These indicators should always be normal! Pressure in the heating system in a private house

Owners of private homes have to personally monitor the operation of the heating in their homes. The most important indicator that needs to be monitored – this is the pressure inside the heating system.
The performance and service life of the entire heating network of the house depends on it.
How pressure is formed in the heating system of a private house

There are three units of measurement pressure:
- Atmosphere
- Bar
- Megapascal
Until water or another energy carrier is added to the system, the pressure in it corresponds to normal atmospheric pressure. And since 1 Bar contains 0.9869 atmospheres (that is, almost an entire atmosphere), it is believed that pressure in an unfilled network = 1 Bar.
As soon as the coolant enters the system, this indicator changes.
The total pressure inside the heating network, which is measured by sensors (pressure gauges), consists of the sum of 2 types pressure:
- Hydrostatic. Creates water in pipes and exists even when the boiler is not working. Static is equal to the pressure of the liquid column in the heating network and is related to the height of the heating circuit. The height of the circuit = the difference between its highest point and the lowest. In an open system, the expansion tank is at the highest point. The height of the circuit is measured from the water level in it. It is believed that a column of water 10 m high gives 1 atmosphere And equals 1 bar, or 0.1 megapascal.
- Dynamic. In a closed network, it is created by: a pump (which makes the water circulate) and convection (the expansion of the water volume when it is heated and its contraction when it cools). The indicators of this type of pressure change at the points where pipes with different diameters join, at places with shut-off valves, etc.
Total pressure affects:
- The rate of water flow and the rate of heat exchange between sections of the system.
- Heat loss level.
- Network efficiency. The pressure increases - the efficiency increases, and the circuit resistance decreases.

From pressure parameters the efficiency of the circuit in the building depends.
Its stability with an optimal indicator in the system reduces heat loss and guarantees the delivery of energy resources to remote corners of the house with practically the same temperature that it received when heated in the boiler.
Optimal indicators
There are generally accepted average statistical norms:
- For a small private house or apartment with individual heating, pressure within the range is sufficient from 0.7 to 1.5 atmospheres.
- For private households in 2-3 floors — from 1.5 to 2 atmospheres.
- For the building in 4 floors and above are recommended from 2.5 to 4 atmospheres with the installation of additional pressure gauges on floors for monitoring.
Attention! To carry out the calculations it is important to understand, which of the two types of systems is installed.
Closed and open heating systems: what is the difference
Open - a heating system in which an expansion tank containing excess liquid is exposed to the atmosphere.
Closed — a sealed heating system. It contains a closed expansion vessel of a special shape with a membrane inside that divides it into 2 partsOne of them is filled with air, and the second is connected to the circuit.
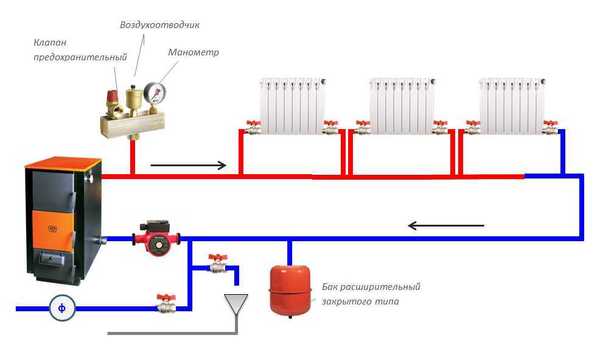
Photo 1. Diagram of a closed heating system with a membrane expansion tank and a circulation pump.
Expansion vessel absorbs excess water when its volume increases during heating. When the water cools and decreases in volume, the vessel compensates for the deficiency in the system, preventing its rupture when the energy carrier is heated.
In an open system, an expansion tank must be installed. at the highest part of the contour and connect, on one side, to the riser pipe, and on the other - to the drain pipe. The drain pipe protects the expansion tank from overflowing.
In a closed system, the expansion vessel can be installed in any part of the circuit. When heated, water enters the vessel, and the air in its second half is compressed. As the water cools, the pressure decreases, and the water, under the pressure of compressed air or another gas, returns back to the network.
In an open system
So that the excess pressure on the open system is only 1 atmosphere, a tank needs to be installed at a height of 10 meters from the lowest point of the contour.

And so that the boiler that can withstand the power is destroyed 3 atmospheres (the power of an average boiler), you need to install an open tank at a height more than 30 meters.
Therefore, an open system more often used in single-story houses.
And the pressure in it rarely exceeds normal hydrostatic pressure, even when the water is heated.
That's why there are additional ones safety devices, except for the drain pipe described, are not needed.
Important! For normal operation open system the boiler is being installed at the lowest point, and the expansion tank is at the very topThe diameter of the pipe at the inlet to the boiler should be narrower, and at the outlet - wider.
In closed
Since the pressure is much higher and changes when heated, it must be equipped with a safety valve, which is usually for a 2-storey building is put on the indicator 2.5 atmospheres. In small houses, the pressure can remain within the range 1.5-2 atmospheres. If the number of floors is - from 3 and up, borderline indicators up to 4-5 atmospheres, but then it requires the installation of an appropriate boiler, additional pumps and pressure gauges.
The presence of a pump provides advantages:
- The length of the pipeline can be as long as desired.
- Connection of any number of radiators.
- Both serial and parallel radiator connection schemes are used.
- The system operates at minimum temperatures, which is economical in the off-season.
- The boiler operates in a gentle mode, since forced circulation quickly moves water through the pipes, and it does not have time to cool down, reaching the extreme points.

Photo 2. Measuring pressure in a closed-type heating system using a pressure gauge. The device is installed next to the pump.
Pressure drop: main causes
If the pressure “jumps” even after several weeks from the start of the heating season, it is worth taking a closer look at possible problem areas. The most common causes of fluctuations are:
- Leaks. Most often occur in places of threaded connections due to a small amount of sealant. In polypropylene pipelines - a violation of welding technology.
Attention! Polypropylene pipes must be welded using a coupling to avoid leaks.
- Release of air from the coolant. When the system is launched for a regular heating season, it undergoes adaptation. For some time, the pressure will inevitably drop due to air dissolved in the water. It is recommended to remove it by feeding the system, increasing the pressure to the standard. When all the air is out, the differences will disappear.
- New aluminum radiators. When in contact with water, oxidation occurs: water breaks down into oxygen and hydrogen. Oxygen forms an oxide film on the aluminum, and hydrogen evaporates through the air vent. This reaction will only end when the entire area of the radiators is oxidized. Then the missing water is added to the system.

Photo 3. Aluminum heating radiators. When installing them, the pressure in the heating system may increase.
Chronic pressure drops can also occur for other reasons. It is best to have them diagnosed and checked by a specialist engineer. serviceability of pressure gauges, air vents, fuses.
Important! In case of pressure surges or boiling, safety valves The valves should be connected to the sewerage system.
What to do when the numbers drop
Losses are created due to malfunctions:
- In the cauldron. Contamination, wear of parts, or microcracks. A leak in the heat exchanger requires soldering or replacement.
- In the outline. The range of causes is also wide: visible and hidden leaks are corrected by sealing.
- In the expansion tank. Cracks in the membrane and water entering the air compartment are corrected by replacing the membrane or the entire tank.
- Clogging with salt deposits. They fix it by cleaning the system with special compounds (Antinakipin, for example).
If the pipeline is hidden and the cause of the damage cannot be immediately detected, a pressure testing procedure is required. Water is drained from the system and air is pumped in with a compressor. It is best to have it done by specialists.

Why the pressure increases:
- Water circulation has stoppedIt is necessary to find out the reason.
- Somewhere in the outline the valve is closed.
- Cork from air or debris/scale in the system.
- The tap is not closed properly and new water is constantly entering the system.
- Incorrect ratio of pipe diameters at the outlet and inlet of the heat exchanger.
- The pump is too powerful. If it breaks down, the system is at risk of water hammer.
- The volume is calculated incorrectly expansion tank.
Another common reason: the water boiled in the boilerIn this case, immediately reduce the temperature.
In any case, it is better to entrust the search for and elimination of the causes to a qualified engineer.
Useful video
Watch a video that talks about pressure standards for a small home heating system.
Control mechanisms
To prevent emergency situations in closed systems use relief and bypass valves.
Discharge. It is installed with an outlet into the sewer for emergency discharge of excess energy from the system, protecting it from destruction.
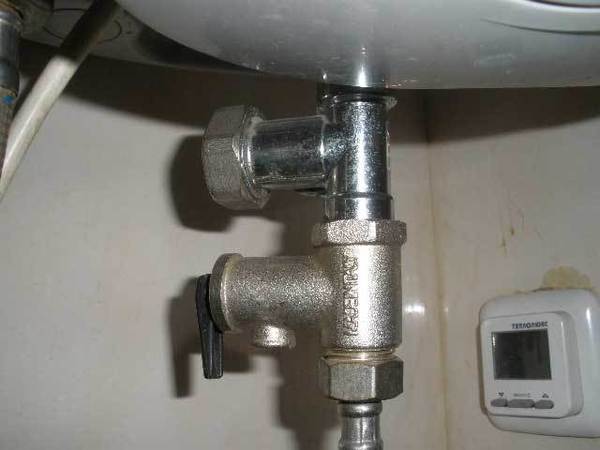

Photo 4. Drain valve for the heating system. Used to drain excess coolant.
Bypass. Installed with an outlet to an alternative circuit. Regulates the pressure drop, sending excess water into it to prevent an increase in the following sections of the main circuit.
Modern manufacturers of heating fittings produce "smart" fuses, equipped with temperature sensors that respond not to an increase in pressure, but to the temperature readings of the coolant.
Reference. It is not uncommon for pressure reducing valves to stick. Make sure that their design includes rod for manual spring retraction.
Do not forget that any problem in the heating system of the house is fraught not only with loss of comfort and expenses. Emergencies in the heating network threaten the safety of residents and the buildingTherefore, carefulness and competence are required in heating control.








