Why is water heating so popular? Its features and schemes

Water heating - technology of heating residential buildings with liquid heat carrierThermal energy is transferred to the room by radiators, pipe registers, and convectors.
For heating the building install registers in each room.
When water heating is operating, the liquid coolant is heated in the heating boiler and flows through pipes into the rooms, where it gives off heat and, already cooled, returns to the boiler, entering a new cycle.
This the process is repeated constantly and heats the rooms.
Content
Classification of water heating systems by operating principle
According to the operating principle, the heating has natural and forced circulation of the coolant.
With natural circulation
Used to heat a small house. The coolant moves through pipes thanks to natural convection.
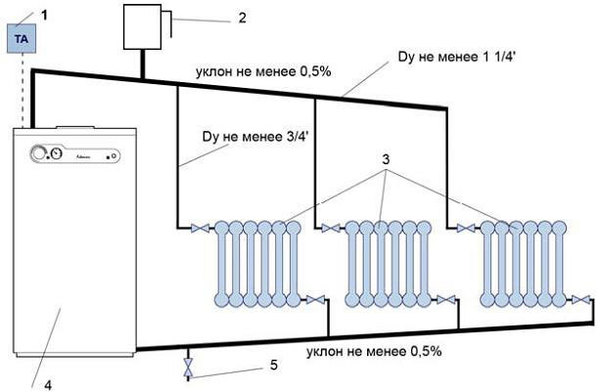
Photo 1. Scheme of a water heating system with natural circulation. The pipes must be installed at a slight slope.
According to the laws of physics, warm liquid rises. Water, heating up in the boiler, rises, after which it goes down the pipes to the last radiator in the system. Cooling down, the water enters the return pipe and returns to the boiler.
The use of systems operating with natural circulation requires the creation of a slope - this simplifies the movement of the coolant. The length of the horizontal pipe cannot exceed 30 meters — the distance from the outermost radiator in the system to the boiler.
Such systems are attractive because they are cheap, you don't need to buy additional equipment, and they make almost no noise when they work. The downside is that the pipes need to be of a large diameter and laid as evenly as possible (they have almost no coolant pressure). It is impossible to heat a large building.
Forced circulation circuit
The scheme using a pump is more complicated. Here, in addition to heating batteries, a circulation pump is installed, moving the coolant through the heating system. The pressure is higher in it, therefore:
- It is possible to lay pipes with bends.
- It is easier to heat large buildings (even those with several floors).
- Small diameter pipes are suitable.
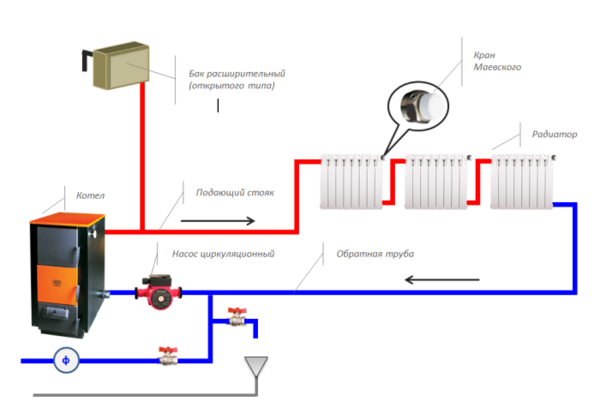
Photo 2. Diagram of a heating system with forced circulation. A pump is used to move the coolant through the pipes.
Often these systems are made closed, which prevents air from entering the heating devices and the coolant - the presence of oxygen leads to metal corrosion. In such a system, closed expansion tanks are required, which are supplemented with safety valves and air release devices. They will heat a house of any size and are more reliable in operation.
Installation methods
For a small house consisting of from 2-3 rooms, they use single pipe system. The coolant moves sequentially through all the batteries, reaches the last point and returns through the return pipe back to the boiler. The batteries are connected from below. The downside is that the distant rooms are heated worse, since the coolant supplied to them is already slightly cooled.
More perfect two-pipe systems - a pipe is laid to the far radiator, and branches are made from it to the other radiators. The coolant at the outlet of the radiators enters the return pipe and moves to the boiler. This scheme evenly heats all the rooms and allows you to turn off unnecessary radiators, but the main disadvantage is the complexity of installation.
Collector heating
The main disadvantage of a one- and two-pipe system is the rapid cooling of the coolant, at the collector connection systems this disadvantage does not exist.

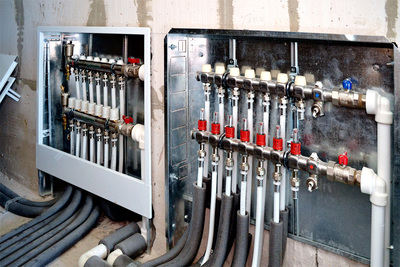
Photo 3. Water collector heating system. A special distribution unit is used.
The main element and basis of collector heating is special distribution unit, popularly called a comb. Special plumbing fittings required for distributing the coolant through separate mains and independent rings, a circulation pump, safety devices and an expansion tank.
Manifold unit for two-pipe heating systems consists of 2 parts:
- Input - it is connected to the heating device, where it receives and distributes hot coolant through the circuits.
- Day off — connected to the return pipes of the circuits, necessary for collecting the cooled coolant and feeding it to the boiler.
The main difference of the collector system is that each battery in the house is connected independently, which allows you to regulate the temperature of each one or turn it off. Sometimes mixed wiring is used: several circuits are connected independently to the collector, but inside the circuit the batteries are connected in series.
The coolant delivers heat to the radiators with minimal losses, the efficiency of this system increases, which allows using a boiler with less power and consuming less fuel.
But also a collector heating system is not without its drawbacks, these include:
- Consumption pipes. It will require spending 2-3 times more pipe than when connecting batteries in series.
- Necessity installations circulation pumps. Requires increased pressure in the system.
- Energy dependence. Do not use where power supply may be interrupted.
How to make water heating yourself
Independent home heating systems, more economical than central heating. It is possible to make a system with upper or lower piping, different types of heat carrier are used - water is considered the cheapest.
Design
Even specially created programs, will not be able to correctly calculate the parameters of the heating system due to a lack of necessary data.
Calculation of real heat losses
The first is to calculate the heat loss of the building. The calculation is made by the maximum value in this region — how much heat can a house or apartment lose when the coldest temperatures possible are outside.
Calculation of heat loss of a room

To calculate, the following data is needed:
- Area of the premises (can be found on the plan).
- The room faces the street through one or more walls or be in the middle of the building.
- Consider the location of the building in relation to the cardinal directions. The sun does not warm the north side, but it warms the south side almost all day long.
- Each region has its own wind directions.. The wind rose indicates from which direction the wind blows most often (search on the Internet).
- Each region has its own temperature indicators. during the coldest time (data is available on the Internet and in SNiPs).
- External walls are insulated or uninsulated.
- It happens under the floor simple soil, uninsulated and insulated rooms.
- Take into account, which is located above the room.
- A lot of heat is lost through windows. (depending on their design, quantity and area).
- Entrance doors - a loophole for the loss of thermal energy.
Attention! Measurements of the premises must be taken on the outside of the building, otherwise the calculation will give an incorrect result.
According to measurements calculate the area of external enclosures for each room, and are used in the formula for calculating total heat loss. The value of will also be useful there. R, which is calculated by dividing the wall thickness by the heat loss coefficient for the building material used in it (for new metal-plastic windows R The company that installed the windows can provide you with this).
Heat losses in winter consist of 2 parts:
- Losses through external walls.
- Losses spent on heating ventilation air.
The basic formula for calculating thermal energy costs looks like this:

Q = 1/R x (tв - tн) x S x (1+ ∑β). In which:
- Q — heat energy losses, W;
- R — temperature resistance of wall material, m²°С/W;
- S — wall area, m²;
- tv — indoor air temperature, °C;
- tн — minimum outside temperature, °C;
- β — additional heat losses possible due to the location of the building.
If the wall was built using 2 different materials, then their thermal resistance is calculated for both, and the result is added. The temperature outside the building is selected both according to standards and according to your observations, and inside the premises - at will. Additional heat losses - special coefficients:
- if part of the roof or wall of the building faces north, then β = 0.1;
- if the wall faces west or southeast, β = 0.05;
- β = 0, looking south.
Types of heating boilers by fuel type
The larger your house, the more powerful the boiler you need to install.
To calculate you need to know that per 10 m² area will be required 1 kW heat (if the ceilings in the room not higher than 3 m). But different regions have their own peculiarities. There are special climatic coefficients in SNiPs.
Heating boilers are divided into types: liquid and solid fuel, electric, gas. If the building has gas, there is no need for better fuel. Other options should be considered taking into account economic feasibility. If there are problems with electricity, it is better to choose a solid fuel boiler.
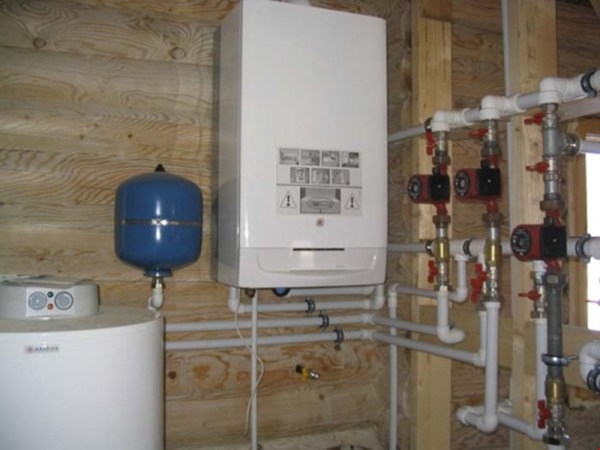

Photo 4. Wall-mounted gas boiler with an expansion tank, connected by pipes to the water heating system.
Pipes
In the heating system, install only heat-resistant plastic pipes that can withstand high temperatures. The diameters of the pipes are selected after calculating the entire system, but not less than 40 mm. For connection to batteries use a diameter of 20-25 mm.
Radiators
Currently the industry offers 4 types of batteries:
- Cast iron.
- Steel (there are panel and tubular ones).
- Aluminum.
- Bimetallic (steel pipes located inside, covered with aluminum on top).
Each species has its pros and cons. For example, cast iron They heat up slowly, but also take a long time to cool down.

Made of aluminum heat up quickly and transmit thermal energy better than others, but suffer greatly from corrosion. The best option is to use steel or bimetallic batteries.
It is important to calculate the required number of sections for the room., the amount of thermal energy entering the room directly depends on this. To do this, you need to know the total area, how much heat one section can give off, and take into account the proportion of heat output and the area of the room.
Expansion tank
The choice of volume and type of expansion tank is an important moment of installation of the heating system. Its purpose is compensate for the increase in volume of water due to heating, in addition it serves to remove air.
There are open and closed expansion tanks. Open — a simple container with an open top. It is mounted at the highest point of the system. Water evaporates through the open top and it must be periodically replenished. Closed — a sealed container with a rubber membrane installed inside, which serves to create pressure in the pipes. The closed model is most often used in systems with a circulation pump.
The expansion tank must be able to accommodate 15% of the coolant poured into the system. The volume of liquid that the boiler contains can be found in the passport. The most difficult thing is to find out the amount of coolant in the pipes, this must be calculated using the formula for calculating the volume of the cylinder, taking into account the diameter and total length of the pipes.
Circulation pump
Such a device is necessary for heating with forced circulation. Thanks to it, pressure appears inside the pipes, increasing the speed of movement of the coolant.
The main characteristic of the pump is productivity. The formula used for calculation is: Q = N/1.16 x (tout - tin), in which:

- 1.16 — heat capacity coefficient of water;
- tout and tin — temperature readings at the boiler inlet and outlet;
- N — indicates the generator power.
Temperature difference — a characteristic that needs to be measured. But this cannot be done until the system is running. For this reason, average data is used.
Features of using a water system as heating in an apartment
Advantages of an autonomous system:
- You can turn on the heating of your home at any time, and not only during the heating season.
- Supported comfortable temperature in the rooms, which is difficult when using central heating.
- Heating easy to customize, for example, no, there is no point in turning on the boiler at full power if the residents have left for a while.
- The fee for central heating is also charged in the summer, with autonomous heating, you will only have to pay according to the meter (electric or gas).
Cons:
- Work must be carried out in accordance with the law., unauthorized reconstruction, will not relieve you from paying utility bills and threatens an administrative fine.
- Need to find a place with good ventilation for installation of equipment.
- Installation of the system must be performed by professionals.
- Expenses for paperwork, and for the purchase of autonomous heating elements.
- All responsibility falls on the owner of the property. The operation of the equipment will be monitored by specialized organizations.
Useful video
Watch a video comparing natural and forced circulation water heating systems.
Is it worth installing your own heating?
Heating systems vary in equipment cost and operating efficiency. They have one thing in common: heating design will require precise calculations And selection of suitable equipment, which still needs to be installed correctly. But your own heating is guaranteed to bring you economic benefits.







Comments