Economical and efficient: popular types of heating layout in a private house

Living in a private house has many advantages, the main one being autonomy heating systems.
Correctly selected heating distribution makes it possible to provide fast and comfortable heating of all rooms.
In practice it is applied several proven types of wiring, differing in the scheme of the coolant circulation organization and the placement of the main pipes.
Single-pipe heating system in a private house

This one of the simplest designs, designed to heat a house. Essentially, it is a pipe coming out of the heating boiler, running along all the rooms in the house and returning back.
The operation of a single-pipe heating system is based on on the simplest physical laws.
The coolant heated in the boiler expands and becomes lighter. Displaced from below by cold and therefore heavy water, the flow tends to occupy the highest point in the heating system.
As it passes along the heating system, the water gives off its heat to the radiators, cooling down. The coolant returns to the boiler already cooled, and the cycle begins again.
Type of circulation, installation and protection
According to the installation scheme in private houses, one-pipe systems are divided into:
- vertical — water rises up several risers, from which it enters the heating radiators;
- horizontal — the coolant is supplied to the upper floor through a single riser, then distributed there to all the radiators, and only after that it reaches the lower level.
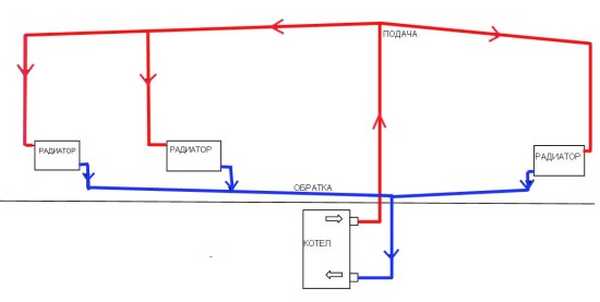
Photo 1. Diagram of a gravity-fed single-pipe heating system with vertical distribution on two wings.
According to the type of circulation, the schemes are divided into:
- forced — to pump the coolant through large systems, special circulation pumps are installed in them;
- gravity-fed — work on the principle of natural circulation of water, rising up when heated and descending down when cooled.
Attention! Natural circulation systems work successfully only in small houses up to 100–120 sq. m.
According to the type of protection against excessive expansion of the coolant, heating circuits can be two types:
- open - when the expansion tank is installed at the highest point and is fully or partially connected to the atmosphere, excess water is drained into the sewer if necessary;
- closed — where a special sealed container is used to collect excess liquid, which is mounted in any convenient place.
Pros and cons

Advantages of a one-pipe system:
- Due to the fact that the coolant passes through the rooms of the house through a single pipe, then, in comparison with other schemes, there is significant savings on materials during construction.
- The interior of the premises suffers less due to the fact that it passes through them one pipe instead of two.
- The system contains less water than a two-pipe system., due to this its inertia is reduced and the house warms up faster.
- Easy to install allows you to carry out the work yourself.
Disadvantages of a one-pipe system:
- As the water passes through the pipes, it cools down. and the further the radiator is located, the less heat it receives and the weaker it heats up. Therefore, individual temperature control in each room is impossible in such a scheme.
Reference! It is possible to obtain the possibility of regulation in a one-pipe system by using a special layout - "Leningradka", which uses bypass lines under each radiator.
- When operating without a pressure pump for high-quality operation of the system a booster manifold is required, which includes an expansion and storage tank at the highest point, i.e. in the attic. To eliminate heat loss, it is additionally insulated, which increases the cost of the system.
How to make a two-pipe system?

To avoid significant cooling of the coolant As we progressed through the house, a two-pipe wiring diagram was developed.
It involves supplying water to each radiator through one pipe, and draining and delivering it back to the boiler through another.
Each radiator is supplied with heat individually and does not depend on others.
According to the method of movement of the coolant, two-pipe schemes are divided into:
- gravity-fed — the coolant moves under the action of thermal convection;
- circulation (pressure) — a circulation pump is installed to move it.
Types of installation and wiring
According to the method of installing pipes connecting heating batteries, the schemes are divided into:
- horizontal — when all radiators located on the floor are fed from one riser, the system requires the installation of a Mayevsky valve on each heating device to bleed air;
- vertical — is characterized by connecting radiators to vertical risers, which is considered optimal for multi-storey buildings, because it allows each floor to be connected to them separately.

The advantage of the vertical design is the absence of air locks during operation.
According to the type of installation of the supply and return pipes, two-pipe systems are divided into:
- dead-end (oncoming) — the movement of the coolant through these pipes occurs in opposite directions;
- passing — water in the supply and return pipes moves in the same direction.
The layout of a two-pipe system can be two types:
- Upper — the coolant is first supplied to the upper part of the building, from where it descends into the heating batteries, while the return line is located in the lower part of the system.
- Lower — the supply pipe is located at the bottom of it, from where water flows through vertical risers to the heating devices. In this case, the return supply pipe should be located even lower.
Advantages and disadvantages

Advantages of the system:
- The coolant enters the heating batteries at the same temperature, which makes it possible not to overheat the boiler and save fuel.
- Radiators can be adjusted to individual thermal conditions, allowing you to set a comfortable temperature in each room.
- Two-pipe scheme allows you to completely exclude individual radiators from the network for their repair or replacement, which does not affect the operation of the others.
- The system is equally good functions in buildings of any number of storeys.
- In such a scheme, pressure losses are small., which makes it possible to install a small and economical circulation pump.
The only disadvantages of two-pipe systems are increased consumption of materials during construction.
Horizontal heating scheme
A special case of heating network layout is the horizontal or collector scheme. With it each radiator on the floor is connected to the riser or boiler with individual pipes supply and return. As a result, the coolant gets to the heating device along the shortest path, bypassing other consumers, and does not have time to lose its temperature.
In this case, pipes are usually placed in the floor screed.
Distribution and reception of the coolant is carried out using collector units, which are located on each floor and regulate the supply of heat to the rooms located on it.
The supply of coolant in the collector system occurs due to the pressure created by the central circulation pump, but additional low-power pumps are installed in individual branches with high resistance, for example, with underfloor heating.
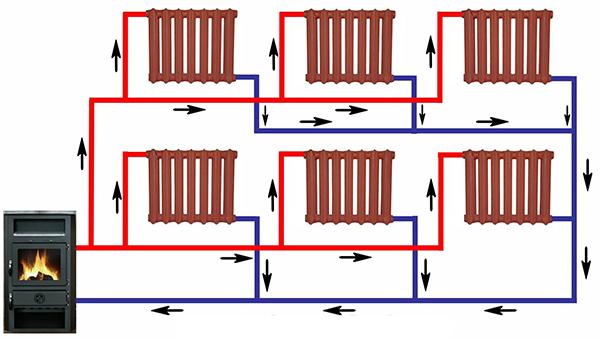
Photo 2. Collector diagram of pipe layout with a horizontal heating boiler of a two-story private house.
Advantages of horizontal wiring:
- Easy adjustment of the temperature of each radiator separately.
- Minimum number of connections, which increases the reliability of the network as a whole.
- There is no need to install air vents on radiators.
- The heating system can include devices with different hydrodynamic resistance: batteries and heated floors.
The main disadvantage of this scheme is the significant consumption of pipes.
Selection of pipes
Experience shows that the best ones for these purposes are polypropylene pipes, which:
- they absorb water hammer well;
- provide little resistance to water movement;
- do not require thermal insulation;
- cheap and durable;
- easy to install.
However, they also have disadvantages:
- reinforced polyethylene cannot be used in networks with a coolant temperature greater than 95 °C;
- PPS plastic can withstand temperatures up to 110 °C, but is expensive.

Photo 3. Polypropylene pipes in the heating system, they do not require insulation, easy to install.
Metal-plastic pipes work well at high temperatures. But they are connected using metal fittings, which greatly reduce the effective clearance of the pipes. As a result, the resistance to water movement in the system increases.
Attention! The connection points of pipes and fittings are very vulnerable to leakage, and they need to be monitored periodically.
Steel tolerate high temperatures well, but installation requires welding and a powerful pipe bender, which is not always possible when doing the work yourself. In addition, steel easily corroded, which over time leads to a decrease in the flow diameter of the system and a decrease in its efficiency.
Copper pipes do not have this drawback, but are very expensive, which has led to their rare use for creating heating systems.
Useful video
The video shows the process of installing a two-pipe manifold heating system.
What to choose
Different types of heating systems are used in the construction of a private house depending on from the architectural features of the building, the selected material and the tasks set.
A careful approach to the question of which heating layout is better in a particular situation will make it possible to make a choice that will suit the house in question. In this case, it is impossible to blindly transfer the experience of building one house to another. By correctly developing the heating system, observing all the rules and regulations during construction, you can guarantee comfortable living in your favorite home.








