It burns for a long time and gives a lot of heat, and what else do you need? Coal for heating houses

Heating a house with coal - one of the cost-effective alternative heating methods.
Modern equipment has nothing in common with outdated ideas about a boiler room - you don’t have to throw fuel into it every hour or worry about cleaning up soot and carbon in the room.
Coal boilers are a type of heating units, the design of which is optimized for the use of different types of coal. They provide complete independence - many of them are completely autonomous and do not require connection to utility lines.
Content
Construction of a coal boiler for heating a private house

In many models of such devices, in addition to what is recommended by the manufacturer, The use of other types of fuel (wood, briquettes, peat) is permitted.
This equipment consists of the following functional elements:
- firebox — fuel combustion chamber;
- ash pan — a container under the firebox to collect combustion products;
- grate - a grate that prevents coal from falling into the ash pan;
- heat exchanger — a system in which the coolant circulates;
- chimney — smoke exhaust channel;
- control systems And temperature control.
Operating principle
Due to the chimney draft, air enters the firebox and the fuel burns. The resulting gases heat the walls of the firebox and transfer heat to the water, circulating in the heat exchanger system. The heated coolant is fed into the pipes, heats the house, and returns to the boiler. Then the gases enter the chimney, where they maintain the temperature necessary to create draft.
The most common type of coolant is water, but sometimes they are used mixtures with antifreeze and antifreeze liquidsThe smoke removal system includes heat-insulated pipes, which are sometimes supplemented with a forced ventilation unit.
Attention! It is forbidden to fire a regular wood boiler with coal, since this type of fuel gives 2-3 times more heat, than a tree.
By functionality equipment is divided into 2 groups:
- with one circuit — for heating the room;
- with two — for heating and hot water supply.
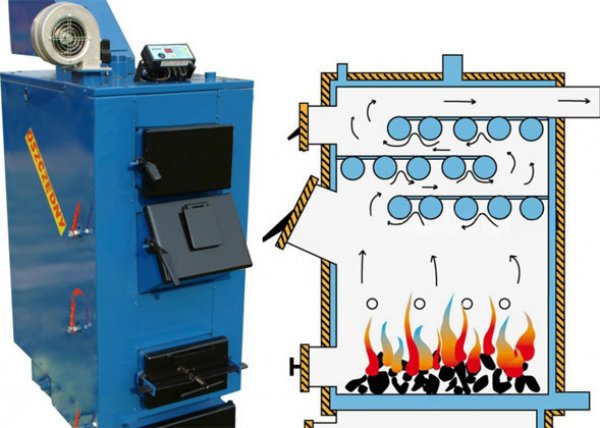
Photo 1. External appearance and diagram with the operating principle of a coal-fired heating boiler.
There are classical (single-chamber) and pyrolysis boiler models. In the first case, traditional combustion of fuel in the chamber is implied, the efficiency in this case is 70%. In pyrolysis models, coal and gases released during combustion burn in different chambers. The efficiency of such advanced models reaches 92%. The fuel in them burns more efficiently with less soot and smoke.
Coal boilers are made of steel and cast iron. Steel models — most often, devices with lower combustion consist of welded elements. Cast iron — cast, have high efficiency, are less susceptible to corrosion and contamination. Long-burning devices have a vertical firebox, the fuel gradually burns from above, due to which they operate without additional loading for several days.
Coal Heating: Pros and Cons
Coal-fired heating systems cope well with increased heating demands during severe frosts. One of its main advantages is the ability retain heat for a long time. In addition, coal stove heating has other benefits:

- independence from the availability of main energy resources (electricity, gas);
- Availability: coal, like the boilers themselves, is domestic and inexpensive;
- efficiency: average efficiency for different types of equipment — 70%;
- autonomy: If you purchase the appropriate model, you will not be dependent on electricity and gas;
- simplicity of design ensures long-term uninterrupted operation of the device;
- automation: Many models resolve issues of fuel supply and temperature regulation themselves.
Despite the advancement of technology, coal devices are not without their drawbacks:
- To ensure maximum combustion efficiency, special conditions will have to be met: requirements for the brand, quality, and humidity of the raw materials burned.
- The need to allocate utility space for storing fuel and installing the unit.
- Cyclicity of the process — different loading frequency (depending on the type of device). Coal will have to be loaded into any boiler.
- Maintenance required: removal of soot, carbon, ash, cleaning.
Many devices require the installation of auxiliary devices such as pumps and forced ventilation unitsDespite the automation of many systems, coal generators require constant monitoring.
Which is better, coal or gas?

It is generally accepted that the most cost-effective option for heating is main gas.
However, having learned the cost of connection and installation, many residents are looking for alternative heating options. It is better to compare these types of fuel according to three criteria:
- Energetic. When burning 1 m3 (0.62 kg) natural gas you will receive 9.45 kW/h heat without taking into account the boiler efficiency. A kilogram of anthracite will give 7.16 kW/h.
- Economic. Tariffs for the population for gas supply, as well as the cost of coal transportation and boiler efficiency are taken into account.
- Ease of use. In all cases, a chimney and ventilation will be required. Space is needed to store coal fuel, and it will have to be loaded manually, while gas is supplied through a pipeline.
Reference. If the house is already connected to the gas main, then you don’t need to look for a more cost-effective heating method. If there is no connection, the best option is coal boilers, operating in automatic mode.
What kind of coal is best to use for heating?
This type of fuel contains many elements that affect its energy properties. The cleanest and most valuable fuel is the one that contains the maximum amount of carbon. The lower the percentage of this substance, the lower the combustion heat and the higher the amount of impurities and moisture. When choosing coal, the following characteristics are taken into account:

- Heat of combustion. The indicator reflects what volume of heat a certain volume of fuel will produce per unit of time. It is measured in MJ/kg or Kcal/kg, in which case it is called caloric content.
- Ash content. Measured as a percentage, it shows the amount of non-combustible impurities. The lower this indicator, the more heat from the fuel. In high-grade brands, its level is within 25%, for low-grade coals - exceeds 40%. The higher the ash content, the more often you will have to remove slag and ash.
- Humidity. If surface moisture is easily removed by drying and ventilation, then internal moisture evaporates only during combustion. The higher the internal humidity, the more thermal energy will be required to dry it and less will be used for heating.
Marking
The first letter indicates the grade, the second the size of the fraction. There are a total of 17 marks. The main types of solid fuel are labeled: anthracite - "A", long-flame - "D", low-caking — "SS".
Coal is classified by the size of the pieces:
| Marking | Name | Fraction, mm |
| P | Plate | More than 100 |
| TO | Large | 50-100 |
| ABOUT | Nut | 25-50 |
| M | Small | 13—25 |
| WITH | Seed | 6-13 |
| Sh | Shtyb | up to 6 |
| R | Private | 0—300 career 0—200 mine |
For example, the fuel is marked AS — anthracite shtyb, DS and DPK — long-flame "seed" And slab with pieces of 50-100 mm.
Types of coal and its characteristics: hard, brown, anthracite, briquetted pressed
How fuels are used three types: brown, stone and anthracite. The first gives off the least amount of heat, for this reason it not used in everyday life.
Coal emits a large amount of heat (up to 7000 kcal/kg), has a humidity of up to 15%, gives a little ash (up to 16%), therefore it is most often used for heating boilers.

Photo 2. Coal in hands. It is small black stones.
In turn is divided into subspecies:
- Long-flame — got their name for their ability to burn with a long flame like wood. The DPK brand is suitable for most boilers, DO, DS — for automated ones.
- Low-caking — burn without smoke and flame, are used economically due to the long duration of combustion. They are used less often due to lower efficiency and difficulty of ignition.
- Skinny — inexpensive grades are short-flame, more often used in industry in cast iron furnaces. Lean coals are difficult to light, they give up to 45% ash, but a lot of heat, so in everyday life they are used in boilers with good draft.
Anthracites have the highest quality indicators among all coals for domestic boilers: calorific value up to 8200 kcal/kg, humidity 1-3%, ash content up to 9%. They emit almost no volatile substances (up to 9%), burn with a short, even flame, with minimal smoke and ash formation. Due to their high combustion duration, they are considered the most economical types of coal. They are suitable for specialized boilers with a large firebox designed for high temperatures and good draft.
Coal briquettes — budget type of fuel. Made from waste from the coal mining industry: small coal fractions, crumbs and dust by pressing with the addition of binding components. The advantages include: low ash and moisture content, good calorific value, provided that the briquettes are made from high-grade coal. Pressed fuel ignites well with firewood, burns for a long time (on average 6-8 hours.), produces little smoke, soot and slag.

Photo 3. Pressed coal in oblong briquettes. Such fuel is good for heating boilers.
How to calculate consumption?
When calculating fuel consumption take into account many factors: quality, brand, duration of coal burning, average outside temperature, area, material and degree of insulation of the house. With the help of calculations, an average value is obtained, since it is difficult to take into account all the criteria, as well as the onset of thaws and frosts.
Before starting the calculation, the total area of the house is calculated. The boiler power is calculated using the standard formula: 1 kW per 10 m2. For example, for an average country house 160 m2 equipment will be required 16 kW power. Efficiency of modern boilers from 50 to 90%, For example, we take the average value 70%. We calculate the duration of the period during which heating is needed (on average 6 months).

Calculation of fuel consumption is produced as follows:
- For the boiler to work, power 16 kW with 70% efficiency will be required 11.2 kW/h. To develop 1 kW need to 0.25 kg hard coal with average characteristics. 11.2*0.25 = 2.8 kg per hour.
- We calculate the daily fuel amount: 2.8*24 = 67.2 kg.
- We determine the coal consumption per month: 67.2*30 = 2016 kg.
- To calculate the amount of coal for the winter, multiply the resulting number by the number of cold months: 2016*6 = 12096 kg.
- To calculate the cost of heating for the winter, we multiply the resulting value by the price of coal per 1 kg.
Reference. To get consumption, preferred brand and runtime data in one tab - look at the technical documentation for the boiler. Instructions are always included with purchase.
Useful video
Watch the video, which provides approximate calculations of the required amount of coal to heat a house for one month.
How to get the most benefit?
In order for the fuel to retain its calorific value, it must be stored properly. Although it is profitable to buy coal in large quantities, it is not worth doing this for several years in advance. The most unstable for storage is brown, it will lie without losing its properties up to six months, lasts the longest anthracite up to one and a half years.
For storing coal choose a dark, well-ventilated, moisture-free place in a basement or barn. The fuel is stored in specially constructed containers. wooden boxes or stored in bags.

Photo 4. Bag of coal. This is the best package for storing coal fuel.
Coal stocks are not afraid of precipitation, so they can be left in the yardFor such storage, a compacted area is selected, coal is poured onto it, and compacted to reduce the air content, which promotes oxidation.






