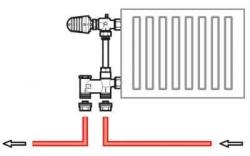
The best choice for connecting radiators in a two-pipe heating system

Double pipe heating system in contrast to single pipe has a parallel connection, which contributes to a more efficient and uniform heating all radiators.
There are several connection schemes for a two-pipe heating system.
Content
Types of radiator connection for a two-pipe heating system
There are the following types of connection.
With the accompanying movement of heat

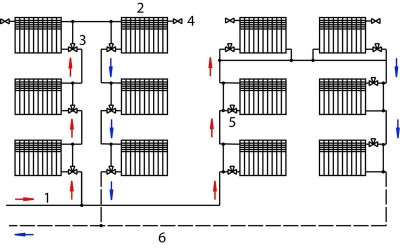
It also has a name "Tichelman loop".
This scheme provides for two-pipe circuit heating, where the circulation of the coolant in the return line is co-directed with its movement in the supply pipeline.
The supply pipe, to which all radiators are connected, runs along the perimeter of the room or building. The end of this pipeline is considered to be the outermost battery in the branch.
Plus: suitable for heating rooms quite well large area, and the lengths of the supply and return pipelines to each radiator are equal.
Minus: complex installation and noticeable consumption of finances and materials.
Dead-end scheme
It is considered the most common type of connection. Its main difference from the above scheme is that the direction of circulation of the coolant through the pipelines feed and return are opposite.
The heated liquid moves along the feed pipe from the boiler to the radiator. After passing through the radiator and transferring heat to it, the liquid returns to the boiler through the return line.
Most often, for heating a private home, such a scheme includes circulation pump. This allows the use of small diameter pipes and the laying of a fairly long pipeline.
A dead-end scheme happens 2 types: horizontal and vertical.
At first In this variant, the supply and return pipelines are located horizontally, and in second case - vertically. The last dead-end scheme is relevant for heating a two-story house.
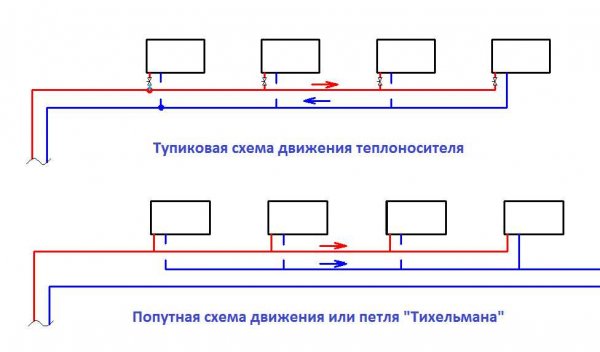
Photo 1. Schematic illustration of dead-end connection options for a two-pipe heating system and the Tikhelman loop.
Gravity flow
This scheme provides a design where the hot coolant is circulated two separate circuits. By alone the heated liquid moves, and to the second - already chilled.
Necessary tools
For installation two-pipe systems must have:
- electrical drills with a set of drills;
- roulettes;
- plumb line and building level;
- pencil;
- expansion tank;
- screwdriver;

- radiators;
- pipes from a certain material;
- special tool for installation of the pipeline depending on its type;
- gas key;
- drain tap;
- adjustable wrench;
- check valve;
- air vents (automatic - for the general line and manual - for each radiator).
Attention! Pipeline diameter for two-pipe system is determined in accordance with the length of the supply pipe and the heat load parameter. The return line is formed with the same cross-section.
Connection methods
The following connection schemes exist.
Diagonal
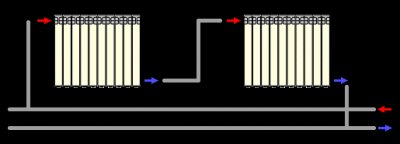
The point is that the coolant supply is located On the one side, and its return is diagonally below, on the other.
The use of such a scheme is relevant in the case where a sectional battery with the number of sections is used exceeding 12 or the length of the panel radiator more than 120 cm.
Vertical
It is actively used for multi-storey buildings. To implement it, you will need a large number of pipes. The main advantage of this scheme is that it allows you to automatically release excess air masses through an expansion tank or valve.
Reference! If such a container (tank) is mounted in the attic, then it is necessary to take care of additional insulation of this space.
The result of forming a vertical scheme will be a uniform temperature regime of all radiators.
Bottom
It is used to mask the pipelines. Both the supply pipe and the return pipe are located at the bottom of the radiator. When using this scheme, when installing the radiator, the supply pipe is connected from one side, and the return pipe is connected from the other. from the other side of the lower branch pipe.
The steel radiator has all the pipes placed at the bottom end.
Top
Not suitable for conventional radiators, since their efficiency will be negligible due to heating only the upper part of the radiator.
In special batteries produced for this type of connection, there is a plug, which redirects the coolant downwards, after which the liquid moves according to the principle of a diagonal pattern.
Radiators of this type have a high heating coefficient over the entire area.
Installation process
This procedure is underway in several stages.
Wiping joints and pipes
The joints and pipes are treated with sandpaper or a kitchen metal sponge. The choice of cleaning agent depends on degrees of corrosion formationAfter cleaning, the surface is treated with a soap solution.
For this procedure, it is permissible to use acid, alkali or special agents.
Important! Trying to mask corrosion with regular metal paint will only lead to aggravation of the process and continuation of pipe rotting.
Securing the radiator
Correct fixing of brackets should be done in such a way that there is no slopes and distortions of the radiator. For such purposes it is essential to use a building level and a plumb line.

It is allowed to create a vent on the air vent side 10mm rise, but not in the opposite direction.
For sectional models of small length, fixation with hooks is provided between the two outer sections and in the middle at the bottom.
The process of fixing the brackets is as follows: dowels are mounted into the drilled holes.
The holders are fixed with self-tapping screws. diameter 0.6 cm and length 3.5 cm.
Reference! For panel radiators fasteners are included with them.
Screwing in adapters
It is made in such a way that the adapters are adjusted to the direction of the pipes to which the battery is subsequently connected. The essence of the process is as follows: if the pipeline runs along the floor, then the adapter is fixed to it with the thread facing down. If the pipe goes deeper into the room, then the adapter also changes its direction.
Fastening adapters
These elements are formed from polypropyleneThey are fixed to the main pipe using a tubular soldering iron.
Installing the tap and plug

Mayevsky crane necessary to remove excess air from the system.
It is simply screwed into the battery plug from the supply side and secured with flax and unipack.
This part must have a thread that matches the specific radiator.
It is installed from below plug with hole, which you can make yourself with a drill.
Useful video
Check out the video that explains the different connection schemes for a two-pipe heating system.
Recommendations for correct installation
Connecting a radiator with a two-pipe system is easy if take into account all the nuances of this process and choose the right scheme wisely. Carry out work better in spring or summer, so that there are no difficulties with disconnecting the riser. Before installing or connecting the radiator yourself, it is better to consult a specialist.