Types of heat exchangers for heating: how to understand them and choose the right one?

The heat exchanger is an integral element of the heating system, in which the heat exchange process between several environments.
There are several types of heat exchangers.
Content
What is the purpose of a DHW heat exchanger in a heating system?

The device is 2 plates: one of which static, and other - mobile. Both They have holes between which plates sealed with gaskets are fixed.
The essence of the operating principle of such a device is that corrugated plates form channels through which the liquid circulates. The increase in the coefficient of heat transfer from its heated part to the cold part occurs due to the increase in the contact area.
In the wall layer of the corrugated type, over time, a turbulence process. On different sides one plate a separate medium is moved. This method of movement prevents them from mixing.
Warm-up both environments occurs as a result of connecting the device to the pipeline. After the medium has completed its passage through all channels, it will leave the heat exchanger.
This equipment makes it possible to:
- exploit if necessary received from the carrier secondary heat energy for household needs;
- apply residual heat when electricity is supplied;
- to form required temperature conditions for carrying out chemical processes;
- maintain the coolant temperature regime at the established level in domestic heating systems.
Types
There are the following types of heat exchangers.
Mixing water

They are devices in which heat is transferred through direct contact. two environments: hot and cold.
The essence of the operation of such a heat exchanger is that in a special chamber liquid and steam are combined, the speed of which exceeds supersonic value.
The calculated nozzle accelerates it to such an indicator. Due to such mixing, it occurs liquid heating and steam condensation, and the coolant of the required temperature circulates through the heating system.
The device's camera provides for the presence of condensation vacuum. Operation of this type of heat exchanger is possible even under conditions of low steam pressure.
Superficial
The design of such devices is presented in the form bimetallic pipes with rolled aluminum fins.
In these devices, the process of air flowing around a solid surface occurs. The temperatures of the surface and the air flow differ.

Heat exchange between the media is carried out through a wall with a special heat-conducting material applied to it. The circuits are completely isolated from each other.
Surface heat exchangers are divided into 2 types:
- regenerative (the direction of the flow of the medium tends to change);
- recuperative (heat exchange from one coolant to another is carried out through the loose walls of the circuit, while the direction of the medium flow remains constant).
Recuperative and its varieties
They are divided according to design features and area of application.
Shell and tube
These are the simplest devices. They consist of a large number of small pipes that soldered into a single bundle and placed in a casing. Such heat exchangers are quite bulky and take up a lot of space.
They are used in evaporators, refrigerators, heaters, condensers.
Submerged

They represent serpentines flat or cylindrical shapes, immersed in a container with liquid.
These heat exchangers are considered inefficient due to the fact that there is a leak on the outside of the coil. low heat transfer, and the process of washing with liquid occurs in extremely small quantities.
Reference! The use of a submerged heat exchanger will be productive if the liquid in the container boils or contains mechanical additions.
Submerged units are used as refrigerators and condensers, as well as for heating of water and technological solutions.
Tubular
Devices of this type are 2 pipes, located inside each other and having different diameters. Thus, the liquid, which needs to be heated or cooled, comes into direct contact with the coolant.
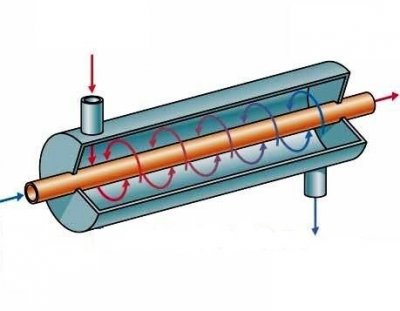
Heat exchange pipes are fixed along each other. Due to the difference between their diameters, the coolant does not experience any obstacles during its circulation.
Such heat exchangers are used mainly in food industry, in particular in winemaking and dairy production.
The use of such devices is also widespread in the oil, gas and chemical industries.
Irrigation
Heat exchangers of this type are straight pipes located one above the other and irrigated with water from the outside. They are fixed by welding or using "rolls" on the flanges. The irrigating liquid goes through the upper trough, the edges of which have the shape of clovesSome of the liquid supplied for irrigation of pipelines evaporates.
The use of such units as condensers in refrigerators.
Graphite: what is it?

Heat exchangers block structures. All rectangular or cylindrical components are firmly fixed with special rubber or Teflon gaskets and covers.
Inside this structure, there is something going on cross flow of fluid.
Initially, to eliminate the porosity of graphite, it is treated with special resins made of formaldehyde. One or both environments are corrosive.
Important! If both liquids are aggressive, then special graphite plates are necessarily applied to the sides of the pressure plates.
Due to the stable impact of such devices, their use is very popular. in the chemical industry.
Plate air with fan
According to their design, they are divided into detachable and soldered. The first are widely used due to the fact that they can be disassemble and assemble, and, if necessary, cleaning and increasing their efficiency by adding additional plates.

The device consists of plates with rubber gaskets between them, 2 end chambers, tightening bolts and frame.
Steel plates have thickness 0.7 mm, their flow side is corrugated or ribbed.
In order to seal the heat exchange process, the plates are fixed rubber gaskets.
The coolant in such heat exchangers can move in the forward, reverse or mixed directions.
Such devices are used in heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration systems. In addition, it is used in textile, oil, pulp and paper and other industries.
Plate-ribbed: operating principle

The essence of the design of such a heat exchanger is that there is single system of separate plates, between which ribbed attachments are located.
Their varieties are presented in a wide range.
For a competent selection of channel shapes for passage of liquid, requires the use of various attachments.
Important! The use of such devices for heat exchange is possible at the temperature of non-aggressive liquid and gaseous media. from +200 °C to -270 °C.
These heat exchangers are used in various transport installations.
Ribbed-plate
They differ from the above-mentioned types in that the base of the structure uses ribbed panels with thin walls, formed by high-frequency welding.

All of them are fixed in turn with the possibility 90°C rotation.
The use of such heat exchangers is often found both in industry (in thermal technological processes) and in everyday life (ventilation systems with heat recovery).
Spiral
They are horizontal and vertical. Their design consists of 2 thin sheets made of metal, fixed to the core and bent into spirals. To give the sheets additional rigidity, distance bosses are welded to them on both sides.
Spiral channels have limitations in the form of end caps. Sealing of such passages is done by welding. On the one side and seals with a gasket on the other. As it wears out, welding occurs on the other side as well.

This eliminates the possibility dismounting heat carriers.
This device is used in food, metallurgy, pulp and paper, mining, oil, gas and other areas of industry.
How to select a heat exchanger for a central heating system
When choosing, it is important to pay attention to the main technical characteristics of the equipment:
Thickness and material of plates
The lower the mass of the device, the higher the heat transfer coefficient. It is important to focus on the recommended thickness of the plates. It mainly varies from 0.4 mm to 0.7 mm, suitable material is stainless steel.
Pressure
The lower this indicator, the lower the cost of the unit. So that it is not observed failures in the heating system, it is necessary to know this meaning and indicate it to the seller upon purchase.
Heat transfer coefficient

This is one of the main selection criteria. It shows what unit of heat the device is capable of transferring in a certain time from a heated environment to a cold one. through an area of 1 sq. m. and a temperature difference of 1 K.
To increase heat transfer, fewer plates are required. The cost of such a heat exchanger will be lower. For equipment with a high price
Reference! As the flow increases, the need for a large number of cleanings due to the formation of deposits.
Recommended and optimal heat transfer coefficient - 7000 W/sq. m*K.
Weight
The weight of the heat exchanger directly depends on what it is made of material it is made. Before purchasing the device, you need to determine how much space there is for it. In small areas, it is better to refrain from large-sized equipment.
Reserve surface for heat exchange

For a quality unit this figure is 10-15%, otherwise its operation will not be effective, since the slightest underheating to the set temperature or contamination will lead to the cessation of the working process.
In addition to the above parameters, it is also worth considering amount of heat loss, main properties of the coolant, characteristics of pipes for heat exchange.
Types and materials
The type of heat exchanger is selected based on its intended purpose and the coolant used.
The most reliable and durable devices are considered to be those made of cast ironThey are not afraid of corrosion and have high heat capacity.

Disadvantages: large size and slow adjustment to a given temperature fluctuation. They take up quite a lot of space.
U steel The price of the units is noticeably lower, but the level of efficiency is also lower.
The most common are heat exchangers made of copperThey have a high coefficient of thermal conductivity and are technologically advanced.
To increase the service life, such devices are covered with a special protective layer on the outside.
Steel heat exchangers are the cheapest, are subject to corrosion and are heavy.
Popular manufacturers: photo
All manufacturers of units provide a guarantee for their products. from 6 months to 1 year.
The products of the following companies are in high demand:
- Sondex;
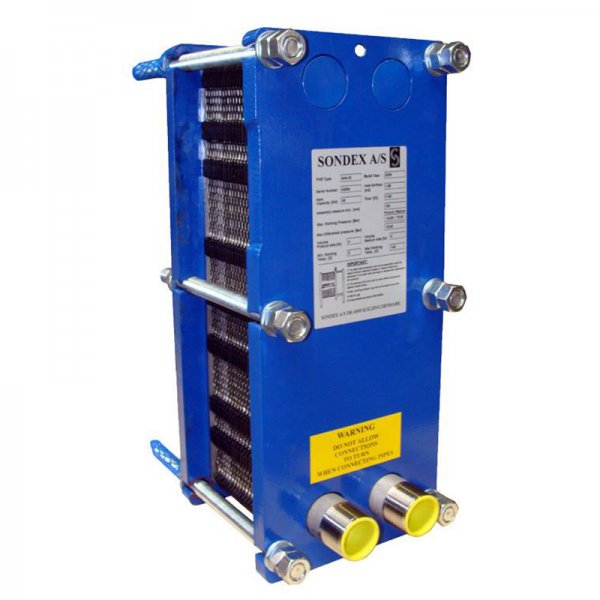

Photo 1. Plate heat exchanger, threaded connection, plate thickness 0.5 mm, manufacturer - Sondex, Denmark.
- Ridan;
- Alfa Laval;
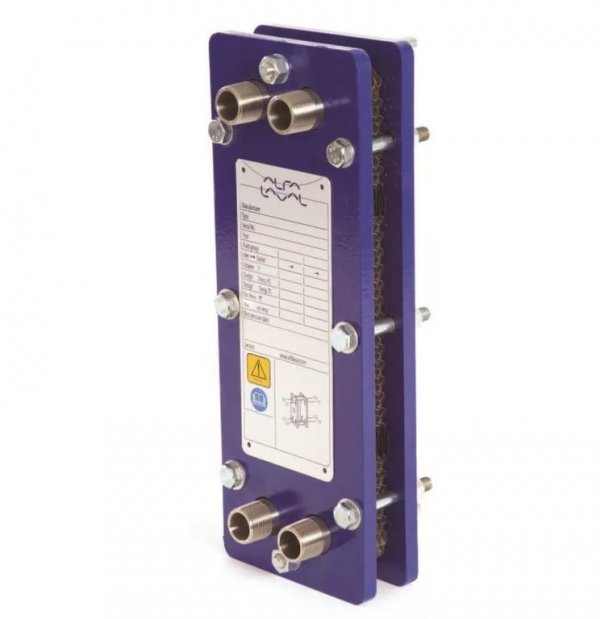

Photo 2. Plate heat exchanger model AQ2S, corrugated plate surface, manufacturer - Alfa Laval.
- Gea Mashimpeks;
- Danfoss;
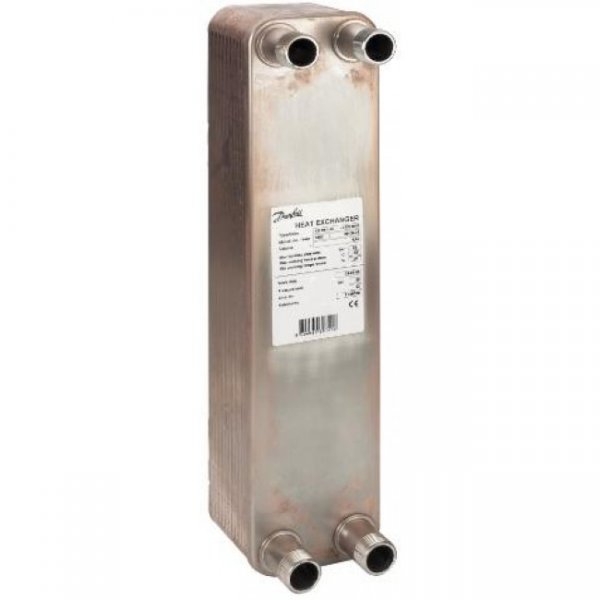

Photo 3. Brazed plate heat exchanger model XB 04-1-8, made of acid-resistant stainless steel, manufacturer - "Danfoss".
- Funke;
- Etra.
Useful video
Check out this video to see how shell and tube heat exchangers work.
Low hot water pressure and other signs of blockage
Signs of clogging
- low pressure hot water;
- accumulates and crumbles under the casing soot;
- after switching on occurs quick burner shutdown;
- bad warming up water;
Important! Before you start the process heat exchanger cleaning It is necessary to make sure that the other elements of the heating system are in good working order.
- constant triggering thermal protection.









