Operating principle and heating scheme for a private house with natural circulation: calculation features

Natural circulation is the flow of the coolant in the heating system by gravity, without the circulation pump working.
Such movement is generated by the forces of gravity due to the property of liquid to expand when heated.
Natural gravity allows heating work without a pump and additional electricity costs, in autonomous mode. What is a gravity heating system made of and how does it work?
Content
The principle of natural circulation

When heated in a boiler water expands, becomes lighter, rises upward and makes room for the influx of cooled liquid.
In its place, cooled water enters the boiler. water from the heating circuit - the one that has passed through the radiators, given off some of the heat to the surrounding space and cooled down. It has a lower expansion coefficient, its density is higher, and its weight is heavier.
The cooled water displaces the heated water from the boiler. This creates a constant circulation of liquid in the heating system, called natural circulation of the coolant in the circuit.
The speed of water movement by gravity depends on several factors:
- the temperature difference between the boiler inlet and outlet – forms the gravitational pressure of the liquid;
- diameter of internal passages in the heating system – can reduce the flow rate;
- indirect movement of coolant in the system – angles, turns, narrowing of the internal diameter of pipes or emitters – reduce the water pressure and slow down its flow.
Advantages and disadvantages

Natural circulation of the coolant in a private house has undeniable advantages in the form of autonomy and low-cost operation. But also accompanied by disadvantages, which one has to deal with when arranging it.
Advantages of gravity flow:
- Autonomous heating operation, independent of the availability of electricity.
- Affordable price, one of the most inexpensive options for arranging a system.
- Durability – the use of cast iron radiators and large-section cast iron pipes ensures long-term heating of a two-story house for 40-50 years or more.
Flaws:
- The heating system looks bulky - large pipes along the walls, cast iron radiators.
- It is not possible to use thermostats.
- When installing a distribution manifold in the attic good thermal insulation is necessary – to prevent cooling and freezing of water.
- Quite large heat losses occur in the pipes in the attic and basement. This means increased costs for heating the house.
Features of construction

To organize the movement of liquid by gravity do the following:
- The heating boiler is placed as low as possible – on the first floor or in the basement. The distribution manifold is raised higher – to the ceiling or to the attic of the building.
Thus, the water receives the maximum allowable height of rise for a given building. Which creates the maximum possible gravitational pressure of the coolant in the pipes.
- They install devices with wide internal openings. Large diameter pipes – not less than 40 mm in cross-section. Radiators with a wide internal passage are traditional cast iron batteries. If it is necessary to install shut-off devices, ball valves are installed, which in the open position minimally narrow the internal clearance.
- Pipes are laid with a minimum number of turns, angles, without coils and without spirals.
- The supply and return lines are laid at an angle.
Attention! The principles listed above allow us to organize natural water pressure and its movement at the required speed.
Elements of a gravity flow system: what it consists of
Let's list them devices, from which a gravity heating system is assembled:
- Heating boiler – can operate on various types of fuel – gas, wood, coal, electricity.

- Radiators – direct heating devices – radiate heat into the room space.
- Main supply and return pipe.
- Distribution collector – is located above the boiler. Water heated in the boiler enters it, then moves (is distributed) into the main pipe.
- Expansion tank – for temporary storage of the coolant, which expands and increases in volume when heated. It is located at the highest point of the system and is made in an open form.
- Rotary ball valves – at the inlet and outlet of heating radiators.
- Water drain tap (also ball) – at the lowest point of the system.
Now let's take a closer look at how the maximum possible pressure is ensured.
Pipe slope
For natural circulation of the coolant, a number of measures are taken to facilitate its movement inside radiators and pipes. One of such measures is laying supply and return pipes at a slight slope. The slope size is selected - 2-3 ° per linear meter.
The specified degrees of slope do not visually violate the geometry of the pipe laying, but ensure the movement of water by gravity. They also allow draining liquid from the system if it is necessary to replace the battery or repair it.
Gravitational pressure

Gravity pressure arises as a difference in water pressure in different segments of a pipeline.
In a system with natural movement of the coolant, gravitational pressure is created heating water and raising it to the height of the attic or the second floor of the house. This ensures gravity flow and heating operation.
Magnitude of gravitational pressure determined by the height of the lift water and the temperature difference.
Attention! How stronger heating coolant in the boiler, the greater the difference in pressure will be, and the faster the water will move through the pipes.
Possible obstacles
To ensure effective natural circulation, they try to reduce the number of factors that interfere with gravitational pressure.

The scheme is being organized with a minimum number of corners and turns. Instead of bending pipes at right angles, smooth turns are made whenever possible. In order for the water not to encounter obstacles, they are removed narrowing of lumens and valves.
The internal sections of the radiators must be large enough. The consequence of wide openings is increased volume of coolant, as well as the inertia of the heating system.
Scheme of a single-pipe heating system in a private building
A single-pipe system is the simplest and most accessible way to organize natural circulation of the coolant in pipes. It works on the principle movement of water by gravity when heated in a boiler. The flow of the coolant inside the main pipe, passing successively through all the radiators of the system. The heating main begins and ends in the heating boiler.
There are two options serial connection of batteries in a single-pipe circuit:
- The highway passes directly through each radiator in the room.
- The highway passes next to the batteries, In this case, a branch line that supplies hot water goes off from it in front of each radiator. And then the cooled coolant is discharged from the radiators into the main line.
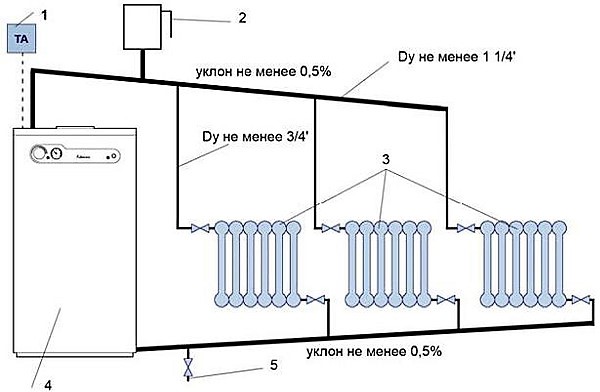
Photo 1. The essence of a one-pipe heating system is the movement of water by gravity when the boiler heats up.
In both schemes the water gradually cools down, moving from the first radiator to the last. That is why the first batteries in the circuit will be significantly hotter than the last ones. At the same time in the first diagram the difference between the temperature of the liquid in the first and last radiator will be greater than in the second. Therefore second scheme ensures more uniform heating of all rooms.
Reference! The second diagram has more angles., turns that reduce the hydrodynamic pressure and complicate the movement of the coolant.
Advantages of a single-pipe system with natural circulation:
- Easy to install.
- The most affordable price – installation is cheaper than all other types of heating.
- Technological accessibility – a one-pipe system is easier to install than a two-circuit heating system. It is also easier to organize natural circulation of the coolant in a one-pipe system.
Two-pipe heating system in a two-story house
The two-pipe heating system stands out the presence of two highways. Heated water moves from the boiler along one line - the feed. And cooled water enters the boiler along another line - the return.
The two-pipe system has an increased number of angles and turns. In it it is more difficult to organize a spontaneous flow coolant. Often – it has to be built into the circulation pump.
The main advantage of a two-pipe system is uniform heating of all rooms. The disadvantage is the reduction of gravitational pressure and the difficulty of natural circulation of liquid in the pipes.

Photo 2. A two-pipe heating system has two main lines and a greater number of angles and turns.
For direct gravity flow in a two-pipe system high temperature required heating of water. Therefore, depending on its size, gravity flow can be more or less effective. For the movement of the coolant into the main they cut in a pump in a parallel circuit. So that it does not create an obstacle and allows for natural flow.
Useful video
The video shows one of the heating systems based on gravity flow of water in a two-story house.
One-pipe or two-pipe system: which is better?
To organize natural circulation of the coolant The one-pipe system is the best choice connections. It creates minimal resistance to water movement, slightly reduces pressure. Its arrangement is simpler than in a two-pipe system.
Double pipe The system can also be with natural circulation. However, its installation will require professional knowledge, calculations and experience.









Comments