For the sake of system stability, calculations are necessary: how to calculate an expansion tank for heating?

The expansion tank (expansion tank) is an important element of the heating system, equalizing pressure indicator and maintaining volume of coolant during its thermal expansions and contractions.
Before installing the device, it is necessary to correctly calculate its volume.
Functions of the expansion tank

According to the laws of physics, when water is heated by 10 degrees, increases in volume by 0.3%.
For a small amount of water this phenomenon is hardly noticeable, but for a ton or several tons that are in the heating system, this is a significant indicator.
The appearance of additional volume of water may affect the condition of heating pipes or even cause them to be damaged. To prevent such a situation, an expansion tank is installed.
Its functions are as follows:
- Removes excess water from the system when it is heated.
- Provides the required pressure and prevents sudden increases (water hammer).
- Removes air from the heating system, which has a destructive effect on it.
Air, initially dissolved in water, begins to be actively released when it is heated (at high temperatures the figure reaches 90%). Together with the coolant, this air moves to the tank, where it accumulates and is then discharged outside.
Varieties
Depending on the design, they are divided into open and closed.
Open
These are cylindrical or rectangular tanks that are mounted at the highest point of the heating system (often in the attic)The tank is connected to the water supply to replenish the water supply and to the sewer system to remove excess coolant.
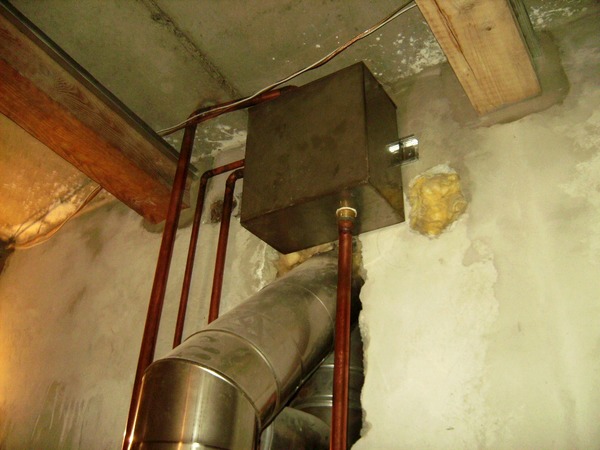

Photo 1. Open type expansion tank. The unit is rectangular in shape and is installed at the highest point of the heating system.
The downside of this type of equipment is that There is no automatic water level control. You will have to control the amount of liquid in it visually, and to add water, open the valve in front of the inlet pipe. Another inconvenience is the complicated installation, because the tank has a considerable weight, and it will have to be lifted into the attic. Due to the described nuances, this type of equipment has almost been replaced by closed-type tanks.
Closed
Design spherical or oval in shape with two chambers inside: one for air and one for water coming from the heating system. They are separated from each other by a membrane, which is a rubber bag-shaped reservoir that can expand and contract.
When water enters the first chamber the membrane stretches and air comes out of the second chamber through a special valve. When the liquid cools, the membrane begins to return to its original position and squeezes the water back into the heating system.
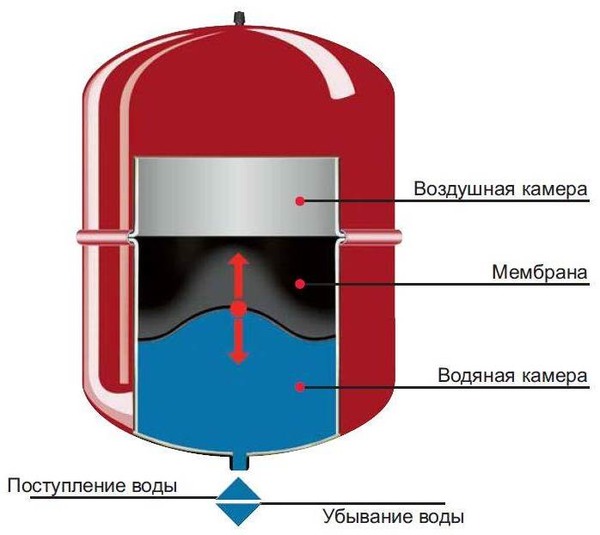
Photo 2. A fairly simple device of a closed expansion tank. The arrows indicate the components.
Depending on the type of membrane, There are two types of closed expansion tanks:
- Equipped with a non-removable diaphragm membrane
The design is very durable due to the cold stamping method. In addition, tanks of this type have anti-corrosion protection of the surface on the outside and inside. The tank cavity is divided into two chambers by an elastic membrane. The coolant flows from the system into the lower chamber. When the membrane takes the right position - it is on the surface of the liquid - the device is ready for operation.
- With flange fastening
The membrane is connected to the inlet pipe by means of a flange fastener, which allows you to replace a worn membrane with a new oneThe coolant is located inside the membrane and does not come into contact with the tank walls, which makes it possible to avoid anti-corrosion measures.
Closed type expansion tanks are often installed next to heating boilers. The second option is installation near the boiler, if you plan to install a double-circuit heating system that provides hot water supply.
How to correctly calculate the volume of a tank for heating systems?

To correctly calculate the volume of the expansion tank, Several factors that influence this indicator are taken into account:
- The capacity of the expansion tank directly depends on the amount of water in the heating system.
- The higher the permissible pressure value in the system, the smaller the tank size you will need.
- The higher the temperature to which the coolant is heated, the larger the volume of the device should be.
Reference. If you select an expansion tank too big volume, it will not provide the necessary pressure in the system. A small tank will not be able to accommodate all the excess coolant.
Calculation formula
Vб=(Vс * Z)/N, in which:
Vc — the volume of water in the heating system. To calculate this figure, multiply the boiler power at 15. For example, if the capacity of the boiler unit is 30 kW, then the amount of coolant will be 12*15 = 450 l. For systems that use heat accumulators, the capacity of each of them in liters must be added to the resulting figure.
Z — the expansion index of the coolant. This coefficient for water is 4%, accordingly, when calculating we take the number 0.04.
Attention! If another substance is used as a heat carrier, then the expansion coefficient corresponding to it is taken. For example, for 10% ethylene glycol it is 4.4%.
N — an indicator of the efficiency of the tank expansion. Since the walls of the device are made of metal, it can slightly increase or decrease in volume under the influence of pressure. To calculate N, you will need the following formula:

N= (Nmax—N0)/(Nmax+1), Where:
Nmax — the maximum pressure indicator in the system. This number is equal to from 2.5 to 3 atmospheres, To find out the exact figure, look at what threshold value the safety valve in the safety group is set to.
N0 — the initial pressure in the expansion tank. This value is 0.5 atm. for every 5 m heights of the heating system.
Continuing with the example of a boiler with a capacity of 30 kW, let's assume that Nmax is 3 atm., the height of the system does not exceed 5m. Then:
N=(3—0.5)/(3+1)=0.625;
Vb = (450*0.04)/0.625 = 28.8 l.
Important! The volumes of expansion tanks available for sale are: meet certain standards. Therefore, it is not always possible to buy a tank with a capacity that exactly matches the calculated value.
In such a situation buy the device with rounding up, because if the volume is slightly less than required, it can harm the system.
Useful video
Watch the video to learn how to select an expansion tank for your heating system.
Recommendations for selection
- If a very large tank is required, pay attention to its dimensions: Sometimes standard-sized doorways do not allow equipment to be brought into the room. In this case, purchase several smaller tanks, the total capacity of which is equal to the calculated figure.

- When using antifreeze as a coolant, the calculated volume value is recommended multiply by 1.5.
- With tank volume 20-25 l the capacity of the recirculation pump is 1.2 kW. Bucky 50-60 l installed with pumps 2.0 kW.
Calculating the tank volume is a simple but important task.
If you are not sure that you will do everything correctly, It is better to entrust this work to professionals.








