How to choose a heating radiator connection scheme in a private house: pros and cons of different systems
Keeping your home warm will help efficient heating system. The method of connecting batteries and radiators, selected for a specific room, will save significantly on payment for electricity.
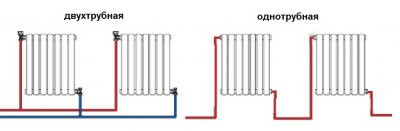
Before you start installation, analyze the configuration of the heated room and the estimated budget. This will help you find the best option for the heating system. There are two types connection diagrams to the system – one-pipe and two-pipe. Each of them is designed to solve different problems and has its own pros and cons.
Content
Single-pipe connection diagram of heating radiators in a private house
A heating system with a single-pipe connection of radiators copes well with heating a private house with several floors. Simplicity and affordability make this type of system the most widespread.
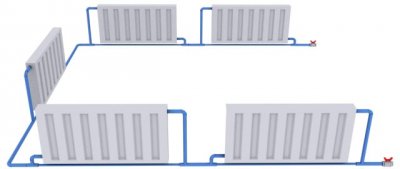
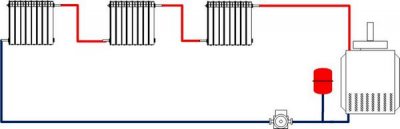
It is very easy to distinguish a single-pipe connection. Single pipeline main, through which the coolant circulates, looped and closes on the heating boiler.
All radiators in the premises connected to it in parallel or in series. The coolant flows through radial paths from top to bottom, and the supply pipes conduct heat to the floors above. The circulation of the liquid can be natural.
Cons single pipe connection:
- Series connection means that input and return remain a chain of a single main line. This means that from radiator to radiator the temperature of the coolant will become lower and lower. If you compare the heating of the first and last "link" of the heating system, the difference will become obvious. The solution to this problem is increase sections along the pipeline route. In this case, the cost may increase significantly.
- There is no way to adjust heat output separate radiator.
- The pressure in the pipes should not drop, circulation must be constant and uniform. Any differences will lead to heat loss. When the coolant moves naturally in the pipeline, observe the slope of the pipes, which is difficult if they are located low. To cope with this problem, install a pump.
- Unable to embed contours water heating floors.
Pros:
- Economical and does not require a large amount of material. Accordingly, the scale of work during connection is reduced.
- With a simple wiring diagram you can handle it yourself, having minimal skills in plumbing work. Does not require installation of additional devices and complex units.
- Does not require increased attention. Provided it is installed correctly, it will be durable and will reliably cope with its task.
- Mounts as in one-story building, and in several floors.
- The pipeline is located low in most cases, which opens up space for decoration and camouflage heating when creating the interior of the room.
Installation principles: photo
The location of the highway is often encountered along the walls of the room, parallel, or at a slight angle to the floor plane. Differences arise only in the schemes of cutting the pipe into the radiator.
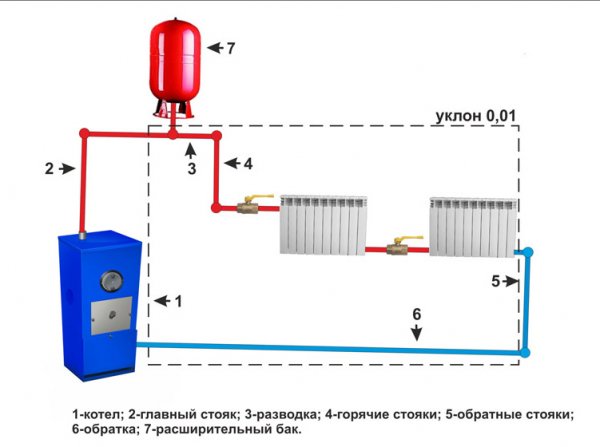
Photo 1. This is what a single-pipe connection diagram with natural circulation of the coolant with a slope of the main line looks like.
The easiest way to connect an open type with by installing an expansion tank at the highest point of the distribution system. The radiators are cut in series, the pipeline is at the bottom, the input and output are located on opposite parts. The installation of a pump is preferable.
With natural circulation of the coolant it is necessary non-stagnation "accelerating manifold" and further compliance slope of the highway. To prevent air locks, Mayevsky taps or air vents are installed.

Photo 2. Standard Mayevsky crane used to prevent air locks.
The improved connection of the one-pipe system is called "Leningradka". This method allows heating apartment buildings, remaining simple to install and economical in terms of material consumption. The difference of the "Leningradka" is bypass - pipe jumper between the input and output of each radiator. Its presence allows for uniform regulation of the coolant temperature relative to the distance from the boiler.
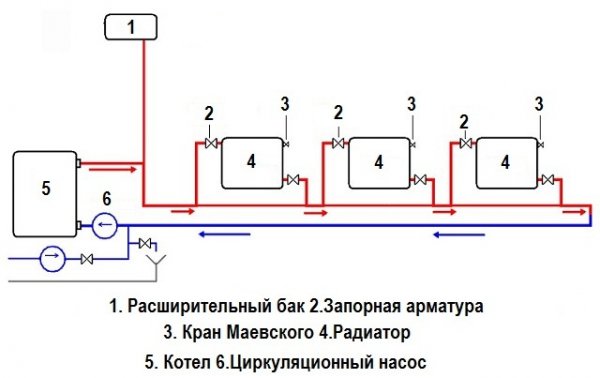
Photo 3. One-pipe connection system "Leningradka" with diagonal connection of radiators.
Two-pipe connection diagram
This version of the system is more expensive than a single-pipe connection, but has a number of advantages. In a two-pipe layout, the return pipeline from each radiator goes to separate closed circuit, and the coolant is pumped separately. The cooled liquid enters the heating boiler through the return circuit. Allows heating of complex rooms using a single boiler.
Installation is in progress in several stages. A boiler connected to an expansion tank is installed in the designated place. Then a coolant wire loop is installed, passing through each battery. At the end, a return line is installed, closed on the heating boiler.
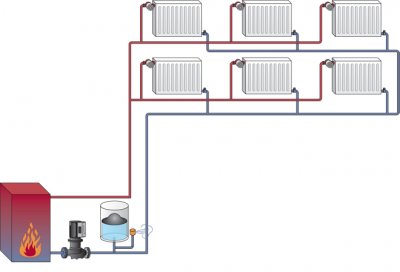
Pros two-pipe system:
- Suitable for any building, regardless of the number of floors and location of rooms.
- Temperature coolant evenly distributed on all radiators, which easily maintains comfortable heating of the rooms.
- Radiators autonomous from each other, it is possible to install individual thermostats and valves for economical water consumption.
Minus - high material consumption, value adding heating system and the complexity of installation, which requires the mandatory involvement of specialists.
Principles of installation of this type
The general architecture of the system consists of two closed pipeline loops. alone heated air comes out of them coolant, second plays a role return linesThere are several possible options for inserting contours.
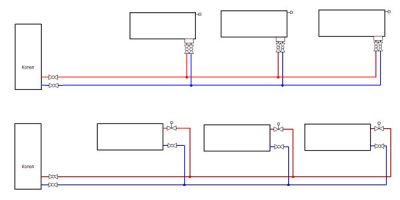
Dead-end system
In this variant both highway contours are in different directions, and the batteries have the same number of segments. For overlapping, first radiator valve should be twisted as much as possible.
Tichelman loop
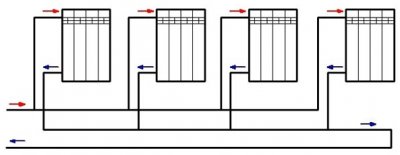
Each radiator is equipped with thermostatic valve or needle valve, which makes balancing easier.
This scheme is ideal for long pipelines.
Horizontal
With this scheme, the supply pipeline can be cut in under the radiators or on a par with them. Suitable for houses no higher than two floors. Installation on each device Mayevsky cranes will help to avoid the formation of air locks.
Vertical
Suitable for houses from two floors and above. Requires significant consumption of pipeline elements, but during operation, automatic air release through the drain valve is possible.
Top-mounted system
The advantage of this system is considered to be no air pockets and high flow rate of the coolant.
Important! The disadvantages include an unaesthetic appearance with open communications, as well as wasteful use of material and the impossibility of wiring in large areas of premises.
What are the ways to connect batteries?
The installation and connection of radiators significantly affects the operation of the heating system. The most common place for placing batteries is under windows, at a distance about 10 centimeters from the windowsill, and not less than 5 centimeters from the plane of the floor and walls. A radiator protruding in front of the window sill will provide a flow of warm air in front of the window opening. There are several ways to connect to the main line.
Saddle and bottom connection
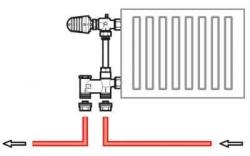
Highway with hot coolant cut in into the lower branch pipe of one radiator segment, and the return line is similar to the opposite segment.
The main lines themselves can be hidden in the floor. The heating remains uneven, The power is reduced by approximately 14%.
This option is suitable for an aesthetically attractive interior appearance, and heat loss is compensated by installing more powerful radiators. Saddle connection is considered for systems with installed circulation pump.
One-sided
The most common type of connection in apartment buildings. Both contours connected on one side radiator, supply at the top and return at the bottom.
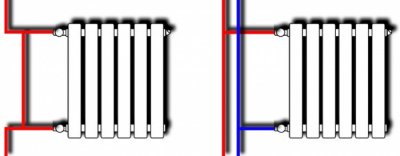
All segments of each radiator are heated evenly, but If the accordion is too large, heat loss may occur. It is also possible to install the coolant from below, but it is not very convenient to use.
Diagonal
If in the battery a significant number of segments, then uniform distribution of the coolant is achieved by cutting the supply line into the upper part of the radiator, and the return line into the bottom of the opposite side. Heat loss with such a connectionand do not exceed 3%, so this option is optimal.
Important! The diagonal connection option is the standard. Manufacturers of heating system elements and devices indicate in technical data sheets of products data based on this option.
Useful video
Check out the video, which discusses various options for two-pipe radiator connections.
Conclusion: Why it is important to install the right option correctly
Selecting a radiator scheme responsible business, on which further comfortable living in the house depends, especially in winter. After studying all the options, choose the optimal one, suitable for the configuration of the room and the expected budget. Do not save on materials. Purchase of low quality radiators or pipeline elements will lead to heat loss and additional energy costs.