What determines the efficiency of home heating? Which heating system is better: one-pipe or two-pipe
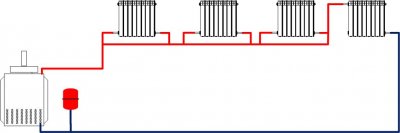
In the process of designing a heating system, the question arises of how best to connect the radiators - single pipe scheme or according to two-pipe?
Each connection method has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. To choose the wiring diagram correctly, it is necessary to determine its efficiency as it applies to your home. What is the difference between one- and two-pipe systems? And what criteria are used to make a choice?
Content
Single-circuit heating system

A single-pipe system is the simplest option for connecting radiators and a boiler. It is used for heating small and medium-sized spaces.
It has an important advantage - it gives the ability to organize work independently from the electric circulation pump.
The main advantages of single-pipe wiring are simplicity and independence from electricity. How does it work?
Operating principle
In a one-pipe system, the same pipe serves both as a hot water supply and a cold water return. Main pipeline connects in series all radiators. In each of them, the water loses some heat. Therefore, in a one-pipe heating system, there are hotter radiators at the beginning and cooler ones at the end of the circuit.
Attention! The warmest rooms will be those located immediately after the boiler. The rooms located in front of the boiler entrance will be cool. This must be taken into account when building a house.
With this heating scheme, the first rooms from the boiler should be large ones - kitchens-dining rooms, halls. And the last ones are small bedrooms.
Arrangement
Single-pipe layout is ideal for organizing the movement of the coolant by gravity. If the heating devices are correctly positioned, the water inside the pipes will move independently, without the help of a circulation pump. To do this, it is necessary to organize significant difference in height between the boiler and the distribution manifold.

The boiler for heating the coolant is located as low as possible - on the first floor of the premises or in the basement.
The collector through which the heated water is distributed is placed as high as possible - under the ceiling of the upper floor or in the attic. Water rises from the boiler to the collector during the heating process.
When heated, it expands, becomes lighter and therefore - rises upward. Then from the distribution manifold it enters the supply pipe, then into the radiators and returns to the heating boiler.
Reference! In heating a large house, a one-pipe system can be divided into several consecutive wirings. In this case, all of them will start from the distribution manifold and end before the boiler.
In addition to the boiler, distribution manifold and radiators, the circuit must include expansion tank. The coefficient of expansion of water depends on the amount of heating; at different heating, water expands differently. In this case, some amount of the coolant is displaced from the system. To collect and store the displaced water, a tank.
The main driving force of the coolant is temperature rise of water. The higher the temperature of the coolant, the higher the speed of water movement through the pipes. The speed of gravity flow is also affected by the diameter of the pipes, the presence of angles and bends in them, the type and number of shut-off devices. In such a system, only ball valves. Even when open, regular valves create an obstacle to the movement of water.
Vertical and horizontal wiring: differences

More often a one-pipe system assembled at the level of one floor — in the horizontal plane.
The pipes are laid along the floor, connecting radiators in adjacent rooms located on the same floor. This type of wiring is called horizontal.
The circuit is assembled less frequently in a multi-story building vertically. In this case, the pipes connect the rooms located one above the other. This heating system is called vertical. What is the difference between the two layouts, and which one is better for a private house?
Vertical diagram:
- Requires connection of specific batteries - elongated in height. Most radiators on the market are designed to be included in a horizontal system - they are extended in width. If the radiators are connected incorrectly, their efficiency decreases.
- Narrow batteries for vertical wiring heat well small areas. And worse - large rooms.
- It is different low probability of air locking in pipes, the formation of air locks - air is removed through a vertical riser.
Attention! Vertical layout is optimal for a large number of floors small room areas.
Horizontal layout:
- Provides great selection of radiators.
- Works more efficient vertical, which is due to the physics of the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
Horizontal wiring is used when arranging heating on one floor. In a multi-story building, water is transferred between floors via a vertical riser. Thus, for two- or three-story cottage will be optimal combined system with vertical and horizontal wiring elements.
Pros and cons of Leningradka
Let's list the advantages of single-pipe heating:
- Simple and inexpensive arrangement, which provides a small number of pipes, connectors, nozzles and other additional devices in the system.
- Ideal scheme for water movement by gravity and for the organization gravity heating system, without the need for a circulation pump.
Flaws:
- Uneven heating rooms - there are hot and cool rooms.
- Not suitable for heating large houses, the area of which more than 150 sq.m, or in the heating system of which is built in more than 20 radiators.
- The large diameter of the pipes makes unaesthetic their appearance on the walls.
Dual-circuit battery wiring
A two-pipe heating system differs from a one-pipe system by being divided into two pipes - supply and return of coolant. It provides uniform heating of all rooms. This type of layout is used in most new houses.
Operating principle

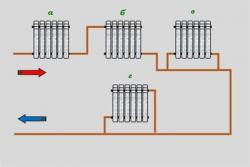
In a two-pipe system, water from the boiler flows to the radiators through supply pipe (main line).
Near each radiator the supply line has a connecting inlet pipe, through which the coolant enters the battery. The supply line ends near the last radiator.
In addition to the inlet pipe, each radiator has a outlet pipe. It connects it to the return pipe. The return line starts from the first battery and ends at the entrance to the boiler.
Thus, the heated water enters the radiators. evenly and at the same temperature. From each radiator, water is discharged into the return pipe, where it is collected and fed into the boiler for subsequent heating. Due to this movement of the coolant, all rooms in the premises are heated equally.
What is the difference
A two-pipe heating system includes elements of a one-pipe system and additional devices. In addition to the boiler, radiators, supply pipes and return water collection (the so-called return), the two-pipe system also includes circulation pump.
The long length of the main lines, the presence of corners and turns in the supply pipes complicates the movement of the coolant. Therefore necessary his forced circulation electric pump.
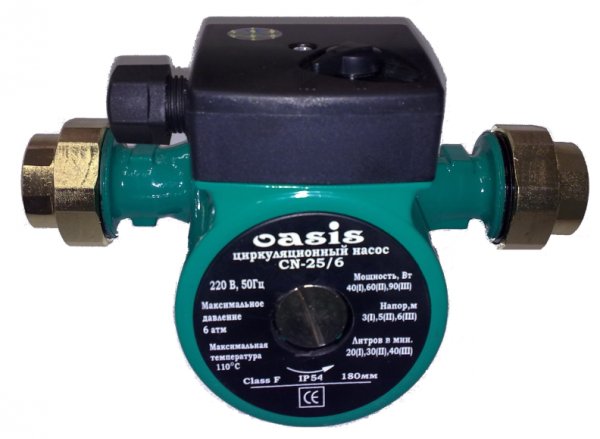

Photo 1. Circulation pump model 32-40, voltage 220 volts, manufacturer - "Oasis", China.
Also in the two-pipe system there is more taps, regulating the water supply and its quantity. Such a tap is installed in front of each radiator - at the inlet and outlet.
Classification by location
In a horizontal two-pipe system, the pipes connect the radiators horizontally. This scheme works in heating one-story house or one floor of a multi-story cottage.
In a vertical two-pipe system, the pipes connect radiators located one above the other in one "riser". However, there are differences from the single-pipe vertical system. Here, thanks to the presence of a feed and return pipe, vertical heating can use batteries of any width — multi-section (since the supply and return risers can be located far from each other). Therefore, the efficiency of two-pipe vertical heating is higher.
Reference! It is desirable that the batteries of rooms located one above the other have the same number of sections. This makes it easier to lay the vertical return pipe.
Bottom and top strapping: which is more effective
The term "lower" and "upper" trim refers to method of connecting batteries to the system heating. With the lower piping, the incoming water enters the battery through the lower branch pipe.

If it also comes out of the radiator at the bottom, then the efficiency of the radiator will be reduced. by 20-22%.
If the outlet pipe is located at the top, the efficiency of the radiator will be reduced. by 10-15%. In any case, when water is supplied to the radiators from below, the heating efficiency decreases.
With the upper piping (feed), the inlet pipe is connected to the radiator at the top. In this case, the movement of the coolant is organized more efficiently, the battery will work by 97-100% (97% - if the inlet and outlet pipes are located on the same side of the radiator, and 100% - if the inlet pipe is on one side at the top, and the outlet pipe is on the other side at the bottom).
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Suitable for heating arrangements private houses of large area, and a circulation pump must be installed in the system.
- Heats all rooms on the floor or in the riser evenly.
Flaws:
- It's manageable more expensive one-pipe system, since it requires twice as many materials - pipes between the boiler and radiators, as well as connecting devices, taps, valves.
- The electric circulation pump makes the system work dependent on the availability of electricity.
Important! Increasing the number of pipes and the amount of coolant in the system leads to increase in hydrodynamic resistance and does not allow the water to move by gravityForced circulation and a working circulation pump are required.
What to choose for a private house
Choice systems - one-pipe or two-pipe - is carried out at the design stage heating the house. If it is decided that the house will be heated by wall radiators, then a diagram of their location on the walls, the location of the pipes is drawn and the optimal connection diagram is selected. By what criteria is one or another type of wiring chosen for your home?

- Economy or the cost of installation and materials.
- Room heating efficiency - it depends on many factors - the number of rooms and their sizes, the location of large and small rooms, their functionality - bedroom, kitchen or storage room.
- Autonomy of heating operation - is it possible to use a pump or is complete independence from power supply required?
The choice of the layout of the batteries in the heating system is individual for each house.
Useful video
Check out the video that talks about the main features of one-pipe and two-pipe heating systems.
Which heating system is better: one-pipe or two-pipe?
Most economical will be the installation of a single-pipe heating system. It can be used to heat a small house. For large building a two-pipe radiator connection scheme is required. It will allow the rooms to be heated evenly, but will cost more expensive.

Moreover, her work will require her presence. circulation pump, powered by electricity.
If required completely autonomous the heating system should be referred to a single-pipe scheme and used in suitable options - vertical heating along risers or horizontal - on each floor of your house.
The main criterion for the quality of work and the correct choice of the system is warmth in the house, low energy consumption and reliability of your heating.








Comments