4 formulas that determine the heat in the house: rules for calculating a circulation pump for a heating system

Correct pump calculation will help to avoid problems during operation heating. The characteristics must be calculated accurately to avoid malfunctions.
For this you need to know four formulas. And one should also understand the meaning of the concept of RT.
Operating point: what is it?
Is intersection of the graphs of two characteristics: pump and pipeline. At this point useful powers of consumption and consumption are equal. The system's performance depends on its position. Water supply is depicted as a value increasing from zero, and pressure is depicted as decreasing from the maximum value of the pipes' throughput.
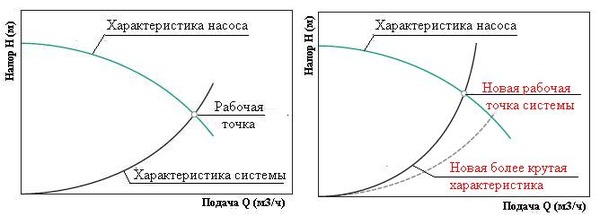
Photo 1. An example of how the operating point can change when changing the characteristics of the heating system.
The feed has minimum threshold. If it is not taken into account, the system overheats, which leads to damage. The pressure may also deviate from the normal value, which partially affects the network characteristics.
Important! Throttling and deposit formation affect the change in position points.
It is necessary to comply Operating requirements:
- heat consumption of the building;
- peak costs.
Having selected the RT, a circulation pump is selected based on its characteristics. It is advisable to take a device with readings located to the right operating point. The reserve will help to avoid problems when changing values.
Formulas for calculating the characteristics of a pump for a heating system
To determine the installation location, it is necessary to calculate the RT. It should be remembered that doubling the pressure is the square of the flow increase coefficient.
Power of the circulation pump

N = (P * Q * H) / (367 * efficiency), Where:
- P — density of water.
- Q — consumption of working fluid.
- H — pressure level.
Power is calculated in kWWhen purchasing, you should focus on this indicator, choosing a device with a similar or higher value. It's better to take with a reserve and manually limit.
How to choose performance
Q = (S * Qoud) / 1000, Where:
- S — the area of the premises in which the piping is located.
- Qoud — specific energy consumption.
Performance is calculated in kW per square meter. In multi-apartment and private houses this meaning is different. In the second case it is 40-45% biggerThis is due to heat losses, which are higher in low-rise buildings.
What water pressure is needed?
H = (R * L * ZF) / 10000, Where:

- R — pipeline resistance.
- L — the longest heating section.
- ZF — safety factor, in most cases it is taken equal to 2,2.
The liquid pressure is measured in meters. Displayed as a descending graph. The maximum value is reached at the starting point, since the indicator decreases as you move away from the boiler.
How to calculate water supply
V = Q / (1.16 * T), Where:
- T — the difference in temperatures of the coolant in the heating system, usually amounts to from 10 to 20 °C.
- Q — pump performance.
The feed is measured in cubic meters per hour. T is taken as the difference between the water temperature in the boiler and at the extreme point of the return. The feed is displayed as an increasing graph. Together with it the flow rate and hydraulic resistance change.
Reference! The latter changes in a quadratic relationship, so looks like a parabola.
Useful video
Watch the video, which shows how the necessary calculations are made when choosing a heating pump.
Correctness of calculations
Very important obtain qualitative values. Otherwise, malfunctions may occur. It is recommended to contact plumbing specialists.





