What are the advantages of an open heating system? Installation diagram and operating principle
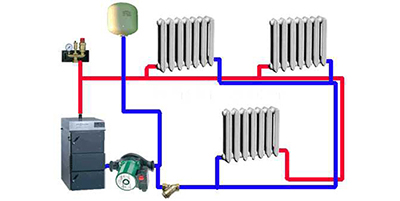
The main difference open or gravity systems (OS) from closed ones is that in OS the coolant communicates with the surrounding air in an open expansion tank.
The coolant is in the system under atmospheric pressure, there is no excess pressure.
Content
Description of an open heating system: what is it
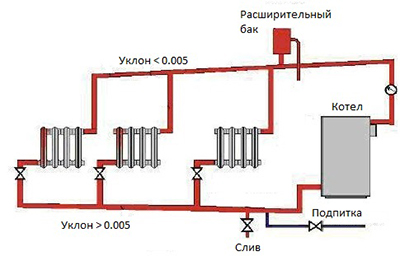
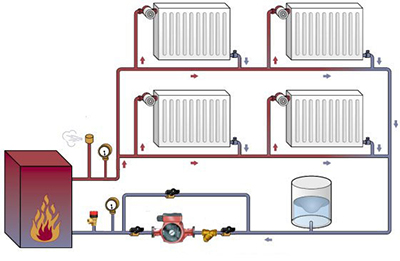
The heating circuit of the OS consists of a boiler located at the lowest point of the building - in a basement or pit.
It comes off the boiler vertical riser for supplying coolant to the highest point of the building (attic or loft), where the expansion tank (ET) is located.
From the RB, horizontal pipes with a slight slope extend along the top of the building to vertical risers, along which the coolant is delivered to the radiators.
From the heating devices, a return line runs along the bottom of the room, also with a slight slope towards the boiler.
Operating principle
Schematically, the heating circuit of the heating system can be represented as a long vertical ring. One side of the ring – with hot water (supply riser from the boiler to the RB), the other side - with cold (riser with return from radiators). The density of the hot coolant is less than the cold one - the water expands when heated.

Consequently, the weight of water and the pressure of the water column in the cold part of the circuit will be higher than the weight of water and the pressure of the column in the hot branch.
According to the law of communicating vessels, the liquid will tend to balance the pressures – to the transition from a cold branch to a hot one.
Since the circuit is a closed ring, circulation or gravity flow of the coolant occurs.
In OS, the physical principle of circulation follows three design features systems:
- The supply riser is insulated as much as possible along its entire height.
- The boiler is located as low as possible below the last radiator.
- The circuit has a capacity for the release of excess volume of heated coolant. – expansion tank (to ensure reduced density and low pressure of the water column in the heated branch).
With natural circulation
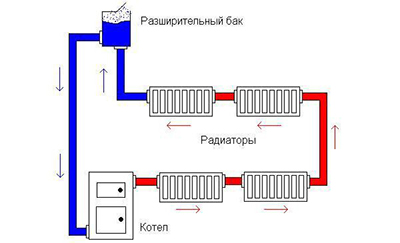
The coolant moves during natural circulation under the action of the circulation pressure Pн (in mm of water column):
Pн=H x (phol - pgor).
- N – height difference between the boiler and the last radiator, m;
- phol — the density of water in the cold return riser, kg/m³;
- pgor — density of water in the hot supply riser, kg/m³.
During circulation along the circuit, the coolant spends part of the pressure to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipes, radiators, and shut-off valves. Therefore, when designing the OS, they choose materials with low hydraulic resistanceso that their total does not exceed the design pressure Pн(the system was not locked).
Important! The coolant of the heating system contains air, which is mixed in the expansion tank. To remove air, the pipes are made with a slope not less than 3–5 mm per running meter of pipe.
With circulation from a pump
To increase the natural pressure, a circulation pump is included in the water supply circuit.
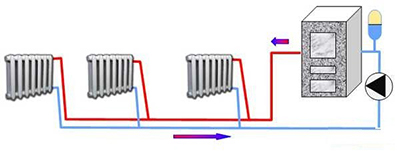
Exists two pump entry points to existing OS:
- On the return pipe before the boiler. In this case, the expansion tank is reconnected to the return pipe in front of the pump (in the suction zone).
- On the upper feed pipe immediately after the expansion tank connection point.
Reference! The pump connection point is equipped bypass with petal check valve.
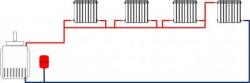
Single pipe
A one-pipe system with natural circulation is made only with upper coolant distribution.
All radiators in the riser of a single-pipe heating system are connected in series – The output of one battery is connected to the input of another.
Pros:
- Small number of pipes.
- Easy to install.
Cons:
- System imbalance - the upper batteries are hot, the lower ones are cold. To equalize the temperature regime, the lower radiators are installed with a large number of sections.
- Inability to carry out thermoregulation due to the high resistance of the control valves.
Double pipe
The two-pipe system is characterized by the fact that each radiator is connected two pipes: one delivers hot coolant from the supply riser, the other removes cooled water to the return riser.

Advantages of a two-pipe system:
- All batteries are balanced by temperature.
- The radiator can be replaced without turning off the boiler.
Cons:
- Increased pipe consumption.
- Labor-intensive installation.
With top feed
Hot water is supplied from the boiler up the vertical riser to the attic or under the roof, from where it is distributed along the horizontal pipes to the vertical radiator branches (both single-pipe and double-pipe). After passing through the radiators, the cooled coolant is collected in the return line and enters the boiler.
With bottom feed
With bottom feed, the heated coolant enters into the radiator branches from bottom to top. The supply and return pipes are laid next to each other at floor level.
Attention! This system does not clutter the room with an abundance of pipes, but requires installation Mayevsky cranes for each radiator to release air.
Advantages:
- Easy to install.
- Durability.
- No electricity is required for circulation.
- The system is self-regulating – the speed of the coolant depends on the temperature in the rooms.
Flaws:
- Not suitable for all rooms – an attic is needed where the expansion tank is installed and horizontal pipes are laid.
- Requires the boiler to be positioned as low as possible - in a pit or basement.
- Slow heating at start up.
- Unpresentable appearance (large diameter iron pipes, cast iron radiators).
- Small radius of action – no more than 30 meters from the boiler.
- Inability to use antifreeze due to the toxicity of the evaporated vapors.
Installation of an open heating system: photo
Before installation, it is necessary to perform calculation of radiators, hydraulic calculation of circulation pressure, develop an installation diagram, and make a list of materials and components.

Photo 1. Steel-colored floor-standing gas heating boiler installed indoors with all equipment.
The OS consists of the following elements:
- Heating boiler – gas or solid fuel.
- Pipes.
- Expansion tank.
- Radiators.
- Fittings (taps, boiler piping, valves).
- Circulation pump (optional).

Photo 2. A circulation pump built into the pipes increases the efficiency of the entire heating system.
Installation features:
- Pipe slope horizontal feed and return beds - not less than 3-5 mm per linear meter.
- They use pipes with a diameter of at least 30 mm.
- The volume of the expansion tank is 15% of the total volume coolant.
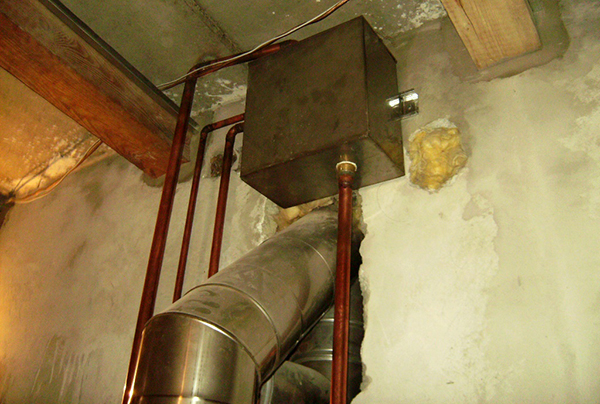

Photo 3. Expansion tank made of metal, mounted under the ceiling of the attic of a private house.
Scheme
On the diagram, made to a convenient scale on a sheet of graph paper, the following must be specified:
- Dimensions of the rooms where the sewage pipes are located.
- Pipe layout diagram.
- Locations of radiators, boiler (ensuring the required height difference between the boiler and radiators), expansion tank, pipe fittings.
- Dimensions of pipe blanks.
- Elements for fastening pipes to building elements.
Installation stages:
- Prepare a set of necessary tools (depending on the selected pipe material).
- Perform installation of the boiler and boiler equipment according to the boiler operating manual.
- Make an expansion tank and install it in the attic.
- Complete installation of a vertical riser.
- Install radiators in the rooms.
- Perform final installation of pipes, connecting all elements of the system.
- Perform thermal insulation of the expansion tank.
- Fill the system.
- Check the system for leaks.
- Perform a test run.
Expansion tank for OS

Any open space can be used as an expansion tank (ET). homemade metal container or a flask with the required volume not less than 15% from the total volume of coolant in the system.
The RB performs the following functions:
- Serves as a buffer tank for storing excess coolant, which arise due to the expansion of the liquid when heated in the boiler.
- Provides atmospheric pressure in the system.
- It is an element through which air bubbles leave the system. The rise of air bubbles is ensured by the slope of the pipes.
Installation recommendations:
- Installation of a vertical riser from a boiler withIt should be made from a steel pipe with a diameter of 40–50 mm.
- The size of the remaining pipes - the bigger the better (less hydraulic resistance).
- It is best to use cast iron radiators.
- Try minimize the number of pipe turns and shut-off and control valves.
- Apply only Full bore ball valves.
Features of installation in a private house
Before starting work, you should make sure that the structure of the house meets requirements of a gravity system:
- Small area (no more than 150 m²).
- Availability of an attic.
- Possibility of low boiler installation in relation to the last radiator.
What to do if the water in the tank boils quickly?

If you find that the water boils quickly, you need to complete the entire procedure as quickly as possible. set of actions for emergency shutdown of the boiler (listed in the operating instructions) to avoid damage to the equipment.
Then you need to figure out the reasons.
If the water boiled when the boiler was first started, it is necessary to check the hydraulic calculation and the correct selection and installation of all elements.
If the water boils after some time of normal operation, then the following parameters should be checked:
- coolant level in the system (need for recharge);
- boiler performance;
- normal operation of the check valve (if there is a pump with a bypass);
- normal operation of the expansion tank.
Useful video
The video shows how a conventional one-pipe heating system with natural circulation works.
Cheap, reliable and practical
The OS is easy to operate and cheap to install.
To carry out circulation in a gravity system, you need to know the principle of its operation and have an accurate hydraulic calculation of all elements, for which it is recommended to contact specialists.






Comments