It is no less important than the feed! Heating system return: what is it?

Reliability and performance of the heating system depends on the efficient operation of all parts, included in it.
These include: a boiler for heating the coolant, radiators connected to it and to each other in a certain way, an expansion tank, a circulation pump, shut-off and control valves, a pipeline of the required diameter.
Creation highly efficient heating systems is possible, thanks to special knowledge and experience in this field of activity. The return pipeline plays an important role in the working process of heating the premises.
Content
Return in the heating system, what is it
The return line is a part of the heating circuit pipeline, carrying out the transfer of cooled coolant, after it passes through the system through the connected radiators, into the boiler to increase the temperature. The coolant is mainly water, sometimes antifreeze.
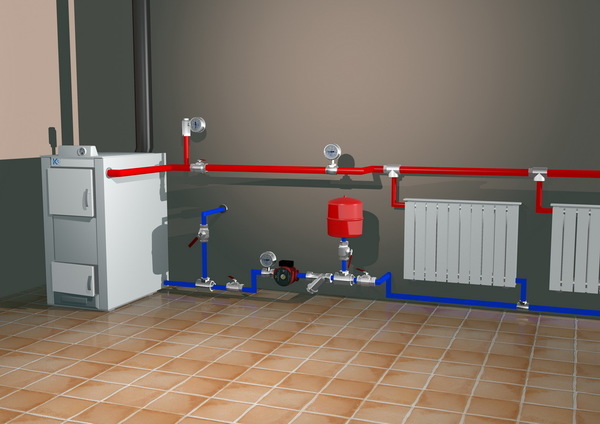
Photo 1. Heating scheme using a solid fuel boiler. The return line is marked in blue.
Types of heating systems
For multi-story buildings, it is often used one-pipe direct distribution system. It does not have a clear division of pipes into the supply of liquid to the radiators and the return, therefore the full circuit is conventionally divided into two equal parts. The riser coming out of the boiler is called the supply, and the pipes coming out of the last radiator are called the return. Advantages this scheme:
- saving time and material costs;
- convenience and simplicity of installation work;
- aesthetic appearance;
- absence of a return riser and sequential arrangement of radiators (the coolant is supplied on the 1st, then the 2nd, 3rd and so on).
For a one-pipe system, it is common vertical wiring with vertical contour and heat supply from above.
With two pipes The wiring system implies the installation of two closed, parallel-connected circuits, one of which provides the function of supplying the coolant to the heating device (radiator), the second - the function of its removal (return).
Radiators are connected in several ways:
- Lower (or saddle, sickle-shaped). Provides for connection of the supply and return to the lower connecting holes of the radiator. A Mayevsky tap and a plug are installed on the upper holes. Used for systems in which pipes are hidden under the floor or baseboard. Suitable for multi-section radiators, with a small number of sections, heat losses reach up to 15%.
- Lateral method, is popular. The pipes are connected to the radiator on one side: the coolant supply is through the top, the return is through the bottom. Not suitable for devices with a large number of sections.
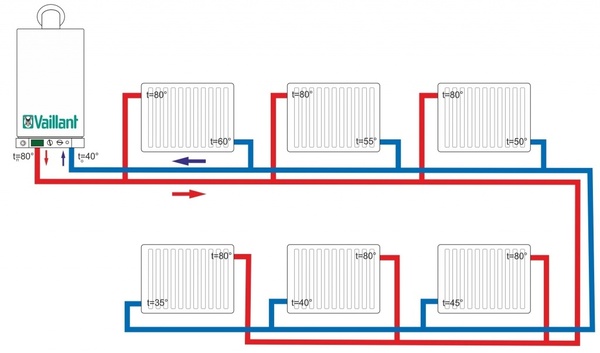
Photo 2. Two-pipe heating system with side connection. The supply and return temperatures are indicated.
- Diagonal (or lateral cross) the method involves supplying hot water from above, connecting the return line from below and from the other side. Suitable for radiators with a number of sections not less than 14 pcs.
- The third option the organization of the heating scheme is hybrid method, based on the simultaneous use of one-pipe and two-pipe systems. For example, the collector scheme assumes the supply of the coolant through a single riser, further wiring on site is carried out according to an individual plan.
How it works, how to improve productivity
A single circuit does not provide uniform heating of heating devices, heat output decreases as it moves away from the boiler (the coolant supplied to the last radiators is colder than to the first ones). The disadvantage of such a system is high values of coolant pressure.
Reference. the performance of a single-pipe system is increased if there is a circulation pump or bypasses, formed on each floor.
Advantages of the two-pipe option heating:
- heating a sufficient number of devices equally, regardless of their distance from the heat source;
- Adjusting the temperature regime or carrying out repairs on a single device does not affect the operation of others.
Flaws:
- complexity of the wiring diagram;
- labor intensity of installation and connection.
The optimal choice for private construction is the most efficient two-pipe system, which is also often chosen for heating luxury homes.
It is advisable to install a two-pipe system with installation of a circulation pump, which allows the use of pipes of smaller diameter.
After it, in order to protect the recirculation circuit from being squeezed, a check valve is installed.
During installation systems without a circulation pump the rule is observed: supply is possible if there is a slope from or to the boiler. The coolant with a higher temperature through the supply (slope from the boiler to the heating device) enters the radiator and heats it, and then exits through the return (slope from the radiator to the boiler), but with a lower temperature. Experienced craftsmen often resort to replacing the recirculation pump ring with a system 3- or 4-way mixers.
Important! With natural circulation, the entire pipeline from the riser to the radiators should not be very long.
Peculiarities
Long-term operation of boiler equipment is possible with a properly designed piping system, which ensures a certain temperature difference between the pipes, removing and supplying the coolant.
Attention! The presence of a significant difference in temperature values is the cause of the formation of a combustion chamber abundant condensation.
Drops of water, especially in combination with the resulting when burning with carbon monoxide (in the case of solid fuel equipment), quickly corrode the walls of the chamber, the tightness of an important element is broken, and the boiler fails.
An acceptable solution in this situation is to connect an additional water heating device - boiler. It is installed next to the boiler in a special way so that the coolant, having passed through all the devices of the system, gets into it, and then into the boiler.

Photo 3. Heating system with a boiler for heating water. The device is installed next to the gas boiler.
Table of temperatures in the heating pipeline
Heating temperature, including return pipes, directly depends on the readings of outdoor thermometersThe colder the air outside and the higher the wind speed, the higher the heating costs.
A standard table has been developed that reflects temperature values. at the input, supply and output of the heat carrier in the heating system. The indicators presented in the table provide comfortable conditions for a person in residential premises:
| Pace. external, °C | +8 | +5 | +1 | 0 | -1 | -2 | -5 | -10 | -15 | -20 | -25 | -30 | -35 |
| Pace. at the entrance | 42 | 47 | 53 | 55 | 56 | 58 | 62 | 69 | 76 | 83 | 90 | 97 | 104 |
| Pace. radiators | 40 | 44 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 54 | 57 | 64 | 70 | 76 | 82 | 88 | 94 |
| Pace. return lines | 34 | 37 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 58 | 62 | 67 | 69 |
Important! the difference between the supply and return temperatures depends on the direction of the coolant flow. If the wiring is on top, fluctuations amount to no more 20°C, if from below - 30°С.
Pressure norm
Efficient transfer and uniform distribution of the coolant, for the performance of the entire system with minimal heat loss are possible at normal working pressure in pipelines.

Coolant pressure in the system subdivided by mode of action in types:
- Static. The force of action of a stationary coolant per unit area.
- Dynamic. The force of action during movement.
- Maximum pressure. Corresponds to the optimal value of liquid pressure in pipes and is capable of maintaining the operation of all heating devices at a normal level.
According to SNiP the optimal indicator is equal to 8-9.5 atm, pressure reduction up to 5-5.5 atm. often leads to heating interruptions.
For each specific house, the normal pressure indicator is individual.and its value is influenced by the following factors:
- capacity of the pumping system supplying the coolant;
- pipeline diameter;
- distance of the premises from the boiler equipment;
- wear of parts;
- pressure.
Pressure control is possible pressure gauges, mounted directly into the pipeline.
Why the return line doesn't work
There are many problems associated with the return line in the heating system.
Suppresses the feed

The temperature of the water in the return pipeline is determined by the heating system design and corresponds to the value in the temperature graph, approved by the service organization.
Often apartment residents face a problem when the return line squeezes the supply line.
A common reason is - transition of hot coolant from the supply line to the return circuit through all sorts of parts (for example, jumpers) of the hot water supply pipeline or ventilation. With an automatic control device, as a rule, it is enough to set it up correctly.
The coolant drains poorly
If the circulation of liquid in the heating circuit is disrupted, the water in the return pipes drains poorly. First, check the compliance of the circulation pump power with the requirements. The reason may be hidden in a banal pipeline leak. The situation with poor circulation is typical for apartment buildings located at the end of the heating main. with insufficient pressure drop.
The return is cold, the pipes are clogged
Low return temperature is a serious problem that prevents you from maintaining comfort in the room. Reasons cold return:
- incorrect wiring heating;
- air bubble in the system or riser;
- insufficient flow water through the network;
- low temperature in underwater pipes;
- enlarged heat loss volumes;
- inefficiency of pumping equipment, result: weak circulation and insufficient temperature difference between the heat supply and the return;
- reduced pressure;
- clogged pipes and radiators.
Application Mayevsky cranes allows you to eliminate air locks that impede the movement of the coolant.
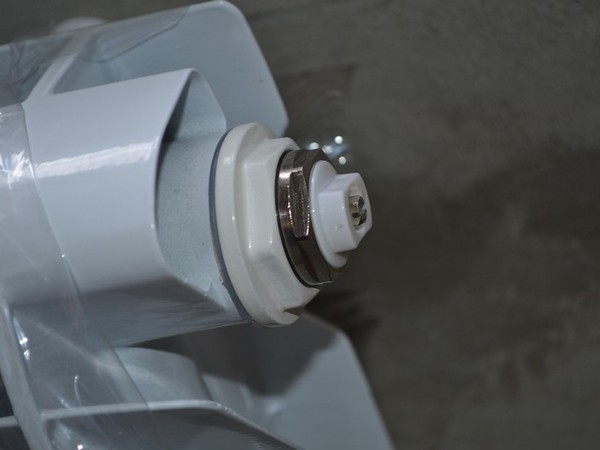

Photo 4. Mayevsky tap installed on a heating radiator. It can be used to release excess air from the system.
It is important to deflate air correctly:
- stop the heat supply using shut-off valves;
- open the Mayevsky valve, release the coolant with air;
- restore heat transfer by opening the valve.
Narrow passage of the control valve often explains the low return temperature, this is a reason to replace it with a new one.
Periodically check the pipeline for blockages that interfere with the movement of the coolant. Dirt and deposits are removedIf it is not possible to restore the patency of the pipes, The section is replaced with a new pipeline.
Attention! Install the exact reason problems can be identified after checking the entire heating system.
Overheating of the return coolant
Sometimes the outlet temperature is the opposite, above the norm by 5% or more, than in the temperature table. If the reason is increased water consumption, then it should be adjusted to normal levelIf the water in the return line is hotter than in the supply line, check the correctness of the pipe connections to the risers of the main system.
Adjustment
Maintain the radiator temperature at a certain level and the temperature difference between the supply and return pipes at a minimum allows a special regulator temperature.
Reference. The device is mounted on a hot water pipe before the inlet of all radiators. The absence of a regulator implies adjustment of all those connected to the riser at the same time.
Why do you need a valve?
Correct design of the heating system are developed taking into account the difference in temperature values in the coolant supply and return pipes.

Often, instead of installing a boiler, another protection option is used, ensuring long-term operation of solid fuel boiler equipment.
It helps bypass connection, which is a specially cut-in pipe that allows the cooled coolant to change direction of movement bypassing the boiler.
The bypass ensures the circulation of the coolant along the so-called small circuit. When forming this circuit, at the junction of the bypass and the return line, a thermostatic or three-way valve.
It operates depending on the preset temperature mode. When the coolant circulating in the small circle reaches the set temperature (usually 55-60°), the valve opens slightly. This ensures the flow of the next portion of cooled coolant from the return system and allows to significantly reduce the time it takes to heat up before entering the boiler.
Continuous mixing of hot and cold coolant maintains liquid temperature, entering the boiler, at the optimal value.
Important! A small circulation circle allows you to heat up a fairly large volume of water, which will prevent the formation of condensation on the combustion chamber and maintains its tightness, and therefore its functionality, for a long time.
Useful video
Watch the video to learn how to balance your heating system.
There are no "little things" in the operation of the heating system
To keep your home warm, it is important to monitor the performance of all components of the heating system. Often, problems with the return pipeline arise due to a malfunction or breakdown of another unit. It is not always possible to fix the defect yourself; sometimes you should seek help from qualified specialists.











