Warm all year round like at a resort with antifreeze for the heating system of a country house!

Heating systems, the operation of which is ensured by due to the circulation of liquid in the heating circuit.
In such complexes, a specially prepared coolant is used as a heat carrier. water or special antifreeze compounds.
Antifreezes are a class of technical liquids based on water-glycol solutions combined with special additives. The main argument in favor of this coolant is in its low freezing point.
Features of antifreezes for heating systems of a country house

Thanks to the composition when the temperature drops below 0 °C the substance does not freeze, but passes into a gel-like state.
When the temperature rises, the liquid returns to its original form, its characteristics remain unchanged.
The risk of heating pipes bursting during the cold season is practically non-existent.
Thus, antifreeze is most preferable. for buildings used irregularly, primarily summer cottages and country houses.
Reference. In addition to ready-made compositions, concentrates are also available for sale. requiring dilution with distilled water before pumping into the heating circuit.
Ethylene glycol
This subclass of antifreezes is characterized by the lowest freezing temperature, reaching down to -65 °C (for antifreezes with a high concentration of ethylene glycol). At the same time, such liquids are distinguished by a higher hazard class - liquid ethylene glycol and its vapors are toxic and harmful to human health.
Attention! The use of ethylene glycol substances is prohibited. in dual-circuit heating systems due to the potential threat of toxic coolant leakage into the hot water supply circuit.
The use of such a substance in single-circuit systems is unacceptable. open type. It is used in the production of liquids. red dye, which allows for timely detection and elimination of possible leaks.
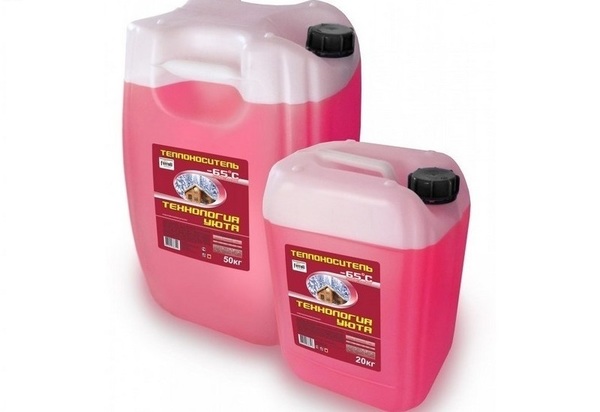

Photo 1. Two packages of ethylene glycol antifreeze 50 kg and 20 kg. The liquid withstands temperatures down to - 65 °C, colored red.
Propylene glycol
Unlike ethylene glycol analogs, propylene glycol do not pose a threat to human health, which allows the liquids to be used safely in dual-circuit heating systems. The freezing temperature varies in the range from -30 °C to -35 °C.
The high concentration of chemically active substances contained in propylene glycol liquids often has a negative effect on the condition of various heating elements, primarily seals, as well as the boiler and pipes. Non-freezing liquids based on propylene glycol painted green.
Triethylene glycol
Such liquids are used less frequently than ethylene glycol and propylene glycol analogues and are considered highly specialized. The main feature of heat carriers based on triethylene glycol is the possibility of their use in heat supply systems with a high operating temperature, reaching a value of 180 °C.
Important! The choice in favor of one or another type of antifreeze is made at the design stage of heat supply, since the efficiency and safety of the entire heating system depend on the physical and chemical characteristics of the coolant.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the undeniable advantages of antifreezes are:

- Resistance to low temperatures. Depending on the composition, different modifications of household antifreezes for heating freeze at a temperature from -30 °C to -65 °C.
- Chemical properties make it possible not to drain the coolant when stopping or preserving the building’s heating system.
- Wide range of applicationsThe average operating temperature value is 75 °CTherefore, liquids are used in most modern boiler models without the risk of equipment failure.
The main disadvantages of antifreeze liquids:
- Increased viscosity. Systems using antifreeze require a high-power circulation pump, as well as increased (compared to water systems) pipe diameters and radiator volumes. In addition, due to the thermal expansion of the coolant when heated, a sealed and capacious tank is required.
- Toxicity of ethylene glycol antifreezes. Leakage of ethylene glycol-based coolant may cause harm to human health.
- Chemical activityThe use of antifreeze as a heat carrier requires the presence of connecting elements made of Teflon or paronite in the heating system.
Correct application
Basic requirements for the efficient and safe use of non-freezing coolants:
- Regardless of the composition, all non-freezing coolants are categorically It is prohibited to use in open heating systems, as well as in complexes equipped with wall-mounted heating boilers.
- Depending on the composition, the effective service life of the antifreeze varies within the range from 4 to 8 years, the average value is 5 yearsAt the same time, manufacturers of heating equipment recommend completely changing the coolant more often than the stated period.

- When replacing, you should flush the system (pipes, as well as the boiler, circulation pump and expansion tank). Pumping in new fluid is only permitted if a special pump is used.
- When choosing a substance, it is important taking into account the compliance of the liquid's thermal stability index with the temperature regime of the heating systemOverheating is fraught with disruption of the structure of the coolant and, as a consequence, a decrease in heating efficiency.
- Using Antifreeze in Heating with Galvanized Pipes fraught with the formation of insoluble deposits on the inner surfaces of pipes.
- It is not recommended to mix antifreezes of different brands and manufacturers.. However, this is acceptable provided that the liquids are checked for compatibility. Otherwise, the quality of the coolant may decrease and corrosion processes may begin inside the pipeline.
- Suitable for diluting concentrate distilled water. When using running water, sediment may form, which significantly reduces the quality of the finished mixture.
Important! Most of the additives included in any antifreeze have a destructive effect on polymers, which are often used in the manufacture of heating system components. Therefore, when choosing an antifreeze It is important to follow the recommendations of the heating equipment manufacturers.
Optimal choice
Choice ethylene glycol antifreeze primarily justified in the event that the heated building is located in the area with extremely low air temperature in winter. In addition, ethylene glycol-based liquids are the lowest cost, which often becomes a decisive factor when buying.
Choice propylene glycol antifreeze optimal for use in standard dual-circuit heating systems. It is important to take into account the average air temperature in winter, since this type of non-freezing liquids begins to decompose when the temperature drops below -35 °C.
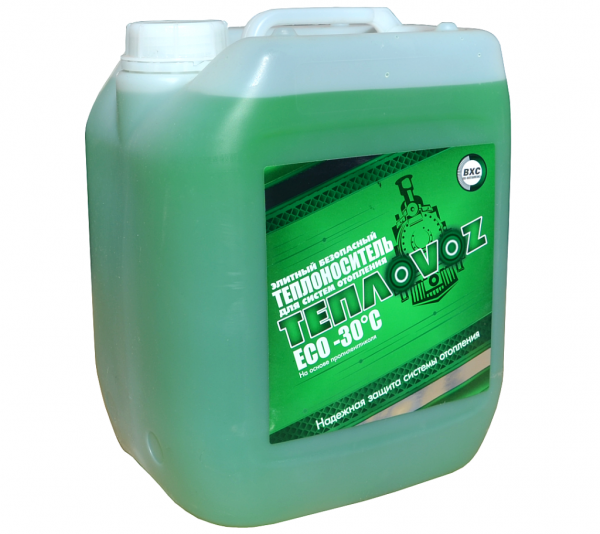

Photo 2. Packaging of propylene glycol antifreeze that can withstand temperatures down to -30 °C. The substance is colored green.
Choice triethylene glycol antifreeze is necessary if the existing heating system has a significant operating temperature, since triethylene glycol heat carriers are characterized by a high boiling point, as well as general temperature stability.
Useful video
Watch the video to learn when to use antifreeze in heating systems.
What should you consider when choosing?
Efficiency of using any type of antifreeze depends on many factors, among which are:

- compound liquids, the purpose of the incoming additives, and also Manufacturer's recommendations in terms of use;
- cost, terms of effective operation and shelf life, packaging material — experts do not recommend purchasing antifreeze in galvanized containers;
- characteristics heating system designs;
- climatic features the area in which the heated building is located.
A comprehensive consideration of the above factors will allow you to select the best-suited antifreeze liquid. for efficient and safe operation of the heating system any private house.








Comments