hex key or star key) and the electrical part is separated from the mechanical part, giving access to the bearings and the pump impeller.

There are several reasons, because of which the circulation pump stops pumping water:
- A foreign object has blocked the wheel;
- The pump is very dirty;
- There are problems with the power supply.
How to disassemble for repair
To disassemble the circulation pump, the following procedure must be followed:
- The pump must be disconnected from the power supply;
- Shut off the water supply using the side valves;
- Drain any remaining water from the system;
- Remove the pump using a hex screwdriver;
- Carefully remove the electric motor with the impeller.
Useful video
Watch the video, which tells you how and where to properly install a circulation pump.
Latest operating instructions
Circulation pumps capable of working without complaints for decadesTo do this, you will need to select them correctly, install them, and during operation, prevent contamination of the coolant by installing mud filters and regularly flushing the system before the start of the heating season.