Alternative energy sources are the future! Heat pump for home heating

Gas or electricity are usually used to heat the premises. However, this method of heating will cost a pretty penny, as both are quite expensive.
That is why alternative energy sources are used for heating private and country houses, and One of the most popular heating methods is the use of heat pumps.
What is a heat pump for heating a private house? How does it work?

A special device that capable of extracting heat from the environment is called a heat pump.
Such devices are used as the main or additional method of heating premises. Some devices also work on passive cooling of the building — the pump is used for both summer cooling and winter heating.
The energy of the environment is used as fuel. Such a heater extracts heat from air, water, groundwater, etc., so this device is classified as a renewable energy source.
Important! To operate such pumps, you need connection to the power grid.
All heating devices include evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion valve. Depending on the heat source, water, air and other devices are distinguished. The operating principle is very similar to the operating principle of a refrigerator (only the refrigerator throws out hot air, and the pump absorbs heat).
Most devices operate at both positive and negative temperatures, but the efficiency of the device directly depends on external conditions (i.e. the higher the ambient temperature, the more powerful the device will be). In general, the device works as follows:
- Heat pump comes into contact with the surrounding conditionsTypically the device extracts heat from the ground, air or water (depending on the type of device).
- A special evaporator is installed inside the device., which is filled with refrigerant.
- When in contact with the external environment the refrigerant boils and evaporates.
- After that The refrigerant enters the compressor in the form of vapor.
- There it shrinks - thanks to this his temperature rises significantly.
- After this, the heated gas enters the heating system., which leads to heating of the main coolant, which is used for heating the premises.
- The refrigerant cools down little by little. At the end it turns back into liquid.
- Then the liquid refrigerant enters a special valve, which seriously lowers its temperature.
- At the end, the refrigerant returns to the evaporator., after which the heating cycle is repeated.
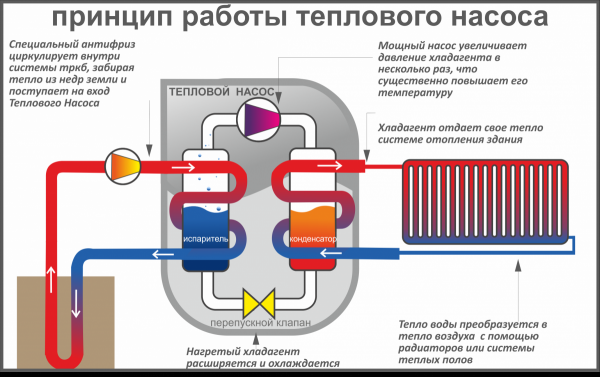
Photo 1. The principle of operation of a ground-water heat pump. The cold heat carrier is shown in blue, the hot one in red.
Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly. Such devices are considered renewable energy sources, which do not pollute the atmosphere with their emissions (whereas in the case of using natural gas, harmful greenhouse gases are formed, and coal combustion is often used to produce electricity, which also pollutes the air).
- A good alternative to gas. A heat pump is ideal for heating rooms in cases where the use of gas is difficult for one reason or another (for example, when the house is located far from all major utility networks). The pump also has the advantage over gas heating in that it does not require state permission to install such a device (but when drilling a deep well, you will still have to get it).
- Inexpensive additional heat source. The pump is ideal as a cheap auxiliary power source (the best option is to use gas in winter and a pump in spring and autumn).
Flaws:
- Thermal limitations when using water pumps. All heating devices function well at positive temperatures, whereas in the case of operation at negative temperatures, many pumps stop working. This is mainly due to the fact that the water freezes, which makes it impossible to use it as a heat source.
- Problems may arise with devices that use water as heat. If water is used for heating, then a stable source of it will need to be found. Most often, a well must be drilled for this, which may increase the cost of installing the device.
Attention! Pumps usually cost 5-10 times more expensive than a gas boiler, therefore, the use of such devices for the purpose of saving money in some cases may be impractical (it will take several years for the pump to pay for itself).
Main types, their operating principles
All heat pumps differ from each other in their energy source. Main classes of devices: soil-water, water-water, air-water and air-air.

The first word indicates the source of heat., A the second means what it turns into in the device.
For example, in the case of a soil-water device heat is extracted from the earth and then converted into hot water, which is used as a heater in the heating system. Below we will consider the types of heat pumps for heating in more detail.
Soil-water
Ground-water type installations extract heat directly from the ground using special turbines or collectors. In this case, the source is the earth, which heats the freon. It heats the water in the condenser tank. In this case, the freon cools and returns to the pump inlet, and the heated water is used as a coolant in the main heating system.
Liquid heating cycle continues as long as the pump receives electricity from the network. The most expensive method, from an economic point of view, is the soil-water method, since to install turbines and collectors it will be necessary to drill deep wells or change the location of the soil over a large area of land.
Water-water
According to their technical characteristics, water-to-water pumps very similar to ground-water class devices with the only difference being that in this case, water, rather than earth, is used as the primary heat source. The source can be both groundwater and water from various reservoirs.
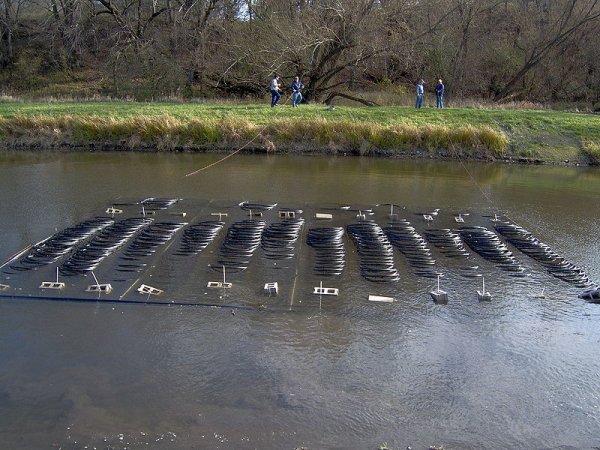

Photo 2. Installation of a structure for a water-to-water heat pump: special pipes are immersed in the reservoir.
Water-to-water devices significantly cheaper ground-to-water pumps, since their installation does not require drilling deep wells.
Reference. To operate the water pump, it is enough to immerse several pipes in the nearest body of water, therefore It does not require drilling wells to operate.
Air-water
Air-to-water units receive heat directly from the environment. Such devices do not require a large external collector to collect heat, and ordinary street air is used to heat the freon. After heating, the freon gives off heat to the water, after which the hot water enters the heating system through pipes. Devices of this type are quite cheap., since the pump does not require an expensive manifold to operate.
Air
An air-to-air unit also receives heat directly from the environment, and for its operation it also requires no external manifold required. After contact with warm air, the freon heats up, then the freon heats the air in the pump. Then this air is released into the room, which leads to a local increase in temperature. Devices of this type are also quite cheap, since their operation does not require the installation of an expensive manifold.
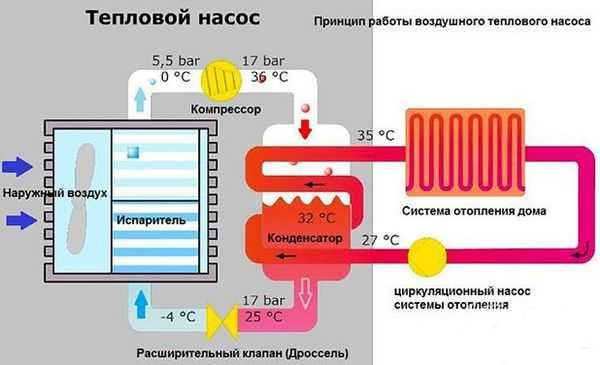
Photo 3. Operating principle of air-to-air heat pump. Heat carrier with temperature of 35 degrees enters heating radiators.
Calculation for heating systems, table
The main indicator that shows the power of a particular heating device is CPT parameter (in English literature it is known by the abbreviation COP). CPT - heat conversion coefficient, which is calculated by dividing the total power of the device by the amount of electricity consumed per unit of time. For example, a certain pump X consumes 2 kW/h electrical energy, and generates it 5 kW/h thermal energy - in this case the value CPT = 5/2 = 2.5.
The conversion factor of most devices is within the range from 3 to 7, however The higher the CPT, the more expensive the device will be. It should also be remembered that the CPT value depends on the ambient temperature - if it is too low, the CPT value will begin strive for 1 (in fact, only electricity is used to heat the coolant, and external heat will not participate in heating the building).
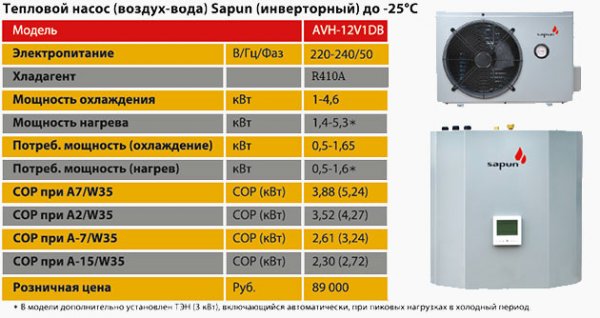
Photo 4. Table with calculation of the power of an air-to-water heat pump from the manufacturer Sapun.
The use of a particular pump must be justified from an engineering point of view. To purchase a device, the building's heat loss is first calculated. The following formula is used for this: CT = (OZ * MTP * KS)/860. It is deciphered as follows:
- Amount of heat (units of measurement - kW/h).
- OZ — the total volume of the building.
- MTP — maximum temperature difference. To determine this figure, subtract the indoor temperature from the outdoor temperature. For example, you want the indoor temperature in winter to be 20 °C, whereas on the street it will be located next to the mark -10 °C - in that case MTP = 20 - (-10) = 30.
- KS — a special correction factor that takes into account the type of walls. For wooden ones, the KS indicator is equal to 3-4 units, for brick walls - 2-3, for brick in two layers - 1-2, for brick in 2 layers with insulation - 0.5—1.
- Number 860 — a correction factor by which the final value is divided to convert kilocalories to kilowatt-hours.
Attention! This formula - approximate, since the temperature regime of a building depends heavily on its design features. Therefore, when purchasing, engineers recommend buying a heating pump "with a reserve".
Heat pump installation
The installation method of the device depends on the type and model of the device, as well as on the terrain features. Let's take a look An example of installing a simple ground-to-water heat pump:
- First, preparatory work is carried out. At this stage, the groundwater level is measured, the power of the power grid is determined, etc. At the end of the stage, the well is drilled according to the plan.
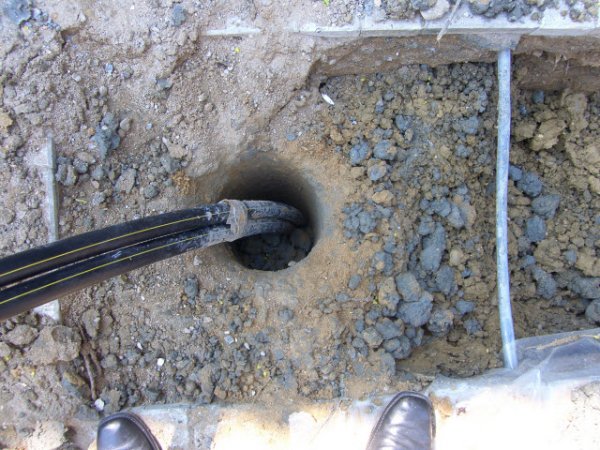

Photo 5. Installation of a ground-to-water heat pump: special pipes are inserted into pre-dug wells.
- After which geothermal probes are lowered into the boreholes, which will extract heat from the ground. At this stage, an evaporator with a refrigerant is also installed, which will transfer heat to the compressor.
- Now it needs to be installed. Typically, the device is placed in a room near the house; the compressor area is usually less than 1 square meter, Therefore, as a rule, such a device is installed in a small room.
- After this happens connection pump to the heating network of the house using pipes. At the final stage, test run, and if any defects are detected, debugging is performed.
Useful video
Watch a video that explains how a ground source heat pump works.
Safety and ecology
A heat pump is a good device that is ideal for heating a building as an auxiliary heat source.

In this case, environmental resources are used as fuel, so the heat pump is considered a renewable energy source.
The main advantages are safety and environmental friendliness, since no gas or coal combustion is used for operation.
Such a device will not harm humans or the environment, but it should be used wisely, because in some cases the use of this device may not be advisable from an engineering or economic point of view.









Comments
All my friends who use heat pumps are very happy.