They are chosen for both houses and apartments: why are water heating radiators so popular?

As a heat carrier, most centralized and autonomous heating systems Hot water is used for residential and non-residential premises.
This type of battery filling effective and time-tested. Therefore, water heating radiators are the most popular on the thematic market.
Content
Types of water heating radiators

When choosing, the buyer pays attention to the appearance of the product. However, the primary importance is material, structure and type of battery mounting.
These parameters affect the favorable operation. It is important that the device is suitable for the heated area.
There are several types of water radiators.
Panel with tap adjustment
Batteries with a single-piece design that are ready for installation and operation - no additional fasteners or radiator kits are needed. Often made of steel. Wide application of panel radiators - in heating networks with an independent circuit. Interacts with the automatic temperature maintenance system.
Advantages of panel radiators:
- Presentable, modern appearance.
- Simplicity installations.
- High heat output - thanks to the presence of convectors.
- Economy — due to the small amount of coolant in the battery and high heat transfer. And also the panel radiator can be equipped thermal head, with which the temperature of heat supply is regulated.
Cons:
- At leak The entire device is changed at once, and not just a single element.
- Low resistance to corrosionIf the operating conditions are not observed (air availability, annual water discharges, unregulated pH), the panel radiator will quickly fail.
- This cannot be allowed water hammerFor this purpose, a pressure reducer is installed at the inlet.
- A strong blow will disable the device and it will have to be change.
Sectional
The design is made up of interconnected sections. They are made under pressure using casting, connected by threaded elements or spot welding. The material is usually cast iron or steel. The type's special feature is high thermal inertia. Sectional steel radiators are more expensive than cast iron ones due to the manufacturing technology. They are used in centralized heating systems.
Advantages of sectional radiators:

- Ease of use - if one section is damaged, it is enough to replace only it. There is no need to replace the entire device. It is also possible to add additional sections.
- The average service life is 30 years.
Cons:
- Over time, the system accumulates sediment — due to the slow movement of the coolant. Therefore, radiators are periodically flushed.
- There is no possibility to change quickly heating temperature - due to high heat capacity.
- Availability connections between sections increases the unreliability of the system.
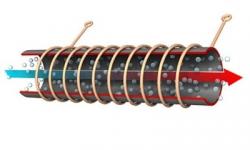
Tubular
By design, these are welded tubular devices. They are produced with the calculation pressure of 10-15 atmospheres. Made of steel. Preferably installed in buildings with an independent heating system, as central heating sometimes causes pressure drops, which leads to depressurization of the seams.
Important! The efficiency of the battery depends on the number of tubes. Optimally - 6.
Advantages of tubular radiators:
- Thanks to welded joints, leaks are not a threat when used correctly. The seams are created laser.

- High pressure threshold - up to 15 atmospheres.
- Hygiene - tubular radiators are easy to wipe off dust, and children will not get hurt due to their rounded shapes.
Cons:
- Small thickness of steel (maximum 1 mm).
- Not tall heat transfer.
- High cost due to the complex manufacturing process.
Plate-shaped
The system of these batteries consists of U-shaped tube, through which water moves. Heat exchange plates are strung on the tube. A common material is steel.
They are used in residential and public premises, industrial facilities.
Advantages of plate radiators:
- Allows heating large areas due to the high speed of water movement.

- The absence of joints ensures complete reliability. The possibility of the device breaking is excluded.
- Operating pressure threshold - up to 40 atmospheres.
- Financial accessibility.
Cons:
- Unattractive appearance.
- The probability that the ribs on the radiator will become clogged dust and will adversely affect the heating temperature.
Selecting a battery by material
It is the material that plays the primary role in the efficiency of heat transfer. After all, each material has its own heat transfer level.
The following materials are distinguished:
Cast iron
They have been used for over 100 years and are recognized as durable and reliable. They are suitable for central heating systems in multi-storey buildings. The capacity of one section is 90-160 W.
The appearance is not very presentable. Radiators made of cast iron are bulky and heavy. For better heat transfer, it is recommended to paint the batteries in a dark color.
Pros:

- Cast iron can withstand water hammer, pressure drops, low quality of coolant.
- Does not rust or give in corrosion.
- Affordable price — compared to other materials.
- Service life - more than 40-45 years.
Cons:
- Low heat output.
- High inertia, which does not allow the use of cast iron in modern thermoregulation systems.
- Absence heat saving — due to high thermal inertia and the impossibility of using thermostatic regulators.
- The need is constant repaint battery to maintain an aesthetic appearance.
- Difficulty in maintenance due to large mass.
- Inner walls of cast iron channels in batteries rough, which over time leads to the formation of plaque, and as a consequence, a drop in heat transfer.
Aluminum
The material has minimal thermal inertia (i.e. it reacts to temperature changes in the coolant in a short period of time), which allows it to be used in combination with a thermostat. Aluminum has good heat transfer, and there is no need for bulky batteries. Thermal power — 190 W per section.
Aluminum is a light, flexible and soft material, so it makes stylish heating batteries. Sections are often made white colors that harmonize with any interior.

Photo 1. Aluminum water heating radiator Eco 500/800 mm, weight 6.18 kg, manufacturer - "Lammin", Finland.
Pros:
- A good ratio cost and quality.
- Method of heating aluminum material - convection, in which dust does not accumulate between the sections.
- Resistant to corrosion, so aluminum batteries do not need to be repainted.
- Allows save heat, as it works in combination with a thermostat.
- Ideal for heating in private houses.
- High working pressure - up to 17 atm.
Cons:
- Low quality coolant quickly spoils aluminum.
- Can't stand it water hammer.
- Not suitable for apartment buildings.
Steel
Heating structures made of steel are preferably used in rooms with autonomous heating due to the technical characteristics of the material. They are produced panel and tubular batteries.
Second type more resistant to sudden pressure changes in the network.
Such designs are quite presentable and laconic. Heat power for one section - 450-5600 W.
Pros:
- If used correctly, the radiator will last a long time. at least 20 years.
- Steel has good heat dissipation.
- Economy — due to the small volume of coolant in the device and its high thermal conductivity.
Cons:
- Requires constant coolant pressure due to open steel seams.
- Water should be used as a coolant exclusively purified.
- Can't stand it water hammer.
Bimetallic
Combined high thermal performance of aluminum and durability of steel. Externally, they are similar to monolithic aluminum convectors, but in terms of strength they are much superior to fragile aluminum. Sometimes bimetallic convectors are made in the form of separate sections - from 4 to 14 pieces. Thermal power one section - 200 W.

Photo 2. Bimetallic water radiator model Base 350, power 1632 W, manufacturer - "Rifar", Russia.
The internal components of the device are welded from seamless steel tubes, which prevents corrosion and allows it to withstand high atmospheric pressure. Convection fins are also installed to achieve maximum heat transfer.
Pros:
- Easy and quick installation.
- Aesthetics.
- Reliability and durability constructions.
- Tall heat transfer.
- Working atmospheric pressure - up to 50 atm.
Cons:
- Bimetal convector - the most expensive type.
- High hydraulic resistance — more energy is required to pump the coolant.
- Small cross-sectional area.
Important! Some manufacturers resort to tricks - instead of a steel monolithic contour, they use steel only in vertical channels radiator, so the buyer will need to be especially careful.
Methods of mounting convector heaters
Batteries are distinguished not only by material and structure, but also by the type of their placement. They are:
Built-in skirting boards

Similar radiators are placed along the wall below.
Such configurations prevent dampness of walls, condensation, and evenly heat hard-to-reach parts of the room.
This heating option is suitable for rooms with extensive glazing, high ceilings and large areas.
Floor and underfloor
The category of this product is different power and compactness. They are often used in rooms with large windows and low window sills, for example, in car showrooms and exhibition halls.
Electrical

Such devices accelerate the natural circulation of air, due to which the room is heated much faster thanks to the special design.
The electric radiator has a large surface area for heat exchange. It is also equipped with a thermostat.
Air or wall mounted
The most common placement option. The place for installation is the walls with the greatest heat loss. Thus, this type of battery creates warm air damper.
Which one is better to choose for home
Several criteria are taken into account:
- Characteristic systems heating (individual or central heating).
- Material manufacturing - is selected depending on the buyer's solvency and the features of the heating system.
- Thermal power. This parameter depends on several factors:
- Square premises.

- Quantity window openings and external walls.
- Type buildings (panel, brick).
- Window (plastic, wooden).
- Square premises.
Based on these indicators, the dimensions of the radiator are determined. For batteries with sections, the following formula is applicable:
K=S x 100 /P, Where TO — the number of required sections, S — area of the premises, P — power for one section.
For panel radiators, a different formula applies:
P= V x 41, Where R — battery power, V — the volume of the room, 41 — general heat energy coefficient.
Reference! The radiator is blocked one fourth of the window length. This prevents cold air from accumulating on the glass, which means it won’t fog up.
Useful video
Watch the video to learn how to choose a bimetallic heating radiator.
In conclusion: why water is used as a coolant
Before buying a water radiator, carefully think through all the details, find out about features of the heating system and the heated area, study the operational capabilities of the convector. Water is an effective heat carrier, so the purchase of water radiators is more than justified.
Consult a specialist who will help you choose the best option.