Is its popularity justified? Two-pipe heating system of a private house: what is it, its schemes

Modern residential buildings must be equipped with communications for normal living of people in them, this also applies to heating communications, which are divided into two types: one-pipe systems and two-pipe systems.
Single pipe central heating systems significantly more economical and easier to build. Hot water flows into them and out through a single riser (pipeline) through the floors of the house, to heating devices connected in series to this system.
A single pipe heating system is often the preferred option for small, single story homes without additional basement space. However, The real preference of most engineers is two pipes.
Content
Why choose two pipes?

The main feature of a two-pipe heating system is considered to be the uniform heating of heating devices on the floors of the house and the highest heat output from heating devices.
Therefore, in Soviet times, in particular in Stalin-era buildings, in buildings of the Soviet nomenklatura, etc., only a two-pipe heating system was used.
So, despite the fact that their installation is much more expensive, the type of installation of the system with two pipelines is used more often today, because This type is universal for most buildings and can be suitable for any type of construction.
The two-pipe system is called this way because the hot water flows through one pipe to the radiators and through the other - away. Heating devices in the system connect at the same time, and the distance to the heat source (boiler or collector) does not affect their internal temperature.
Main pros and cons
The system has many positive crap:

- hot water is supplied to the heating devices installed in the house with the same temperature;
- thermostats can be easily installed on a battery or radiators, with their help the speed of water flow into the heating device and, accordingly, the temperature are regulated;
- even if one of the heating devices breaks down or fails, this will not affect the performance of others;
- the system works in buildings with all types of configurations and number of floors.
However, there are also flaws:
- a lot of pipes, risers, connections and other elements;
- by itself installation is complicated and time-consuming;
- high cost, compared to a one-pipe system.
Types of systems
There are several types of two-pipe heating systems.
Open
In such a system need an expansion tank, because the heated water expands. The expansion tank takes in the remaining water after cooling, when returning, and when it is discharged if there is excess volume. A pump is not used here.
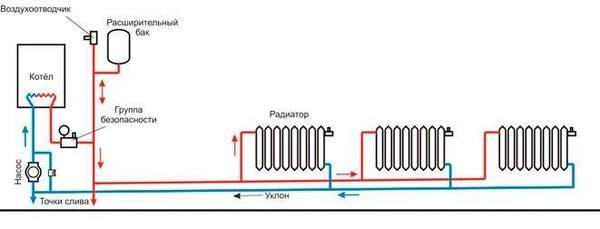
Photo 1. Diagram of a two-pipe open heating system. Water circulates through the structure without the aid of a pump.
Coolant (mainly water) moves through the pipeline naturally. This happens because hot water has a higher density than cold water. And so, according to the laws of thermodynamics, hot water goes through pipes in a place with low pressure, gradually cooling down. After that, the coolant, having lost temperature, ends up in the boiler, where it regains its temperature again. Natural circulation occurs, due to which the radiators heat up.
Reference. The tank is not sealed, so the water evaporates and needs to be replenished periodically.
Into an open heating system includes the following components: boiler, expansion tank, risers, radiators, pipes. In order for the coolant to circulate to the required degree, the boiler must be installed in the deepest part of the building - for example, in the basement, and at the same time, an expansion tank must be installed at the highest point - for example, in the attic.
Pros systems:
- simplified maintenance;
- clean, silent operation (since there is no pump);
- balanced heating of the heated building;
- instant start and shutdown;
- does not depend on the availability of electricity in the house, will work even without electricity supply;
- reliability;
- No extensive assembly skills are required during installation.

Cons systems:
- when air gets inside, heat transfer is disrupted, corrosion occurs, circulation deteriorates, air locks appear, etc.
- the coolant in the expansion tank is subject to temperature decrease, and its temperature level must always be regulated to prevent evaporation;
- warms up slowly;
- Do not use antifreeze;
- bulkiness;
- low efficiency.
Important! In winter time the tank is insulated. When installing a riser in an open system, it is necessary to use fewer turns and complex mounting connecting elements.
Closed
In a closed heating system complete tightness is maintained, the liquid does not evaporate. A circulation pump is usedThe so-called forced circulation of water is done with the help of risers, radiators, pipes, a boiler, an expansion tank, and a pump.
If the temperature increases, the tank valve will open and take away the excess liquid. If the temperature decreases, the pump will pump it back in. In a closed system, the pressure is maintained within pre-defined limits. So deaeration of the heat-transfer fluid occurs.
Pros systems:
- easy to install;
- there is no need to always monitor the temperature of the coolant;
- antifreeze is used as a coolant;
- the room temperature is regulated;
- the pressure is controlled by you;
- high performance characteristics;
- additional heating sources are connected.
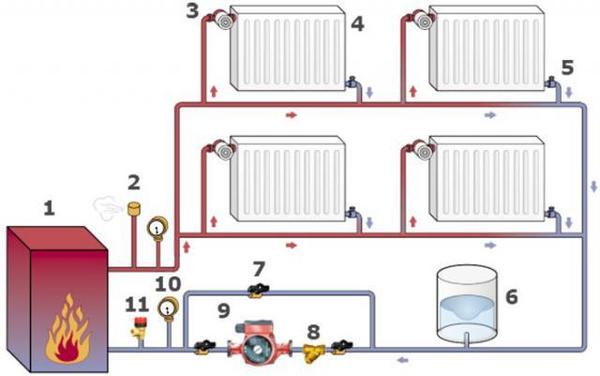
Photo 2. Scheme of a two-pipe closed-type heating system. A circulation pump is required for operation.
Cons systems:
- a regular power supply is required (including for the pump), so for emergency situations an electric generator is usually purchased;
- butt joints can allow air into the system;
- dimensions of expansion membrane tanks in large closed spaces.
Natural circulation design
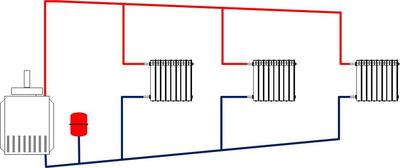
Also known to the people as gravity systems. They work based on how the heating devices and the boiler are located in the room, and what the density of hot and cold water is. The hot liquid squeezes the cold liquid out of the boiler and redirects it up the pipes. In this way, the heat is transferred to the radiators, and the cold liquid returns to the boiler.
In our case two pipelines mounted in parallel: The first one is for hot water from the boiler, and the second one is for cold water from heating devices.
Liquid from the boiler is moving into the distribution tank, from where it drains to the heating devices. If the riser is too narrow in diameter, then hydraulic resistance is formed, which prevents the circulation process.
Pros:
- energetically independent;
- easy to install;
- does not make noise;
- long service life;
- easy to maintain;
- subject to repair;
- self-regulating.
Cons:
- during installation, only open wiring is used;
- it is necessary to always monitor the temperature of the coolant;
- Efficiency is insufficient;
- a wide diameter riser is required;
- the coolant may freeze.
With forced circulation of coolant
Forced circulation system diagram works like a gravity feed, but at the same time withwith built-in circulation pump.
Some people doubt the efficiency of this scheme, because there is a possibility of mixing hot water with cold water. However, this would only be realistic if the water speed corresponded. The pump creates such a pressure level that the water inside moves at its natural speedThe increase will not be a reason for mixing the waters.
Pros:
- It doesn’t matter what diameter of pipes will be used during installation.
- The absence of temperature changes here improves operating conditions.
- The temperature in individual rooms is independently regulated using a heat carrier.
Cons:
- It is energy dependent, so you will need to additionally purchase an electric generator.
- The operation of the pump causes serious discomfort due to the noise it produces.
Layout types
The two-pipe heating system also differs in the types of layout.
Vertical
With this scheme with bottom wiring, the supply and return risers are laid to the very bottom of the building, and the liquid moves through them separately to the radiators.
Pros:
- excellent control of the heating concept;
- Each heating device is switched off separately.
Flaws:
- extended pipes;
- do not install apartment meters.
Horizontal

For each heating device according to the area of the room The floor contains lines of pipes from the supply risers. Apartments in this system are entered into it separately.
The radiators are equipped with air bleed taps.
This type of system is exactly what is popular. in a modern multi-storey building.
Pros:
- the same as in the vertical type;
- the meters are connected.
Cons:
- if the building is high, it will be necessary to use pressure compensators;
- The solution is more complex in operation than the vertical type.
Upper wiring diagram
The feed riser is installed along the upper area of the room. The main distinguishing feature: heavy pressure in the main pipeline, due to the significant difference in the levels of the pipes (return and supply, respectively). Due to this circumstance, they can be the same in width, even if we are talking about a scheme with a natural circulation process.
The pump turns on and reaches normal pressure even if narrow diameter pipes are used. The best effect is achieved. in two-story houses, because natural circulation is improved by the difference in how high the boiler, located in the basement, and the radiator are mounted on the 2nd floor.
The hot liquid will be directed to the expansion tank. a cistern located on the 2nd floor or in the attic. After which it will go through the pipeline to the radiators.
Pros:
- increased speed of movement of the heat carrier;
- the fact that air does not penetrate into the main line.
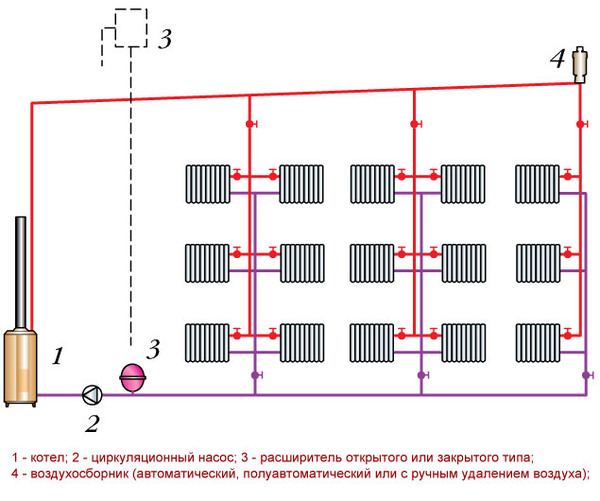
Photo 3. Two-pipe heating system with vertical distribution. The numbers indicate the parts of the structure.
Cons:
- not very aesthetic appearance of the premises;
- large expenditure on components;
- large rooms are not heated;
- you have to spend money on additional decoration to mask the pipes.
Bottom wiring
The horizontal type of wiring has two distinctive features: extended pipeline, and also its special location at an angle to the plane. It is possible to install a horizontal type of layout and natural or forced circulation. The two-pipe concept assumes that the supply pipeline is installed at the same level as the radiators. In this case, periodically air pockets may form.
Pros:
- the efficiency factor is higher here;
- installation even in unfinished buildings;
- it is possible to leave the heating on the lower floors on if the upper floors are not being used at the same time;
- Most of the control equipment is installed in a single room;
- automation of work.
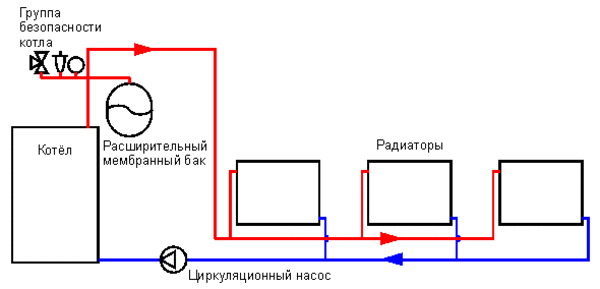
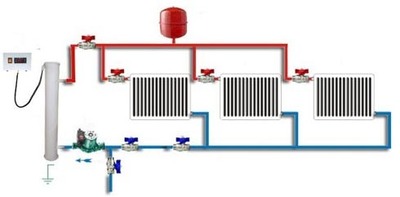
Photo 4. Diagram of a two-pipe heating system with bottom wiring. The hot coolant is shown in red, the cold one in blue.
Cons:
- pipelines and other materials are quickly used up (unlike the single-pipe type, a lot of material will be required during installation);
- low pressure of the heat carrier fluid in the supply risers;
- Due to the regular formation of air locks, it is necessary to install Mayevsky taps and release the air.
Do-it-yourself installation of a two-pipe heating system in a private house
The construction is manufactured in several stages.
Calculation
Before starting installation, it is necessary to create a clear plan, for which specialists always carry out a hydraulic calculation. During this process the following results are achieved:
- the number of heating devices is determined;
- the dimensions and quantities of the circular risers are calculated;
- future losses are determined.
Attention! The calculation is being made in strict accordance with the heating schemeI. Hydraulic calculation provides an understanding of the current resistances, provides information on water flow rates and the temperature of each individual section.
Installation
- First, in a separate ventilated room, a heating boiler is being installed. Its location should be remote from the walls, and access to it should be open. The walls themselves, as well as the floors in the room, should be finished with fireproof material.

- After that need to install a pump, distribution hydraulic manifold, And measuring instruments/counters at the boiler.
- From the boiler room, straight through the walls, The pipeline is laid to the radiators.
Connection
The final stage is connecting the radiators.. The batteries are mounted on brackets, under the window. It is also recommended install temperature sensorsWith their help, the flow of water, as well as its temperature, is regulated.
Test launch
Once the structural elements are connected, pressure testing is being done. A test run of the boiler is possible after preparation of relevant documents, in the presence of gas specialists.
Useful video
Watch the video, which tells you how to make a two-pipe heating system from polypropylene with your own hands.
What conclusions can be drawn?
This article brings out a simple idea: installation of a two-pipe heating system Everyone can afford it, there is nothing complicated about it. It is important to initially draw up a correct plan, select the type you need and make an individual calculation.












Comments