Review and characteristics of different types of heating radiators for a private house: advantages and disadvantages

Radiators, or batteries, are elements of the heating system that radiate heat into the room space. The construction market offers a wide range of models and designs heating batteries made of various materials.
What types of heating radiators are there for a private home

Most country houses are equipped with an autonomous heating system.
This allows regulate the temperature inside the room and the costs of heating a private home, as well as using thermostatic devices.
Advantages of an autonomous system over centralized heating:
- Control of coolant consumption and saving money.
- Using multiple heating boilers in one system, operating on various types of fuel, allows you to organize heating without interruptions.
- Possibility of using a liquid with the required properties as a heat carrier: anti-corrosion, non-freezing.
Flaws:
- Need for self-help monitor the safety level and possible breakdowns of heating devices. Responsibility for the operation of the system.
- Necessity allocate space for placing a boiler room, boiler, and collector.
- Do-it-yourself installation of the heating system, selection of boilers and other heating equipment, which requires some knowledge from the field of construction and thermal power engineering.
During the design of the system, questions arise about the choice of the type of energy carrier, heat carrier, boiler and radiators.
Cast iron
Traditional heating batteries of the CIS countries. They are cast made of cast iron. They are characterized by high heat capacity and long-term heat output. At the same time, they have significant weight and a fairly long service life: over 50 years.

Photo 1. Classic cast iron battery with good heat capacity, has a long service life, and is resistant to pressure drops.
Advantages:
- High strength, durability.
- Resistance to pressure drops and water hammer. This is why cast iron radiators are installed in multi-storey buildings with a common heating system from the boiler room.
Reference! The working pressure of cast iron radiators is low, up to 10 atm.
- Resistance to air, alkaline hard water, higher than other heating batteries made of steel and aluminum.
- Relatively affordable price.
Flaws:
- Significant weight and physical difficulty of transportation, unloading, installation, load on the foundation - the weight of the segment is from 5 to 7 kg. There may be one radiator from 4 to 10 sections.
- Inertia - slow warming up when starting the heating. This makes it impossible to regulate the temperature - reducing the heating during the day when the owners are not at home, and increasing the heating in the evening.
- The largest volume of coolant: 10 l per section.
Steel
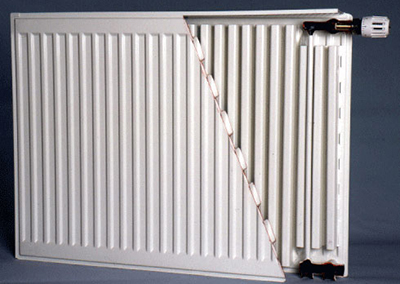
Traditional heating devices of Europe. Unlike cast iron, they are lightweight and average thermal inertia, which ensures easy installation and allows use in temperature control systems.
Steel radiators have a smaller volume of internal cavity, which means less liquid in the heating system. The working pressure is slightly higher than that of cast iron: up to 15 atm.
Advantages:
- Light weight.
- Simple container shape, no corners and, as a result, reduced risk of injury, easy to maintain and clean.
Flaws:
- Quite a short service life – 25 years.
- Relatively low heat output.
- Possibility of corrosion.
- Insufficient resistance to water hammer. Therefore, steel radiators are not recommended for installation in multi-story buildings, but are installed in the private sector.
Since steel corrodes especially strongly from the inside, in places of constant contact with liquid, such radiators require control of the quality of the coolant. Therefore, their installed in closed heating systems individual residential buildings with a closed expansion tank.
Aluminum

They are characterized by low weight, low inertia and high heat transfer.
They give off heat quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for thermoregulation and cost savings for heating. Thanks to its light weight (1-1.5 kg per section) are easy to install.
However, they are subject to corrosion with gas formation. Therefore, when installing aluminum batteries, it is necessary It is essential to install automatic valves to release gases and preventing air locks. Otherwise, the service life of aluminum radiators will be significantly shorter than that stated in the passport (25 years old) due to leaks that have formed.
Advantages of aluminum radiators:
- High heat transfer: 3 times more than cast iron and steel. Figures for comparison: the heat output of aluminum batteries is 230 W, while for cast iron this figure is equal 50 W, and for steel ones – 65 W.
- Light weight.
- Low thermal inertia, possibility of temperature regulation and saving.
- Flat shape without protruding edges and corners.
Flaws:
- Corrosion with gas formation inside the heating system.
- Sensitivity to pressure and water quality. Considering this disadvantage, in a private house aluminum batteries are placed in a closed system, purified water is poured inside and its pressure is controlled. The working pressure is maintained up to 20 atm.
Bimetallic
Batteries made made of two types of metal. On the outside is aluminum, which provides high heat output and heating efficiency. Inside is steel, which is more resistant to corrosion, thanks to it no gas or air pockets are formed. The aluminum surface provides high heat radiation and efficient operation of the heating system.
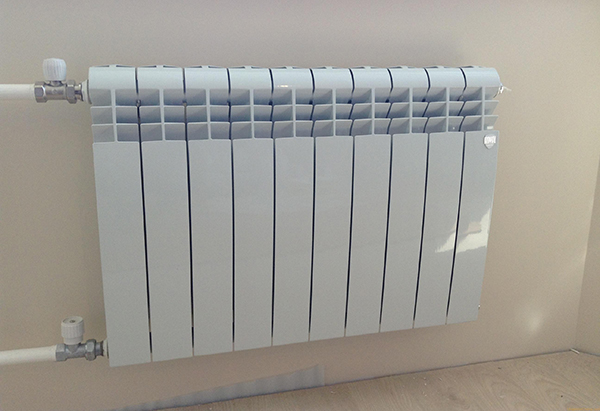

Photo 2. Bimetallic radiator made of steel and aluminum has high thermal radiation and is resistant to corrosion.
Bimetallic radiators have the smallest internal volume, one segment can accommodate no more than 0.18 l of water, and the smallest weight (from 1.5 to 2 kg – section). Their service life is up to 25 years.
Advantages of bimetallic batteries:
- High heat output – 185 W per section or 380 W/m K.
- Any coolant can be used.
- Flat, simple shape.
- Highest working pressure among other types of heating batteries: up to 35 atm + insensitivity to its surges.
Flaws bimetallic radiators belong to the so-called incomplete bimetallic structures. In them, only part of the core is made of steel, which allows solving the issue of pressure surges, but not the problem of corrosion. Most of the Chinese systems in our markets are made using "incomplete" technology.
Design of radiators
All types of heating batteries are different by type of construction.
Tubular sectional
Tubular batteries consist of from separate cavities in the form of pipes.
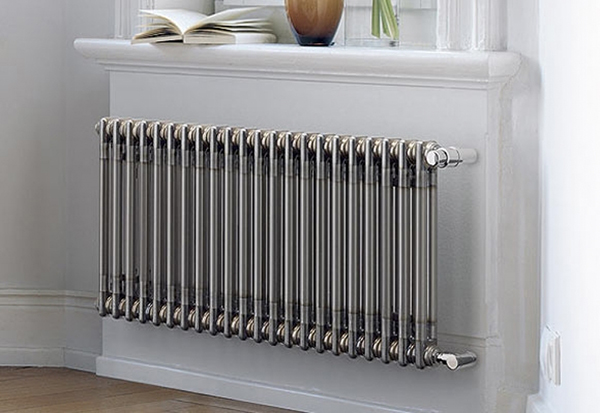

Photo 3. A tubular sectional radiator with vertical cylindrical sections looks harmonious in the interior of the house.
Exists three main options:
- Harmonic - is an analogue of traditional cast iron radiators. Their appearance resembles cast iron batteries, but differs in rounded stiffening ribs.
- Vertical pipes – cylindrical sections located vertically.
- Horizontal pipes – cylindrical segments located horizontally.
The pipes in the radiators are arranged in sections, hence another name – “sectional”. The power of such a battery is determined number of pipe sections.
Panel
They are a construction from two plates (panels) welded along the perimeter. The plane of the panels has small depressions - ribs. Under them, inside the cavity, there are tubes through which the heated coolant moves. Thus, the panel radiator has a tubular core inside and a flat, safe and aesthetically pleasing surface.
The area of the heated room determines the size of the plates.
Convector

The design of such heating devices includes ventilation devices that accelerate the movement of warm air. This increases the efficiency of the heating system.
Convectors have disadvantages:
- Use additional energy for work - usually electricity.
- They raise dust into the air, which usually settles on various surfaces.
Depending on the type of coolant and the method of obtaining heat, convectors are divided into electric, gas and water. The most popular are electric convectors, which have the appearance of a flat panel and a slot for blowing out warm air.
Quartz sand batteries
They are made from a material whose main element is – quartz sand. The main characteristic of the radiator is thermal inertia, the ability to accumulate and retain heat for a long time, and radiate it into the surrounding space.
Attention! The base is heated by the release of heat in a metal nickel-chromium heater. The temperature can be varied by applying electric current to the device.
Advantages of quartz batteries:
- Do not have a liquid coolant, therefore, they do not require draining when installed in houses where people live periodically.
- Warms up quickly, reach maximum temperature + 95 °C for 20 minutes of operation.
- Optimally consume electricity compared to other electric heating devices. For an area of 20 sq. m., about 0.5 kW/hour is consumed.

- They give Possibility of temperature regulation and different heating temperatures.
- They have aesthetic design.
- Can be used as main radiators and as additional heating.
- Safe to operate, easy to install, and undemanding to maintain.
Flaw such a battery - fragilityEven with light impacts, cracks form.
Distinguish two types quartz radiators:
- Monolithic - solid plate thickness about 2.5 cm, the heater is built directly into the quartz panel material.
- Tube – represent one of the types of infrared lamps with a quartz heater, which is located inside a flask with quartz sand. The flask is protected from impacts by a metal "casing", the front wall of which is made in the form of a grid for the passage of heat.
Quartz heaters are a simple solution to the heating issue. To connect, they only require the presence of an electrical outlet.
Solar gels
One of the new ways to heat a house using solar energy. To accumulate heat, panels are installed on the roof of the building, in which solar energy is converted into electrical energy.
Attention! In many batteries, the electrolyte is in a form thickened to a gel state. Such storage devices were called "gel"They are often used in solar heating systems, which is why such panels are also called "gel" batteries.
Then it enters the electric heating circuit of the house. For a constant supply of heat to the system battery required. Advantages:
- If you don’t count the cost of installing the heating system, its operation is low-cost.

- Does not require gas, coal or firewood.
- There is no need to connect to the general power supply system or gas pipeline. Allows you to heat your home completely autonomously.
Flaws:
- Expensive in the arrangement and periodic replacement of batteries. In terms of costs, it is comparable to gas heating.
- The need for disposal used batteries.
Useful video
The video provides some recommendations on how to choose a suitable heating radiator from a wide variety.
Choice options
The range of radiators for a private home is large. The choice is influenced by features of the heating system and the dimensions of the interior spaces, preferences of the owners, love for old proven methods or interest in novelty. In addition, the amount of money you are willing to spend to arrange autonomous heating for your home has an impact.









Comments