Ensuring high-quality heat: standards for pressure testing of heating systems

Long-term operation of the heating system is possible thanks to timely checks and adjustment worksThe latter are called pressure testing.
It includes three global tests, which are carried out in a specific order. with the participation of a heating service provider or his approval.
This does not apply to private houses that have one owner.
Pressure testing of heating system batteries with a pump according to SNiP: what is it

System testing is necessary for a comprehensive check of the circuit for pipe strength, filling density, maintaining high efficiency.
The standards are regulated SNiP 41-01-2003, 3.05.01–85, as well as the rules for the technical operation of thermal installations number 115The general principles are the same, some meanings are different.
According to building codes and regulations, the process is carried out by creating pressure one and a half times higher than the working pressure, and not less than 0.6 atm.
The second document indicates other values: 1.25 standard pressure, minimum 0.2 atm. The latter is more favorable, so tests are usually carried out according to it.
First, find out the working pressure. In houses up to 3 floors it does not exceed 2 atm, in five-story buildings it is in the interval 3–6, in large ones - 7–10. If there is an excess, the drain valve is triggered if automatic control is installed. Otherwise, this is done manually.
Effect test

The test pressure value for the action effect is always selected within the range between the minimum and maximum:
- The first one is 20–30% larger than the working one.
- The second one is selected by the engineers of the service provider company.
For development, the data provided in the device passport is taken.
And they also take into account characteristics of all elements of the circuit: boiler, pipelines, radiators, even valves.
The maximum pressure value in the system provides protection of the piping from excess, which will damage the components.
Hydraulic
Designed to test the strength of system components, and partially remove scale and rust.
The process looks like this:
- The circuit is filled with liquid at a temperature of ~5 °C.
- The pressure is increased to one and a half working hours. The latter depends on the size of the house.
- The indicator is maintained for about 10 minutes. If it doesn't crash, the system is functioning normally.
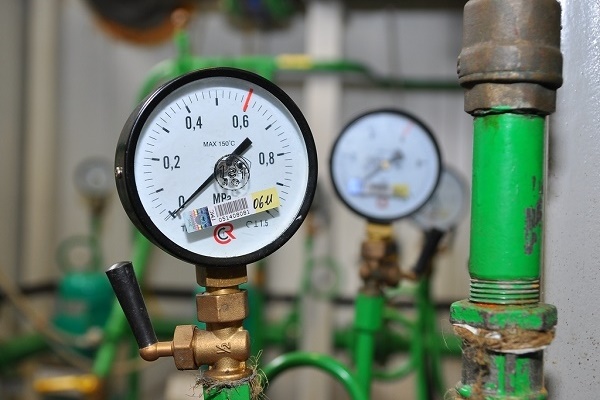

Photo 1. Pressure gauge with pressure readings. If it remains at one level for several minutes, then there are no problems in the system.
If the value has decreased more than 0.1 atm, begin troubleshooting the system.
Reference! A hydraulic test is done in the summer, usually in June. This is done by the management company. If necessary, the owner can contact the supplier with a request to conduct a pressure test. This is a paid service.
Pneumatic
Intended for testing tightness and density of water filling piping in the system. Using pressure gauges, it is possible to measure networks in the cold season.
This part of the system pressure testing is done by supplying air through the pipeline. In the first launch use excess pressure 0.15 atm. If any faults are found, they are eliminated. In the second test overstatement is reduced up to 0.1 atm. A compressor is used for pumping.
Having set the required level, they wait 5-7 minutes, then they conduct an examination. During this time, the indicator may fall no more than 0.1 atm. Otherwise, the test is started over again. If no problems arise, the system is allowed to operate.
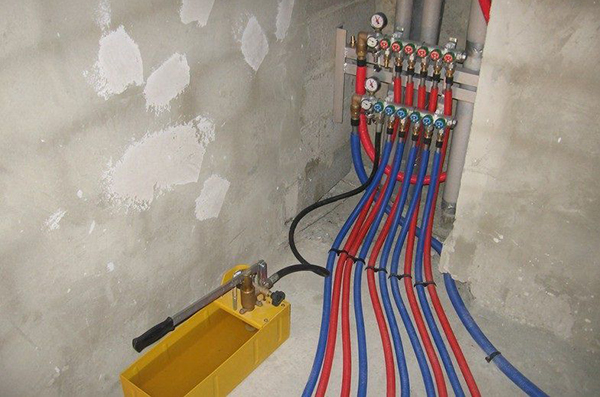
Photo 2. Pressure gauges for pneumatic testing. It consists of finding out the degree of tightness of the system.
SNiP provides for a pneumatic test when a hydraulic one is impossible. It is also done for quality control of radiators after assembly. The device is filled with air, closed and immersed in water. If no leaks are detected, such a battery is considered fit for use.
This procedure is usually performed in summer or late spring.
Thermal

They are designed to check the pipes for uniform distribution of heated water along the system piping. They are done when the outside temperature is above zero, near the boiler - not less than 60 °C.
If the process needs to be carried out in winter, then immediately after turning on the heating device.
According to SNiP, testing is carried out at the average temperature of the liquid in the system 50 °C, at least 7 hours in a row. During this period of time, all heating sections are checked.
The bottom line is in continuous water supply through the pipes of the system. Specialists walk around the floors of an apartment building and measure the heating of radiators in several places.
Procedure for carrying out work in an apartment building
Hydraulic tests are carried out under several pressure indicators. For example, the input unit can be tested with the indicator 16 atm, and the heat supply of the ITP is ten. This applies to any buildings. The numbers change. depending on the area to be heated.
Flushing the pipeline

First, the circuit is filled with flushing liquid. If the working substance is frost-resistant, the initial pressure testing is done with water, and the second one is done with a solution.
Heat carriers based on inorganic substances are more fluid, therefore, requirements are imposed on them lower requirementsWhen minor leaks are detected in such situations, it is sufficient to tighten the connections.
If preparations are underway for operation during the heating season, the old coolant is first drained. The pipeline is filled with clean water and hydraulic pressure testing begins. The process is carried out from below, through the boiler or drain cock. In the latter case, using a compressor. At the same time, all gas present in the system is removed through the Mayevsky tap.
Important! You can also get rid of air through any valve, in the upper branches, through air vents on the risers. To prevent future cleanings the contour after pressing is filled from the bottom part of the harness.
Increased pressure
Next comes the increase in pressure to the test level. The readings are compared with the pressure gauges located at equal intervals along the entire length of the pipes.

Along with this, a visual inspection of the components, units, connections, pump, etc. is carried out. This helps to detect leaks, cracks and other problems.
They need to be resolved by sealing or replacing parts. If condensation is found, it is necessary drying.
Faults are fixed one by one so as not to lump them together. Mandatory inspection All components of the circuit are subject to.
The various tests of the system are carried out in the order described above:
- Hydraulic for testing the strength of elements, cleaning from air, scale and rust.
- Pneumatic for monitoring the filling of the system and the tightness of joints.
- Thermal ones for ensuring uniform heating of pipelines and radiator sections.
Attention! All three tests are carried out at elevated pressure. Its drop is allowed, but only by an insignificant amount in 0.1 atm. Along with this, a visual inspection of the contour parts is carried out, for which invite several people.
Any negative result means that further repairs are required systems. Its complexity and cost depend on the state of the system, the need to replace the equipment. Then follows repeated pressure testing, the result of which is an act of completion of work. Its form is specified in the building codes and regulations, and filling depends on the results of the work.
Useful video
A video in which a technician shows how to independently pressure test a heating system.
Price
Self-pressurization of heating is a complex process that requires certain skills. For the work, you should invite a company specializing in such services or Contact the management company.

An annual inspection by the supplier is free. The price of an order from a private company depends on the type and size of the premises. Approximate cost crimping:
- One riser of a multi-storey building - 30 thousand rubles.
- A specific apartment - 5 thousand rubles.
- Private house - 15 thousand rubles.
These figures may vary depending on the company performing the work, as well as the dimensions of the rooms, the total area of the piping, and the amount of equipment placed in the system.






