The choice that determines the weather in the house: heating radiator connection diagrams
You are viewing the section Installation, located in the large section Radiators.
Subsections: Calculation.
To keep your house or apartment warm, it is important to connect the heating radiators correctly. Efficiency is determined by the correct choice of the scheme connections.
There are several schemes that are used to make the right decision.
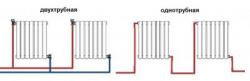
One-pipe heating system
This is a common heating option, and is used more often in multi-story buildings, the private sector, apartments - this variation is possible everywhere. Single-pipe wiring accessible and economical. Heat goes from the coolant first to one heating device, then to another, returning from the last one to the boiler inlet. There is no return riser, as the water cools in the radiator and returns to the heater.

Pros:
- easy installation;
- low material consumption.
Cons:
- different temperatures of batteries that are closer to the heater and those that are further from it;
- heat supply cannot be adjusted;
- Radiators can only be connected from below.
To the heating boiler All radiators are connected in series, the outlet of the last one goes to the boiler inlet or to the riser in a multi-story building. Water circulation occurs due to temperature differences.
Two-pipe system
It has a parallel connection: each radiator is connected separately to the coolant. Two pipeline channels: feed and return.
Pros:

- the temperature of the batteries is constant;
- a thermostat can be connected to each heating element and the process can be controlled, changing the amount of heat as desired;
- heat loss is minimal, the room is heated more evenly.
Cons:
- this combination requires twice as much material (pipes);
- greater labor intensity implies higher costs.
They use smaller diameter pipes, than with a single-pipe system.
How to connect radiators?
You can connect devices in different ways: from the side, from below, or diagonally.
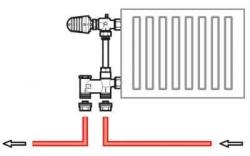
Bottom connection
With this method, pipes are most often laid along the bottom of the wall or under the floor. Hidden wiring rather for design purposes, so as not to spoil the appearance of the room.
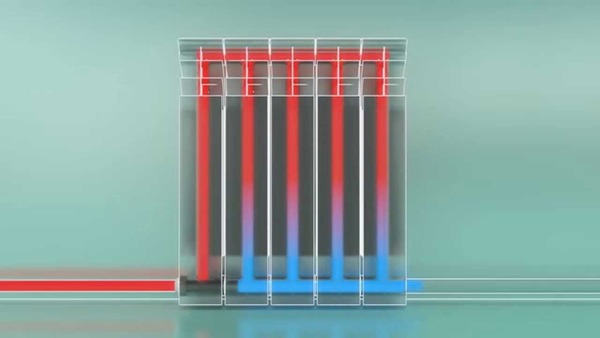
Photo 1. Diagram showing the movement of the coolant through the radiator with the lower connection method to a one-pipe system.
The method used is for forced circulation type water. A difference in height is created in the system, the heat rises, then falls, and at the window level it is distributed through the heating elements.
Pros:
- possibility of hidden installation;
- ease of installation;
- There is a built-in thermostat.
Cons:

- significant heat loss;
- the need to install an air vent on each radiator;
- low efficiency.
First, the batteries themselves are attached to the walls, then the pipes are connected to them. There are two pipes at the bottom: for input and output. After passing through the heating element, the water returns back to the boiler.
There are universal ones batteries, with four holes, they can be connected in any way.
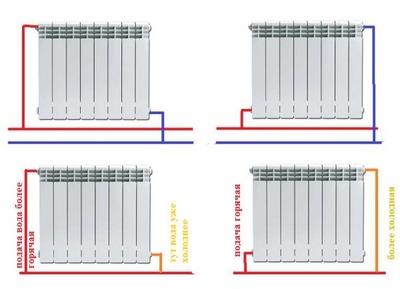
Side connection
Lateral connection is called differently one-sided, since both pipes fit on the same side heater. This is usually the case in city apartments. Method effective for small sections.
Pros:
- quite effective warming up;
- easy installation.
Cons:
- reduced performance for larger radiators;
- rapid clogging of the distant sections.
Side connection there may be two options:
- direct; in this case, the pipes are supplied from below;
- angular; pipes come out of the wall.
The supply and discharge pipes approach the radiator from one side. It is advisable to install ball valves at the connection points., which, if necessary, turn off the radiator.
Diagonally
An effective scheme that works with natural circulation water, but is not used in multi-storey buildings because there is a forced water supply system. With a diagonal connection, the radiator heats up evenly and gradually from top to bottom. The name comes from arrangement of pipes opposite each other, from corner to corner.
Pros:
- uniform heat distribution;
- maximum heat transfer;
- the ability to heat large radiators.
Cons:
- The pipes come from different sides, making it difficult to hide them.
- A level installation of the battery is required. The pipes are connected from two different sides: water supply - from above, outlet - from below. It is advisable to install valves on the pipes so that the battery can be disconnected if necessary.
Natural circulation of water through batteries
In individual apartments, private houses and cottages, natural water circulation is most often used. This system consists of the following elements:
- pipeline (feed and return);
- heating element;
- boiler;
- expansion tank.
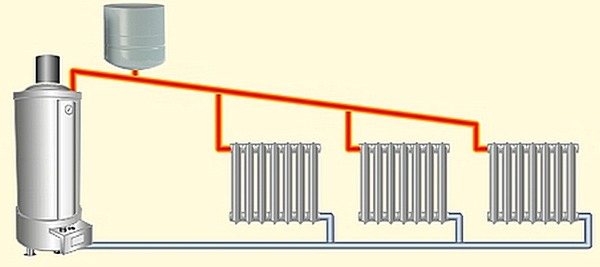
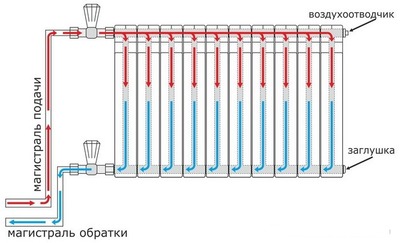
Photo 2. Diagram of a heating system with natural circulation. The coolant moves through pipes located at an angle.
Water moves in such a device according to the natural laws of physics, without any forced action. The heated liquid rises up the riser and is squeezed out by the cold flow from the return line and moves to the radiators.
First, the water is heated in the boiler and flows through the radiators, where it gives off heat. Then, through the return pipeline, it returns to the boiler already cooled and heats up again. The cycle is constantly repeated.
Pipelines are being laid with an inclination towards the direction of fluid movement.
When installing a heating system with natural circulation take into account some points.

- Heating boiler is being installed below the level of the radiators.
- The diameter of the pipes is not less than an inch, and in some cases more.
- Slope pipes approximately 1 cm per meter.
- Expansion tank — a necessary element of the system.
- Minimum water temperature - 55 °C.
- The pressure in this case is small., therefore the diameter of the pipes must be large.
When installing the pipeline, it is necessary that there is as few obstacles as possible for the movement of the coolant: bends, turns, rises. The most successful option for laying pipes is selected.
The pipes can be from various materials: plastic, metal-plastic, metal. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, metal-plastic is lighter and does not require painting. Metal pipes have the ability to heat up, which makes it easier to heat rooms.
Forced circulation
The process itself occurs in exactly the same way as in the case of the natural water cycle. The only difference is the presence of a circulation pump., which creates the pressure necessary to move water of different temperatures through pipes. Forced circulation used in large buildings, when the power of natural movement is not enough.
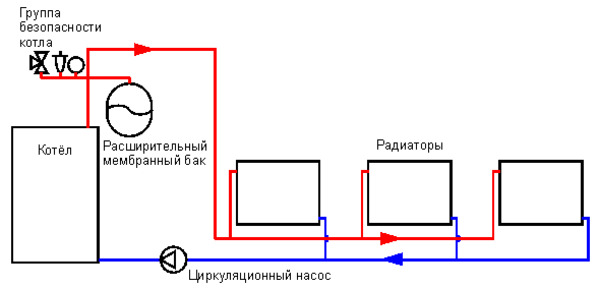
Photo 3. Diagram of a heating system with a circulation pump, which ensures the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
The connection of all elements is the same as in the first case. The pump is installed to the main pipe, closer to the expansion tank. Its use increases efficiency heating, It is possible to heat a large area, even several floors.
Attention! The pump must not run idle, only when the system is filled with water! Otherwise the equipment will fail!
Useful video
Check out this video that discusses the effectiveness of different radiator connection methods.
The Importance of Choosing a Heating System
From the correct choice of heating system the performance of the heating system depends. The weather in the house is an important issue!
During the design, the connection of radiators is calculated, and the arrangement by power is successful. Each system has its own characteristics., which must be taken into account.













Comments
Warmth to everyone's home!