The warmest houses are those of mathematicians: calculating the required power of a circulation pump for heating
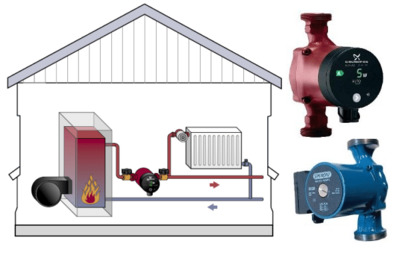
Circulation pumps for heating systems are devices that the coolant is driven through the entire network at a low speed, which ensures uniform distribution of hot water across the radiators.
This is the main advantage of the pump, which allows you to heat all rooms at home, regardless of the distance to the heating boiler.
The advantages include:: small size and weight, adjustable rotation speed, possibility of connection to heating automation, reduction of energy consumption due to efficient use of heat carrier.
Content
What capacity of circulation pump is needed for heating?

This is one of the main technical characteristics by which the unit is selected.
By power we mean performance device that indicates volume of coolant pumped circulation pump for a certain period of time (measured in m³/h).
To carry out the calculation you will need two parameters heating boiler:
- power;
- the temperature difference between the coolant from the boiler and when it enters it (in the return circuit).
Calculation formula
This is what the formula looks like:
Q=0.86R(tF-tR), Where:
- Q — the power or performance of the circulation pump.
- R — required heat for the premises (measured in kW).
- tF — temperature after the heating boiler.
- tR — the temperature of the coolant at the entrance to the heating unit.

Parameter "R" - heating capacity of the heating boiler. It is calculated based on the ratio: per 10 m² area of the heated room is consumed 1 kW thermal energy taking into account that ceiling height in the house does not exceed 3 m.
For example, if the heated area is 100 m², that means, to heat it up need a 10 kW boiler. It will correspond to the parameter "R". This indicator is a tabular value and is required indicated in the passport heating unit.
Temperatures «tF" and "tR" are also passport values. In standard heating boilers first — temperature range from +90 °C to +95 °C, the second - from +60 °C to +70 °C.
Calculation options
The parameter "R" is determined not only by the ratio indicated above. There are other ways to determine it.
In Europe
In European countries they do it simply. To do this they take already standard values, revealed empirically:
- For small private houses the consumption of thermal energy is (R) — 100 W/m²;
- For multi-apartment houses - 70 W/m²;
- For industrial buildings — 30-50.
For northern regions

The above European standards are suitable only for Russian regions with a mild climate. Therefore, for northern regions, other parameters are used, which are fixed in SNiP "Heat networks" number 2.04.07-86.
- For houses, the number of storeys of which does not exceed two, the specific thermal power of the heating boiler is 173-177 W/m².
- For houses of height more than two floors This indicator varies within the range from 97 to 101 W/m².
Thermal power in houses with different degrees of wear
Newly erected buildings and those that have been in use for many years, have many features. When selecting heating equipment, the degree of wear of the structure is taken into account.
After all, in houses built many years ago, modern technologies were not used, related to the insulation of load-bearing structures, facades and roofs. Therefore, they have greater heat loss, than in modern buildings. Hence the increased requirements for the selection of heating boilers, circulation pumps and radiators, the main task of which is to create comfortable living conditions inside the house.
Table for different rooms
The table shows what power heating equipment should have to heat a certain volume of rooms in new and old houses, taking into account that temperature difference (tF-tR) will be 30 °C.
| Thermal power, kW | Volume in old houses, m³ | Volume in new houses, m³ |
| 5 | 60-100 | 70-150 |
| 10 | 130-230 | 150-300 |
| 20 | 250-450 | 320-600 |
| 30 | 450-650 | 650-1000 |
| 40 | 650-900 | 1000-1300 |
| 50 | 900-1100 | 1300-1600 |
| 100 | 1700-2200 | 2600—3300 |
| 200 | 3500-4500 | 5000—6500 |
Calculation features for private home systems
Thermal power of the heating system located in a private house, depends on the volume of the space being heated.
Photo 1. Example of a plan for a private one-story house. To calculate the volume of the heated room, you need to know the area of the rooms.
Based on this value, the boiler power is found, and accordingly, the circulation pump. In this case, the productivity of the second is taken as the basis for the power of the first. That is, R=Q.
Attention! The calculation is based on the volume of each heated room. After all, in private houses the height of the streams can be more than 3 m, and not necessarily the same in each room. This means that the ratio proposed above (10 m² - 1 kW) is not suitable for carrying out mathematical calculations.
In private houses other parameters are used:
- If the house brick, That per 1 m³ space must be spent 34 W thermal energy.
- If the house is built from concrete blocks, then the ratio is: 1 m³ - 41 W.
Useful video
Watch the video to see how to calculate the required power of a circulation pump.
What happens if you calculate incorrectly
Eat two situations. The first is that the power of the circulation pump turned out to be much higher than required. In this case the following will happen:
- Increased speed of the coolant, which means it will not be able to give off the required amount of heat through the radiators, respectively will return to the boiler at a higher temperature. This affects the correct operation of heating equipment.

- Overpayment for the device itself. The higher the performance, the higher the cost.
- Higher operating costs, especially the payment for consumed electricity.
The second situation is power underestimated.
- The speed is less than required, which means the required amount of thermal energy will not be supplied to the farthest radiators from the boiler.
- The boiler will overheat.
Therefore it is very important carry out calculations accurately the capacity of the circulation pump taking into account the capacity of the heating boiler.







Comments