Safe heat: diagrams and principles of gas heating in a private house

The advantage of heating a house with gas is its economy. Heating cheaper than wood (up to 2.5 times) or electric (up to 7.5 times) heating.
Gas heating is a system of heating a building using thermal energy generated by burning gas in a special boiler.
As a coolant in Russia it is most often used water (in this case, the pipes are laid out with radiators), but in some countries, preference is given to air heating, when the heat is redistributed from by air through special air ducts. Air gas heating up to one and a half times cheaper water.
Content
- Features of heating a house with gas
- Types of gas heating in private residential premises
- Advantages
- Flaws
- Types of boilers
- Heating system diagrams
- Operating principles
- Methods of wiring
- Pros and cons of different types of gas systems
- Gas consumption for heating a house
- Useful video
- Why it is better to entrust design and installation to specialists
Features of heating a house with gas

We are talking about about autonomous heating systems houses with their own gas boiler. Here are their main features:
- Suitable for gasified settlements.
- Connecting gas equipment requires approvals and involvement of specialists.
- The basis of the heating system is the boiler.
- There are rules for placing a gas boiler (only in non-residential premises with the required characteristics, except for bathrooms).
- This heating system complemented by various devices, maximally automating the heating process.
- For equipment operation electricity is needed.
Attention! The choice of a land plot for construction with a main gas supply will allow the future residential building to be used significantly cheaper.
Types of gas heating in private residential premises
By type of gas supply - these are:
- systems with natural gas pipelines;
- with liquefied gas in cylinders or gas tanks.

First option is one of the most economical types of heating. Second costs the owners several times more expensive (according to one source, five times).
When connecting to the main gas supply, it is necessary to order a gasification project and undergo approvals from regulatory authorities.
Gas the pipe is connected directly to the equipment in the house. Gas is supplied continuously and automatically.
Heating with cylinders or a gas tank requires an independent gas supply. The cylinders need to be changed constantly (every 2-3 days). Gas holder (private gas storage facility) will allow the creation of a more automated system, since gas can be pumped into it once every six months to a year.
In general, the cost of a gas storage facility and gas for it will make heating several times more expensive. But if there is a generator, such a system is autonomous, does not depend on a gas pipeline and can withstand long interruptions in the supply of electricity.
Gas holders with a capacity of 2–3 cubic liters enough order to heat a cottage 150 sq. m., building in 300 sq. m. will require a significantly larger volume (according to some sources up to 9 cubic liters).
Advantages

The advantages of this type of heating include:
- economy when using main gas;
- efficiency factor up to 95%;
- the ability to heat large houses;
- variability heating, since there is a choice between liquid and air options;
- eco-friendliness (combustion products minimally pollute the environment);
- automation (with main gas, the system operates independently, including control and provision of special heating modes in different rooms);
- when using air heating no need for radiators and pipes in the rooms;
- wide range of additional functions: with air heating - air purification and humidification, ventilation, air conditioning;
- safety provided by sensors;
- into the system The hot water supply circuit for the house is connected.
Flaws
- Difficulties and significant costs when connecting to main gas pipelines;

- the need for precise matching of the combustion chamber or other location of the boiler in accordance with the required standards, as well as passing the approvals;
- high cost of heating when using cylinders or a gas tank;
- danger of explosion of gas cylinders;
- energy dependence (in case of power outages in the house, a generator is required);
- danger in case of violation of the rules of placement and operation of gas equipment, or the absence of an automatic leak monitoring system;
- Possibility of equipment failure (especially imported ones) due to power surges in Russian power grids.
Attention! Ignoring the requirements for connecting and operating gas equipment creates not only problems with regulatory authorities, but also danger to residents.
Types of boilers
There are different types:
- by installation method;
- by power;
- by the number of contours.
According to the installation method, there are wall-mounted and floor-standing boilers. Low-power boilers with one circuit and a minimum set of additional equipment are often placed on the wall in the kitchen. More powerful boilers require a separate room (boiler room), and are supplemented with various equipment.
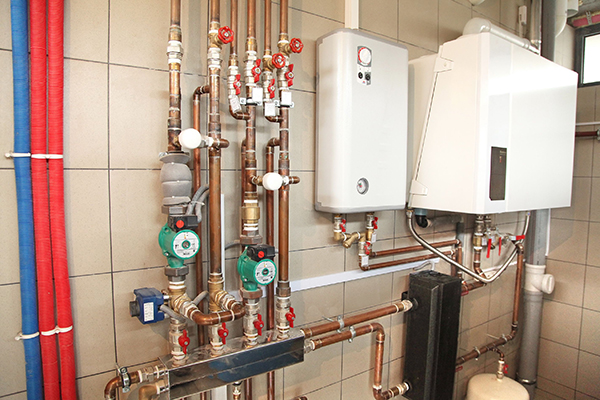

Photo 1. A wall-mounted single-circuit gas boiler installed in a small semi-basement room on ceramic tiles.
Power
Each boiler has a certain capacity. When used mainly for heating, the basic calculation formula is used: 1 kW of power per 10 sq. m. well-insulated house. For a cottage with an area of 200 sq. m. boiler power required 10 kW. Additionally, it is recommended to add about 15% for peak loads. The planned hot water supply through the same boiler will require additional power.
The design expert will calculate required equipment parameters, taking into account the wall material, the number of floors and windows, the climatic characteristics of the area and other aspects.
Number of contours
There are:
- single-circuit;
- double-circuit boilers.
Single-circuit often more expensive and more powerful, but without additional equipment they are intended only for heating. If you want to have hot water supply, you can buy a boiler. A single-circuit boiler of sufficient power will cope with heating a large house and heating a significant volume of water.
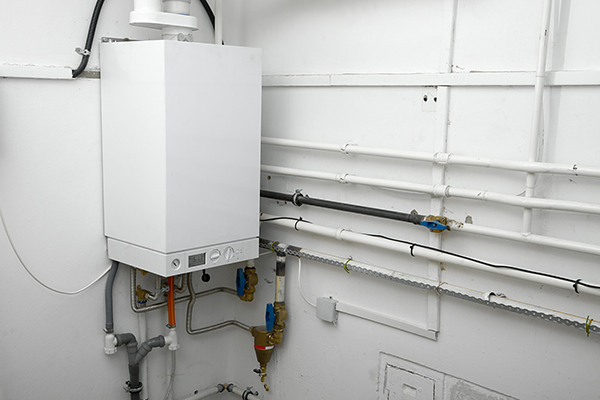

Photo 2. Single-circuit gas heating boiler, installed on the wall. Suitable for a large private house.
Double-circuit boilers are less powerful, cheaper and more versatile: one of their circuits works to heat the house, the second - to heat water.
They have a built-in heat exchanger, and water heating occurs either with the help of a boiler included in the boiler, or in a flow-through manner. 15-20 liters per minute — the maximum heating volume for such boilers. They are more suitable for small houses where few people live.
Reference! Models of such boilers can be used in summer for heating water only with the heating circuit switched off.
Heating system diagrams
Heating system diagrams can be liquid and air.
Liquid
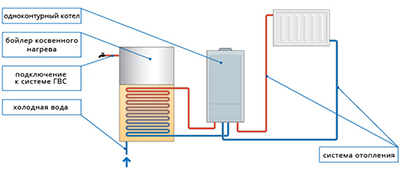
A simplified diagram with a single-circuit boiler consists of:
- gas boiler (gas, water and electricity are supplied to the boiler room);
- boilers;
- circulation pump;
- expansion tank;
- equipment that ensures safety in case of gas leaks;
- chimney;
- piping and radiators from the boiler room to most rooms in the house.
Important! Do not allow sub-zero temperatures in the house if there is water in the pipes, so as not to unfreeze the system. This problem can be solved by using antifreeze as a coolant, but its leakage is dangerous to the health of residents.
Air
The standard scheme includes a boiler room (often installed in the basement under the central part of the cottage), in which the following are installed:
- gas heat generator;
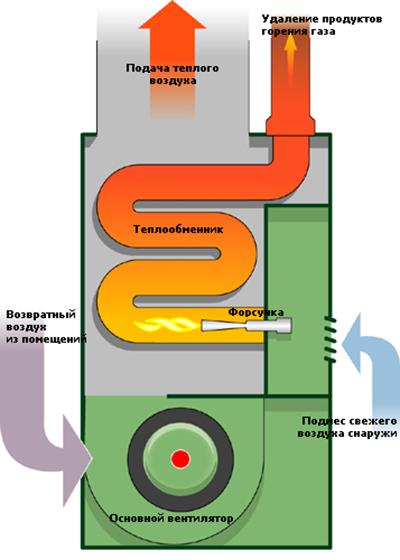
- fan for forced air circulation;
- purifiers and filters;
- if necessary air humidifier;
- air conditioner (its second part is installed outside);
- all kinds of sensors;
- main air duct, running vertically through the center of the house;
- horizontal air ducts of each floor with ventilation openings in heated rooms;
- set of vents and fittings to draw air into the system inside and outside the house, as well as to remove some of the air from the building.
If you want to save money, you can exclude the air conditioner, humidifier, and fan from the system. The system is functional without forced circulation, but the heating quality will deteriorate significantly in this case: warm air in the rooms is distributed less evenly, accumulating under the ceiling. And The temperature will depend on the opening of the windows.
Operating principles
- Liquid system. A gas boiler heats up a liquid coolant, which is delivered to the rooms through pipes to radiators (batteries) installed under the windows. The house is heated by an external circuit. The coolant heats up and cools down for a long time, so it will take a long time to heat the house.
- Air system. Using a heat generator, air is heated in the boiler room, which is then supplied directly to the heated rooms via air ducts (usually through openings in the floor).

There are no radiators or pipes in the rooms. After passing through the rooms, the air is discharged through special ventilation grilles.
The main part of the heated air circulates inside the building, but some is renewed. Cleaning, humidification and air conditioning can be built into such a system. When working on gas, it is fully automated.
Methods of wiring
Methods of wiring differ for liquid and air systems.
Liquid
Basic schemes for water movement options two:
- with natural circulation liquid coolant;
- with its forced circulation.
The first option is used for single-story houses with a contour of no more than thirty meters. If the length of the pipes is greater, a circulation pump is required.
There are also several different piping layouts:
- in one and two pipes;
- horizontal and vertical.
Two-pipe heating allows you to turn off some of the radiators in the house. The horizontal scheme makes it possible to turn off the heating on the entire floor.
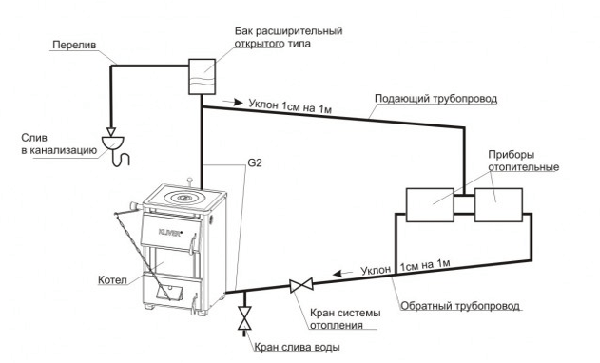
Photo 3. Layout diagram of a liquid system with natural circulation, which is usually used in small private homes.
Air
According to the methods of air mass circulation, there are:
- straight-through circuit;
- recirculation scheme.
- partial recirculation scheme.
The recirculation scheme, in turn, can be:
- with natural movement air;
- with forced movement in the presence of supply and exhaust ventilation.
The direct-flow scheme was used for heating buildings initially, all the hot air was removed from the house, which is extremely uneconomical. The recirculation scheme, on the contrary, kept the heated air inside the building, running it through the heat generator several times. This is economical, but unhygienic, since the air is not renewed.
Today the most commonly used scheme is with partial recirculation, when heated air circulates inside the house, partially being renewed from the outside.
Pros and cons of different types of gas systems
Each type of system has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Water

Advantages of a liquid system:
- partial recirculation scheme.
- due to its wide use in the market many specialists and equipment;
- possibility to install heated floors;
- sufficient economy.
Cons:
- partial recirculation scheme.
- coolant problems (water freezes, antifreezes are potentially hazardous to health);
- long-term heating of the house;
- increase in the weight of the building and the load on the foundation;
- dependence on the availability of electricity.
With air
Advantages of the air system:
- partial recirculation scheme.
- a cheaper way to heat compared to liquid;
- high speed of heating of premises;
- there are no problems with liquid filling of pipes, as well as the pipes and radiators themselves;
- additional functions (air purification, humidification, air conditioning option);
- safety.

Cons:
- partial recirculation scheme.
- installation difficulties (the system is made during the construction of the house, it is difficult to hide the air ducts later);
- need for maintenance;
- there is less equipment and specialists on the market;
- energy dependence.
Gas consumption for heating a house
For liquid heating systems the formula used is: A = Q / (q * B)
A — calculated gas consumption per hour of heating operation.
Q — boiler capacity (may not be used at full capacity in warmer weather).
q — specific heat (gas G20 – 9.45, gas G25 – 8.13 kWh/m3).
IN — efficiency coefficient of the gas boiler (indicated in the product passport).
For example, a boiler with a capacity of 10 kW, gas powered G25, with 90% efficiency will consume per hour, operating at full capacity: 10/(9.45*0.9)=1.17 – i.e. more than 1 cubic meter of natural gas per hour.
Such calculations will allow you to predict heating costs when buying boilers with different efficiency. Calculating costs for the entire season sometimes leads to the idea of the need to buy a boiler with a higher efficiency.
Useful video
The video provides advice that will help you avoid making a mistake when choosing a gas heating boiler for a private home.
Why it is better to entrust design and installation to specialists
If there are mistakes, the heating will be of poor quality and ineffective. And the price of an incorrectly prepared boiler room will be requirements of the supervisory authority in cutting out additional windows and the like.








