Every system needs it! Expansion tank for heating

The operation of autonomous heating systems is associated with fluctuations in the volume of the coolant caused by its heating and cooling.
To smooth out water hammer and compensate for thermal expansion, a special tank is installed in the heating circuit.
The technical name of the device is expansomat. (from the word expanse – “to expand”). It is a metal tank of a certain volume with a branch pipe for connection to the system.
Content
- Expansion tanks: what they are, their purpose, differences from other hydraulic devices, types
- What is the difference between hydro tanks for water heating systems and devices for water supply?
- Open tanks: device, operating principle, advantages and disadvantages
- Closed type expansion tank with air and valve
- Calculation options
- 5 criteria for choosing products
- Photos of products
- Useful video
- Service
Expansion tanks: what they are, their purpose, differences from other hydraulic devices, types

The liquid coolant circulating in the circuit has the property of expanding during heating and decreasing in volume during cooling.
Since water is incompressible, when it expands, excess liquid remains inside the pipes.
This physical phenomenon increases the hydrostatic pressure of the closed circuit, which may cause damage to the pipeline, inadequate operation of the heating device, failure of the pumps.
Important! The degree of thermal expansion of water depends on temperature. This means that when heated up to 90º C 300 liters of watercirculating in the system, their volume will increase by 3.4% or approximately for 10 l.
To prevent emergency situations, special reservoirs - expansion tanks - are installed in autonomous heating networks. They are made in the form of containers spherical, cylindrical or rectangular in shape, into which excess hot coolant flows.
Depending on the type, the devices have internal membranes, pipes for connecting to the pipeline, draining cooled water, discharging excess into the sewer, as well as safety valves.
What is the difference between hydro tanks for water heating systems and devices for water supply?
- Purpose.

Expansion tanks for heating systems compensate for thermal expansion of the circulating element.
Functions hydraulic accumulators — accumulation of a reserve volume of water to ensure pressure when the pump is turned off and protection of the system from water hammer.
- Design.
In the cavity of the expansion tank, the hot liquid either comes into contact with the walls of the device (membrane and open type), or contacts only with the elastic membrane (balloon type). For water supply hydraulic accumulators the first option is excluded.
- Partition material.
In heating networks, the diaphragm is loaded slowly, so the key requirement is heat resistance. For water supply hydraulic tanks, food grade rubber membrane, resistant to frequent and rapid stretching.
Open tanks: device, operating principle, advantages and disadvantages
Expanders of this type used in heating networks without circulation pumpsThey are a container without a lid, connected to the heating system and installed at the highest level (in the attic).
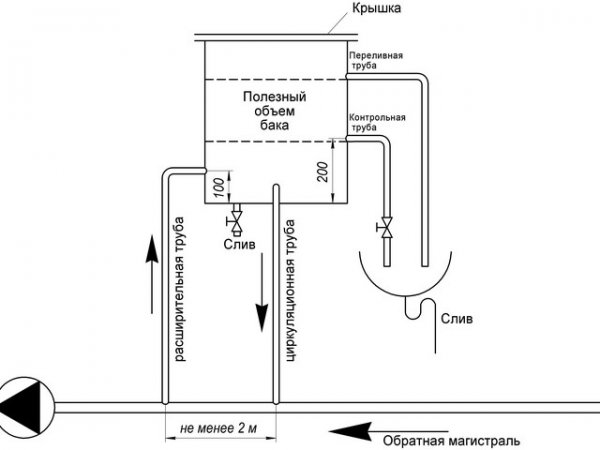
Photo 1. Installation diagram of an open expansion tank in a heating system. Each part of the structure is labeled.
During heating, the volume of the heat-transfer fluid increases, the excess flows into the reservoir. When the temperature decreases, the water returns by gravity. If the liquid boils, its vapors escape through the open top.
Since the coolant can spill over the edge, such tanks are supplemented with an overflow nipple. Through it, excess water is discharged into the sewer. The benefits include:
- simplicity of design, ease of repair;
- low cost of the device;
- the possibility of making the tank not only from steel, but also from plastic.
Reference. An open expander for a country house can be made independently from improvised means - plastic canister or barrel. Despite the name, it is better to make a cover - this will protect the system from debris getting in.
Open expansion tanks have more disadvantages than advantages.These include natural evaporation of liquid, the appearance of corrosion of metal containers, the need for constant monitoring and the impossibility of use in heating networks with antifreeze.
Closed type expansion tank with air and valve

In networks where the coolant moves under the influence of pumping equipment, closed expansion tanks are installed.
The main design feature of such tanks is complete tightness, allowing to maintain constant pressure.
The housings are made of steel, the internal cavity is divided into two sections by a balloon or diaphragm membrane.
The first one is called the gas (air) chamber, filled nitrogen-containing mixture or air. Second - liquid compartment, where the heated coolant enters. Each chamber is completely sealed, so the liquid does not come into contact with either the environment or the gas. The device is supplemented with a branch pipe for connection to the heating network and a valve for pressure relief.
Operating principle
Due to expansion, the hot coolant is pushed out of the circuit into the liquid compartment of the tank, pressing on the elastic membrane. In another chamber, the gas mixture is compressed, the pressure becomes excessive.

As soon as the liquid cools and loses volume, it is compressed by the action of compressed air is pushed back into the pipeline.
When the pressure and temperature increase rapidly and the volume of liquid in the expansion tank reaches critical values, the safety valve is triggered: excess water is drained out.
Types of membranes
Compensation devices are produced with elastic partitions of two types:
- Diaphragm — fixed around the perimeter inside and dividing the space in half. The liquid contacts the walls, so they are additionally coated with heat-resistant moisture-proof compounds.
- Balloon — externally resembling a balloon and fixed at the inlet pipe. When entering, the coolant remains inside the membrane, without touching the walls of the device.
Stationary diaphragm type partitions, it is impossible to replace them if they break. The cylinders are changed through the expansion tank flange, which is attached with bolts.
Advantages and disadvantages
There are other advantages in favor of closed-type expansion tanks:

- compact dimensions;
- no contact between the coolant and the external environment, which eliminates the evaporation process;
- minimal heat loss;
- the ability to create additional pressure;
- installation in any part of the boiler room;
- high values of ultimate pressure;
- extension of service life boiler, radiators, pipelines.
There are few disadvantages to closed expansion devices., these include the relatively high cost and the impossibility of replacing the diaphragm membrane.
Calculation options
For small circuits in which fluid circulates 150 liters and less liquid, they acquire expanders with a volume of 10% from the total capacity of the system. When calculating devices for complex large heating networks, three methods are used:
Method #1. Calculation of the total expansion volume of the liquid moving in the network. The method allows to calculate the membrane hydraulic tank with an accuracy of 10%. To do this, determine:
- The total volume of heat-transfer fluid in the entire system (value C). An approximate value can be obtained by knowing the boiler power - 1 kW consumed about 15 liters. Filling the contour through the counter gives an accurate result.
- The value of thermal expansion (E) taking into account the type of coolant. For water at t 90º C is the coefficient accepted 0.034, the value for antifreezes is shown in the table.
- Indicator of the maximum possible pressure in the circuit (Pmax) — corresponds to the threshold of the safety valve.
- Minimum (setting) pressure (P0), at which the heating network operates.

Photo 2. Table with an example of calculating various characteristics of an expansion tank depending on several conditions.
The data is substituted into the formula:
V=(E×C)÷(1-(P0÷Pmax))
The resulting number is rounded up., since the expansion tank must compensate for the calculated volume with a small reserve. For this, the filling factor of the device is also taken into account.
Method No. 2. Contacting specialized design organizations. A priority option, as it allows you to get the most accurate result. The high cost of the service is fully compensated by the rational choice of the tank (you will not overpay for unnecessary volume) and savings on emergency repairs.
Method No. 3. Using online calculators. Internet resources allow you to obtain values with varying accuracy, so such results are taken as approximate.
Attention! If you plan to replace the water in the future on antifreeze, calculate the tank taking into account the liquid that has the greatest expansion.
5 criteria for choosing products
- Type of coolant circulation. For systems where water moves naturally, an open tank is used. In autonomous networks with circulation pumps, membrane hydro tanks are used.

- Type. Tanks with a non-replaceable (diaphragm) membrane have a lower cost than expanders with a balloon flange partition. However, if the diaphragm ruptures, the tank will have to be replaced completely.
- Volume. It is a calculated value and is always rounded up.
- Maximum working pressure. Must correspond to (be no less than) the maximum possible value for the entire heating system.
- Technical specifications. The permissible operating temperatures, pressure, volume, membrane type, mounting options and connection to pipes are taken into account.
Reference. When buying, choose products designed specifically for heating. Most manufacturers paint such tanks red, white ones are considered universal, but they are oriented towards low maximum temperatures (up to 70º C).
When choosing, pay attention to the manufacturers. Branded brands value their reputation, so there is no risk of purchasing a low-quality expansion tank. Reputable companies include: AQUASYSTEM, REFLEX, WESTER, IMERA, BOSCH and others.
Photos of products
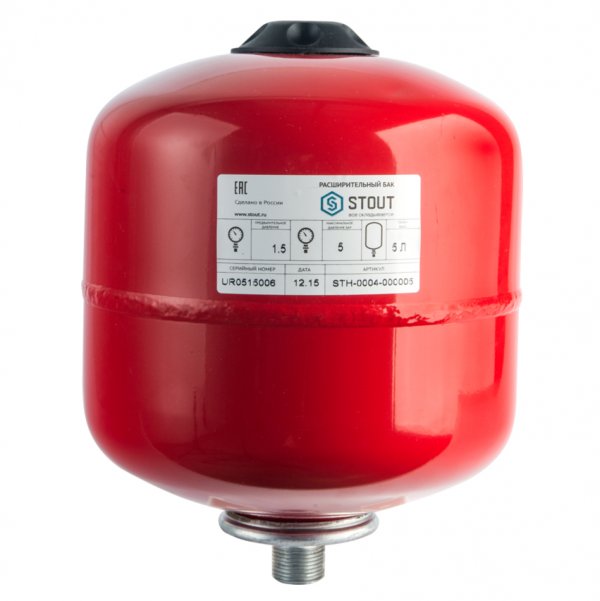

Photo 3. Closed expansion tank for heating system. Manufacturer of the product Stout.
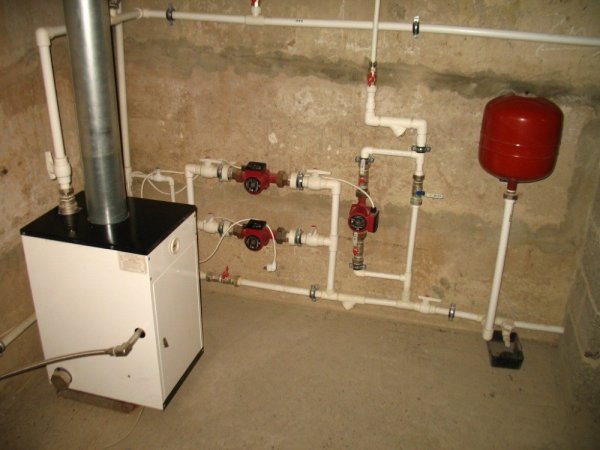

Photo 4. Closed-type expansion tank (red product) connected to the heating circuit.

Photo 5. Open expansion tank connected to the heating system. The tank is located at the top point of the structure.
Useful video
Watch the video to learn where to install the tank in your heating system.
Service
For correct operation of the heating circuit and long service life of the expansion tank Preventive measures must be carried out once every six months. The work includes checking for external damage, leaks, initial pressure, membrane integrity, and replacing it if necessary. If the dismantled tank is not planned to be used for a long time, then the water from it must be drained and stored in a dry room.







