4 installation options: when you can’t do without a heating system with forced circulation?
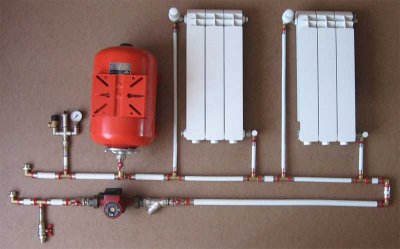
"Classic" heating systems use gravity and changes in water density to achieve circulation in pipes. In this case, the key parameter of the pipeline system is hydraulic resistance.
The pressure created by the hot water may not be enough to create a stable circulation. This will lead to the formation of steam in the heat source and its failure. The solution to this problem was a pump, added to the circuit before the boiler.
Content
Circulation pump for heating
Circulation pump allows the coolant to be pushed through the heat source, usually it is a hot water boiler that can run on different types of fuel. The liquid passes through the supply pipes, radiators and outlet pipes, giving off heat to the rooms. After that, it goes back to the pump for repeating the cycle.
Equipment composition in a forced circulation system
The heating circuit contains the following are the main elements:

- Boiler or another heat source, raises the temperature of the coolant to heat the room, usually located in the boiler room at the basement or first floor level.
Depending on the design, it may contain electrical elements or be completely autonomous (solid fuel boilers).
- Coolant — the working fluid for this circuit, it transfers heat from the source to consumers. The cheapest and most accessible is the usual water, are used less frequently antifreezes, which allow you not to drain the heating system even in very cold weather.
- Pipelines And reinforcement provide circulation to the radiators, the hydraulic resistance and service life of the entire system depend on them. The greater the resistance of these elements to corrosion, the longer the heating will last.
- Radiators, the heat exchange and temperature in the room depend on their configuration.
- Circulation pump, provides stable circulation, can be either low-power, with little system resistance, or large.
Peculiarity! The sealing elements of the circulation pump are not adapted to work at high temperatures. Therefore, it is always installed in front of the boiler entranceThis is how the most gentle conditions are created.
Expansion tank — an important component of this heating system. It provides compensation thermal expansion of the coolant. If it is absent, the maximum permissible pressure may be exceeded and pipes or batteries may burst. It protects against water hammer when starting the system. There are several types of construction of this element.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the system:
- Opportunity quick warm up due to the early start of the coolant movement.
- Using pipes minimum size, where you can save a lot of money.
- Equal distribution of heat on radiators, in all rooms the temperature in the batteries will be approximately the same.
- For complex circuits there is a possibility temperature regulation in every room.
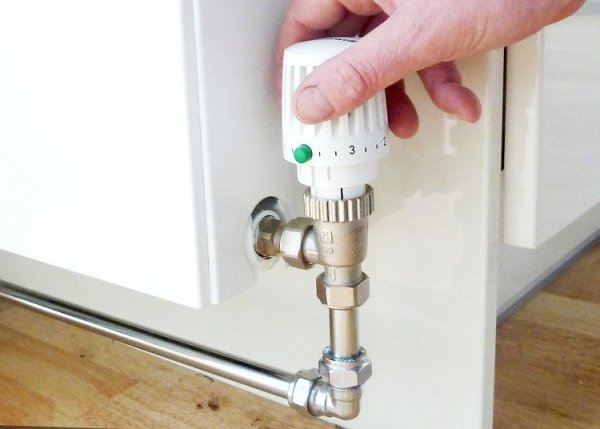

Photo 1. A heating system with forced circulation allows you to install similar temperature regulators for radiators.
It should be understood that the use of an additional pump becomes necessary when a certain length of pipes or with a larger quantity radiators.
At the same time, the appearance of a pump in the circuit leads to the following problems:
- Pressure drops when switching on pumps can lead to the appearance of leaks In systems, an expansion tank is installed to neutralize them.
- The heating scheme becomes energy dependent. Even a low-power pump requires electric current to operate, and in the event of problems in the central network, only the installation of a pump will help against the cold. diesel generator.
Differences between closed and open systems
Depending on the application expansion tank type forced circulation systems are divided into closed and openThis device allows the water to expand slightly when heated, thereby protecting pipes and equipment from excess pressure.
Open the expansion tank has contact with air. Because of this, water gradually evaporates from the heating pipes, which is why there is a need to periodically top up a certain amount of coolant into the system. In addition, oxygen dissolves in water, which increases the rate of corrosion and clogging of metal parts, which is especially critical for boilers. An undoubted advantage of such a tank is its cheapness.
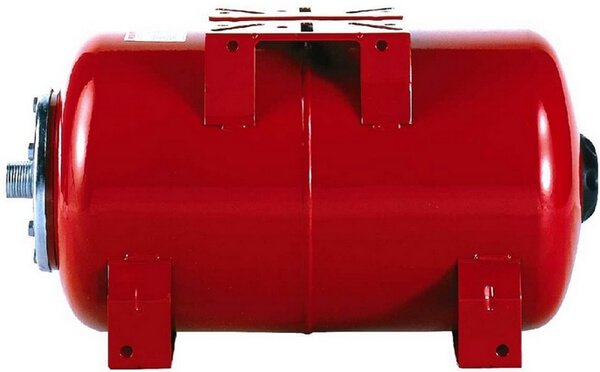
Photo 2. Example of a vertical sealed expansion tank of a closed type with a diaphragm membrane.
Closed The expansion tank forms a sealed system. It does not have the disadvantages of an open circuit, however, and the cost of such equipment significantly higherThere are two main types of sealed tanks on the market: with diaphragmatic membrane and membrane balloon type. The more complex the design, the more reliable and expensive this device is. In any case, it will cost more than an open tank, the advantages will be the absence of losses and contact with the atmosphere.
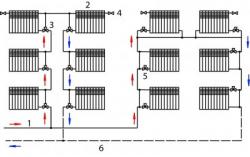
Wiring options for a circuit with a circulation pump
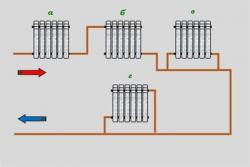
Exists two ways of connection radiators between each other: consistent And parallel connection.
At sequential when connecting batteries to each other, only a total of one pipe, that is why this scheme was called one-pipe. parallel when connecting one pipe is serving, and the other collecting.
Series connection

Single pipe the scheme saves materials, installation works take little time. Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide the same temperature in each radiator, since the coolant moves consistently.
With a large number of batteries, this version of the system becomes inoperative. The first consumers receive too high a temperature, and the coolant enters the last batteries with underheating.
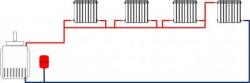
Two-pipe system
The costs, compared to a single-pipe layout, are significantly higher, but due to the uniform distribution across the radiators, the temperature in the rooms is the same. Hydraulic resistance decreases, which has an excellent effect on the operating mode of the circulation pump.
Important! When using horizontal two-pipe wiring, air is trapped in the batteries. circulatory disorders due to an airlock. To eliminate it, they provide Mayevsky cranes.
Horizontal and vertical wiring
Vertical the layout is classic one-pipe scheme, in which hot water is supplied to the top of an apartment building, passing from there to all the radiators. This scheme saves materials. Therefore, it is still used by unscrupulous builders.

Double pipe vertical the layout is used in modern houses, when the hot riser (together with the collecting one) is extended through all floors and distributes the coolant to each radiator separately, therefore each apartment has approximately the same temperature.
This scheme allows reduce heat loss, but is characterized by high costs for pipes.
When heating both multi-storey and private houses, it is used horizontal two-pipe layout, sometimes called floor by floor. Heating devices on the floor are not connected in series and in parallel, which may cause air locks. For this reason, it is necessary to install in such a system shut-off valves and air valves for each battery without exception.
Useful video
Check out the video that explains the forced circulation heating system.
General recommendations
For installation work on the heating system there are SP.13330.2012. They are used to calculate number of radiators, coolant flow rate. The first stage is the most important. Correct calculation and drawing up of the scheme will save you from overspending of materials and inconsistencies during installation. For such work it is better to choose a person with experience in construction.






Comments
And I would advise, since we are talking about circulation pumps, to make a system with a closed circular circuit, where the coolant moves around the system as if in a circle. For example, we have a two-pipe system in our house, the pump moves the water, but at the end point, in the room from which the water (read - coolant) returns, it is quite fresh, because on the way to this point the water gave up some of its heat to other radiators. If the system were not just two-pipe, but also circular, then the cooled water would get into the boiler again faster and would heat up faster, as a result - the temperature would be more or less the same everywhere.