Types of heating system devices: features of operation without heat loss
You are viewing the section System components, located in the large section Heating.
Subsections: Coolant, Pump, Hydraulic arrow, Three-way valve, Thermoregulator.

The heating system is a set of devices, pipelines, control valves and technical parts that are designed to generation and transfer of thermal energy into a heated room of a private house.
Heating systems classified by energy sources, types and features of the movement of heat carriers, equipment used, installation schemes.
Features of heating systems: how does the technology work?

Types of heating systems:
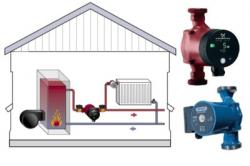
- Water ones. The most common and profitable option. The main element of the scheme is the boiler. The device heats the liquid, it flows through pipes to the radiators, which heat the air in the rooms.
- Airborne. Heat sources are calorifiers that supply warm air to the rooms. Water or hot steam is used as a primary heater.
- Electric. Electric heating systems are safe, automated, and efficient. The disadvantage of the device is its high cost.
Each system has its own pros and cons. When choosing, you should focus on your personal needs, goals, and priorities. Owners of private houses most often install water heating. This is a rational solution that allows you to create comfortable living conditions with minimal costs.
Popular heat sources
The following are used as energy sources:
- Solid fuel. Coal, firewood, fuel briquettes or pellets are beneficial if there is no possibility to connect to the central gas supply line or install a gas tank.
- Natural gas. So far, this is the cheapest resource. Gas heating has been popular for several decades. If you calculate correctly and install the system well, the heating will work stably for many years.
- Liquefied gas. Autonomous gasification is a great option for a house located far from centralized communications. The disadvantages include large expenses at the stage of arrangement.
- Liquid fuel. Diesel boilers are not often installed in residential buildings, but as a backup solution they are a practical option.
- Electricity. Warm floors and infrared heating are often installed. The systems are economical, but are not suitable for all regions, so they are often used as additional ones.
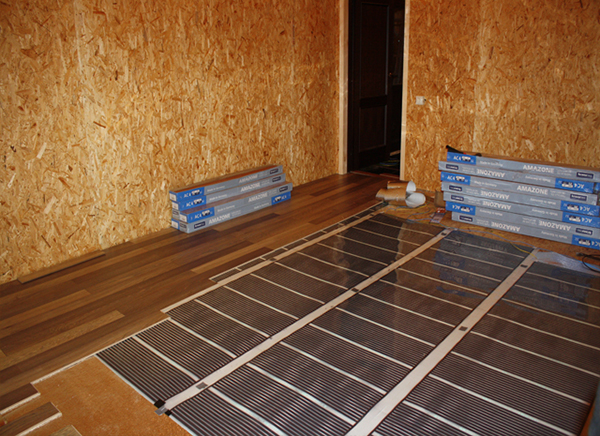

Photo 1. Installation of infrared heated floors powered by electricity in a private home.
- Alternative sources. There are systems that use solar, wind, and earth energy. Heating equipment operates using solar panels, wind generators, or heat pumps. "Green" heating is environmentally friendly, but too expensive.
Important! With all the advantages of energy sources, it is difficult to find an alternative to gas heating. Such systems are cheap to operate and pays for itself in about 5 years. Boilers and radiators are installed as heating equipment.
The principle of operation of water heating
The system is a closed circuit in which the coolant circulates through pipes from the boiler to the radiators.
As it cools, the water returns to the boiler, and the cycle repeats itself many times.
Water is most often used as a coolant, and less often, antifreeze. The first option is more profitable, and the second is safer., since the systems will not freeze in harsh winters.
The operation of the heating is regulated by additional devices, which include an expansion tank, pressure gauges, safety valves, and shut-off valves.
To create a closed circuit, use pipelines. When choosing pipes, you need to pay attention to the material of manufacture. Popular options are galvanized or stainless steel, copper, polymers.
Reference! More often chosen metal-plastic pipes. The products are durable, corrosion-resistant and long-lasting. The inner walls of such pipelines are smooth and do not become covered with scale and scale, due to which they do not lose their properties over time.
Natural and forced water circulation
Water circulation is ensured by natural gravity processes or special pumps (forced circulation).

Gravity systems are advantageous in terms of installation and operation.
For him no additional equipment required, and there is no noise during operation. The heated water rises and is distributed among the radiators, and the cooled water descends and enters the boiler.
The movement of the coolant does not depend on the energy supply, therefore during periods of power outages the house stays warm.
To design and install a system with natural water circulation, no special skills are required. It is enough to think through the scheme and maintain the required slopes.
This type of heating is capable of operating without interruption. within 30-35 yearsThe most that may be required is minor repairs.
Important! Heating with natural water circulation has a significant disadvantage: the system is effective if a two-pipe system is installed. When there is one circuit - radiators heat up unevenly and each subsequent one is colder than the previous one. When saving on equipment, you have to overpay for pipes and components.
For forced circulation of the coolant, a pumps.

Such systems are more efficient because hot water quickly reaches the radiators without having time to cool down in the pipeline.
The heating works perfectly, no matter which scheme is chosen - one- or two-pipe. However, when the power goes out, the heating stops and the house cools down quickly.
A compromise option is a well-thought-out scheme that provides for natural and forced circulation simultaneously. When the power goes out, the heating is simply switched to gravity mode, bypassing the pump.
One- and two-pipe, manifold wiring
Depending on the specifics of the coolant movement and the operating principle, a distinction is made between one-pipe, two-pipe, collector system. Each of the schemes has its own advantages:
- Single pipe. This is a standard scheme, in which the resistance of the system increases as it moves away from the boiler, which leads to uneven heating of the radiators. To solve the problem, balancing valves are used.
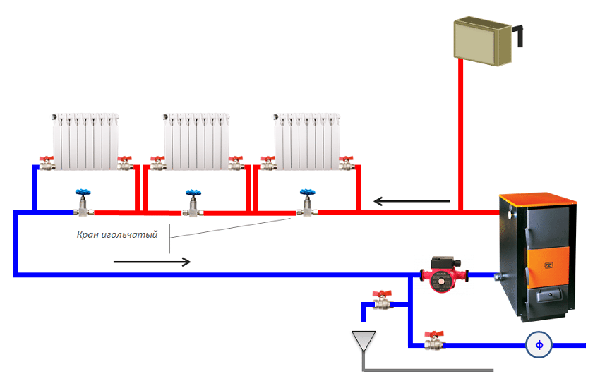
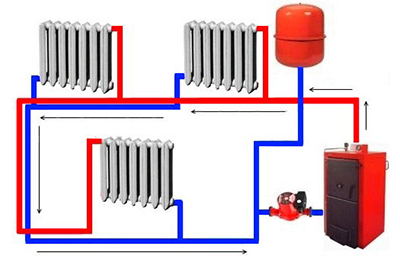
Photo 2. Single-pipe heating system diagram with a boiler, radiators, expansion tank, and circulation pump.
- Two-pipe. The scheme provides for two pipes — supply and return. The heat carrier from the boiler is supplied to all radiators in the circuit, due to which they are heated evenly. Two-pipe wiring is convenient, practical, but metal-intensive, therefore it requires serious costs for arrangement.
- Collector (radial). This is an ideal option in terms of operational characteristics and hydraulic stability. To regulate the technology of radiator operation, a cabinet is installed where the collectors, all shut-off and balancing valves are placed. If necessary, one or more radiators are switched off without damage to the other devices.
Useful video
The video shows the operating principle of different types of heating systems in a private home.
Brief summary
Single-pipe heating is advantageous from the point of view lower material costs, but this is where its advantages end, since the home owner has to solve the problem of uneven heating of the radiators.
Two-pipe systems provide comfortable temperature in all rooms of the house. Collector wiring is universal and allows you to regulate the degree of heating in each room separately. When choosing a suitable scheme, it is better to consult a specialist.