The quality of heating directly depends on it! Do-it-yourself heat exchanger for heating

The heat exchanger is an important element in the heating system, which transfers thermal energy from the generator to the coolant.
A suitable option for making the device yourself is calculated based on the design elements.
In heating systems, there are devices that operate with boiler designs that run on gas, solid fuel, and electricity.
Content
Heat exchanger device for heating systems

The device is designed to transfer heat from one element to another. The role of the heat source and heat carrier is played by various liquids, gases or steam.
Unstable environments are separated by a material with a suitable type of thermal conductivity.
A simple example of a heat exchanger is room radiators, in which the heat source is water in the heating system, and the heated medium is the air in the room.
The separating material is the metal that the radiator is made of. The intermediate material that is used in the construction is must have a high degree of thermal conductivity.
A good option for designing a heat exchanger would be to use copper elements. Copper has a higher 7.5 times thermal conductivity than steel. Plastic products conduct heat two hundred times worse than steel. Comparing under the same conditions 1.7 m copper, 12 m steel and 2 thousand meters plastic pipeline will transfer the same amount of heat.
How to do it yourself
There are several types of heat exchangers, each of which has a special production technology.
Manufacturing using the "pipe in pipe" method, connection features, diagram
The device works on the following simple principle: hot liquid passes through a small diameter pipe, Heat is transferred to water through the pipe walls, which is located in the cavities of a larger pipe. In this way, thermal energy is transferred and liquids of a heterogeneous nature, such as oil and water, are not mixed. This type of unit is easy to manufacture and operate.
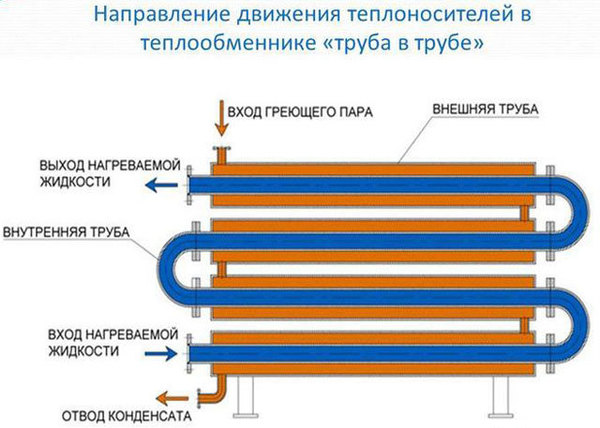
Photo 1. Diagram of a heat exchanger of the "pipe in pipe" type. The direction of movement of the coolant is indicated.
Tools and materials
- two two-meter copper pipes with different diameters - 102 mm and 57 mm;
- two tees with 90 degree angles, the diameter must be equal to the larger pipe;
- two short pieces of pipe that fit the size of the tee;
- electric or gas welding, a powerful soldering iron with copper solder will also do;
- grinder, cutting disc;
- roulette.
Manufacturing process
- On a larger diameter pipe profile on both sides the tee is welded, which should be positioned on its side so that a smaller pipe can be inserted into it.
Reference. When connecting such a design, it is recommended to place the heat exchanger in a horizontal position, the liquids should circulate in different directions, this will increase efficiency.
- After the smaller diameter product has entered the tee, welded from the ends.
- To the free edges of the tees pipes are welded, which are designed to supply and discharge heating fluid.
Air plate

Adaptation installed in a gas heating system. The operating principle is to transfer thermal energy from a gaseous coolant to a corrugated plate structure that will heat the liquid in the pipeline.
This type of device is also suitable for transferring heat from one liquid to another.
Tools and materials
- welding equipment;
- Bulgarian;
- two sheets of stainless steel (corrugated), thickness 4 mm;
- 1 sheet flat stainless steel, thickness 4 mm;
- electrodes.
Work order
- The corrugated steel sheet is cut into equal squares with sides 30 cm. For the design you will need: 31 square.
- Cut strips from a flat sheet of stainless steel. Width 1 cm, length 30 cm. The total length of the parts should be 18 meters - it will work out 60 pcs.

- Weld the squares of corrugated material together using a strip 1 cm. The connection goes through two opposite sides of squares, the sections are located perpendicular to each other.
-
In one case, having the shape of a cube, it should be 15 sections, which are facing the same direction and 15 to another.
Due to the corrugated surface, there is an effective transfer of heat from one carrier to another without mutual displacement of different or homogeneous heat carriers.
- In cases where heat will be transferred using a liquid coolant, it is recommended to weld the manifold. It is better to make the distributor from stainless steel. To do this, you will need to cut rectangles from a steel sheet using a grinder 30x30 cm (2 pcs.) And 30x3 cm — 8 pieces. From such a set of parts it is constructed two collectors having the appearance of a square box lid.
- Make a hole in the manifold for a pipe, which will serve as a connection to the heating pipeline.
- The hole on the manifold is made closer to one of the corners. When mounting it on the heat exchanger, the location of the inlet pipe should be at the bottom of the unit, the outlet pipe is always located at the top.
Water heat exchanger for a furnace
A typical wood burning stove capable of heating an entire house, if it is connected to a water-based heating system.
Tools and materials
- meter steel pipe, diameter 32.5 centimeters;
- iron pipe - 6 meters, diameter 5.7 cm;
- sheet steel 4 mm thickness;
- welding machine;
- gas cutting torch.
Work order
- A meter-long section of pipe with a diameter 32.5 cm place it horizontally on a sheet of steel and trace it with a marker.
- Cut a hole of the required size with a gas cutter. Cut a second identical circle using the metal circle model.
- Cut out in metal disks five holes each with diameter 5.7 centimeters. The holes should be evenly spaced relative to each other, both from the center and from the edge of the surface. Weld the disks to the pipe cylinder and try to ensure that the holes are parallel.
- Product 5.7 mm cut into pieces using a grinder 1 meter each. It will be required five segments.
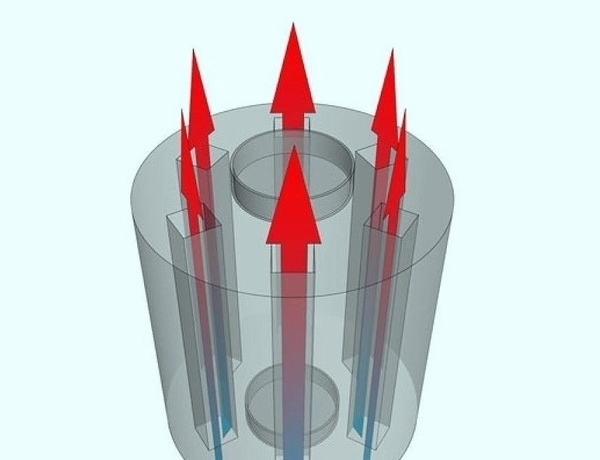
Photo 2. Scheme of water heat exchanger for the furnace. It is a cylinder with smaller diameter pipes inside.
- Each part of the pipe is mounted in a hole, it is necessary that the pipes extend beyond the holes by 1 millimeter. The device is welded using electric welding. As a result, a structure in the form of a metal cylinder should be obtained, inside of which smaller tubes are located. Hot air and smoke will flow through this pipeline, the pipes will heat up and accordingly heat the liquid coolant inside.
- To allow liquid to circulate within the metal system at the bottom and top follows weld small pieces pipes. Cold water will be supplied through the branch pipe at the bottom of the unit, and directed to the heating mechanism through the upper branch pipe.
How to calculate thermal power
If selected lamellar heat exchanger, it is necessary to take into account the following facts:
- what power of the device is required;
- type of construction;
- quality of materials.
Power calculation is in progress according to the following formula:
P = 1.16 x ∆T / (tx V), Where
R — the power that is required;
1.16 — a specially selected constant;
∆T — temperature difference;
t - time;
V - volume.
System productivity depends on the current of the working media in both circuits. The appropriate model for assembly is determined taking into account the volume of the room that needs to be heated. The larger the area, the more materials will be needed.
How to connect a homemade heat exchanger
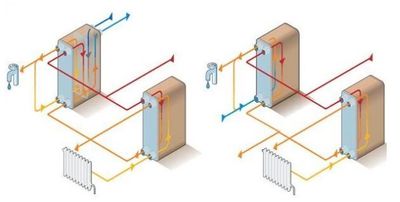
There are 3 Basic Connection Schemes heat exchangers - parallel single-stage, mixed two-stage and sequential:
- Parallel type the simplest and most reliable, because the water is heated directly in the device. The heat exchanger is mounted parallel to the heating pipeline.
- Two-stage scheme designed to reduce the consumption of coolant. This makes it possible to use the thermal energy of the return water in the heating system.
Useful video
Watch the video, which explains the structure and operating principles of a heat exchanger.
Advantages and disadvantages
DIY heat exchanger for heating, easy to manufacture, suitable for all types of coolants, easy to clean. The speed of movement of liquids is easily regulated by the correct selection of pipe sizes. The only minus — high cost copper building materials.









Comments