Type, volume of expansion tank for heating and other important characteristics

The expansion tank is used for reducing the impact of pressure changes on the heating system.
There are several types of expansion tanks for heating systems.
Expansion tank device for heating system
The device consists of the following components:

- crane;
- membranes;
- fuse;
- liquid storage containers;
- gas chamber;
- branch pipe.
The complete set depends on the manufacturer and type of construction. For heating circuits there are tanks three types.
Open type expander is a large-volume vessel with a lid. The latter serves to protect the working substance from dust and other solid particles. It is maintained inside constant atmosphere, what are they installed for pipes.
Enough for work one, but it is recommended to use devices with three or more. Pipes are required to control: pressure, maximum level and water drainage, supply of liquid to the system.
First section is a small piece that the meter is attached to. It usually comes out of the bottom of the container. Others are attached from the side, at different levels. In the simplest case one pipe directed towards the circuit for communication with it, and second — into the sewer, to remove excess liquid. Accordingly, they are located at the bottom and top of the tank, at the end.
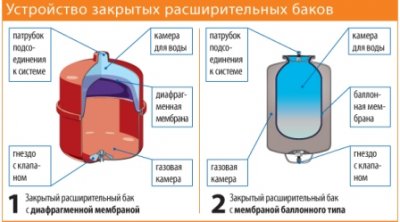
Closed dilator differs slightly in design. The coolant tank is placed in gas chamber. A pipe for connecting to the circuit comes out of the inner one, and an air bleed valve comes out of the outer one.
Third type device came from the previous one. The chamber is common, but divided into two parts flexible rubber membrane.
IN on one side volatile substance or vacuum is located in one, and the coolant in the other. When the latter becomes larger, the second space is compressed. When the pressure increases significantly, some of the liquid is removed from the circuit until it stabilizes.
Operating principle
Varies slightly depending on the type of device.
Open

Installed at the top of the piping. This allows water to circulate normally throughout the volume and system. Manometer determines the pressure level.
The liquid, traveling along the circuit, enters the tank. When the indicator is exceeded, part of the water is drained into the sewer or soil.
In other cases, it is simply stored inside. It opens automatically under the pressure of hot liquid and vice versa. The volume is replenished if necessary. Thanks to this, pressure control.
Attention! An open system is easy to configure by setting electronic pressure gauge value.
Closed tank action
Does not interact with external conditions. The device consists of from two cameras built into each other. The increased pressure due to the heating of the water affects them bothAs a result, an exchange of indicators and displacement of air occurs.
As they cool, the gas and liquid return to the chamber and, accordingly, circuit. Thus, normal values are maintained in the system. In this case, the tank is placed at any point except the area in contact with the pump.
How a membrane or vacuum tank works
The tank is divided for two cameras. The upper one is air, the lower one is liquid. A membrane is installed between them. The latter can be:
- Balloon, which separates the coolant stored in a rubber container and the compressed gas, usually nitrogen.
- Diaphragmatic, which performs the same function, but in the second half pump in air.
The shape has virtually no effect. The only visible factor is the larger volume of the balloon system compared to the diaphragm system.

Photo 1. Membrane expansion tank, weight 4.3 kg, cylindrical design, 24 l, manufacturer - "Dzhileks".
The pressure in the upper part is set according to calculations previously performed in a certain situation. In some cases, the numbers are specified by the manufacturer in technical data sheet of the expansion tank. Sometimes it is allowed to replace the membrane if problems are revealed during operation. The manufacturer specifies such a possibility. This increases the price, but it allows you to fix the malfunction that has arisen. And you should also remember that replacing a part is cheaper than buying a new device.
Operating principle two tanks is similar. As the coolant pressure increases during heating, the membrane stretches, reducing the volume available to air. This prevents the water from overflowing the container. As cooling down the process is reversed. According to this principle, automatic control of pressure indicators occurs.
Important! The expander must be carefully selected, following the calculations. Otherwise, the work will be unstable: excess volume will lead to a drop in pressure, and a deficiency will lead to an increase.
How to calculate volume
Usually, a tank with a capacity of 10% of the total coolant. There is a formula for calculations, some of the components of which are taken in tabular values.
Formula
It has the following appearance:
V = (Vc * K) / D, Where

- V — the desired number.
- Vc — the total volume of the coolant in the circuit, cubic meter (or liter).
- K — tabular constant of liquid expansion upon heating.
- D — efficiency coefficient of the device.
To determine the indicator, you need to have the following values:
- Vc can be calculated in several ways. The first simple option - install a water meter and record the readings by filling the circuit with liquid. Second — determine the power required for the system and multiply it by the amount of coolant sufficient for one liter. Third more complicated: manual addition of the volumes of all pipes, radiators and heating boilers, as well as other devices.
- D = (Qm - Qv) / (Qm + 1), where Qm — maximum system pressure, and Qv — the indicator in the air chamber. Both numbers are often indicated in the technical data sheet of the product. The second value can be changed by pumping or removing part of the gas. It is taken equal to any number in the range from 1 to 1.5 atm.
Values of the coefficients

Coefficient K depends on the substance used as a heat carrier. It does not change linearly, which makes direct calculation difficult. The indicator depends on glycol content in the liquid.
It directly depends on the temperature volume: the size of the expansion tank is selected based on the maximum and minimum heating of the coolant. When calculating, the selected number divide by 100to remove interest.
Useful video
Watch the video to learn how to choose the right expansion tank for your heating system.
Bottom line: what kind of tank do you need?
When choosing a device, you need to focus on two indicators: volume, the calculation of which is performed according to formulas, as well as type - open, closed or membrane. For this, you should consult a specialist.








